-
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Yes. Metaphysics is useless for putting bread on the table. But it can be used for building clarified concepts in your mind. Likewise, Philosophy won't put a man on the moon, but it might allow mankind to work together, despite differences, to reach such goals. Philosophy & Metaphysics are not focused on the material world out there, but on the mental world in here. Science allows us to control the natural world, but Philosophy helps us to control the cultural world. For example, Putin is not a platonic philosopher-king, but a typical thug warlord. Would it be pragmatic to teach a young Putin about the hubris of Hitler, and the harmony of Confucius & Pythagoras? Maybe, maybe not; but it's worth a try.Taking into account the fact that only the empirical is useful to us in any way at all, would you agree that metaphysics is useless. I'm taking a pragmatic approach I believe, but it is a question worth asking.
Your theory of Enformationism, what's its selling point? As far as I can tell, it seems to have utility in a yin-yang sorta way; in other words is Taoism metaphysics or not? Taoism is practical advice, oui? — Agent Smith
As a 21st century worldview, Enformationism could conceivably update the mind-set of humanity, from the ancient spooky belief system of Spiritualism (e.g. Animism), and the dispiriting effects of Materialism & Capitalism. Marx's critique of industrial age Capitalism, revealed its internal contradictions, but his proposed Communism had its own destructive paradoxes. So, all general worldviews begin to fall-apart as human cultures split into factions, each justified by an incomplete (hence biased) understanding of how & why the world works as it does.
Don't get me wrong. Enformationism is not a political manifesto, but simply a personal analysis & synthesis of how the world works, from quantum to cosmic scales, and why it doesn't work perfectly. Historically, each dominant cultural worldview, has provided philosophical insights to the remaining mysteries of reality. But all have a limited shelf-life, before the gaps in understanding become pit-falls for failure. So, humanity has to learn from its social breakdowns, and to patch the gaps with new insights. The key perception, and conception, of Enformationism is basically, what philosophers & sages of all eras have preached : unity & harmony are threatened by Entropy. So we must constantly repair the cracks in the foundation of society.
To find appropriate spackle to smooth over the rough spots in modern cultures, we can learn from the positives & negatives of ancient cultures. For example, Taoism was a general worldview that allowed the high culture of China to survive for centuries, despite the usual tribulations of complex human societies. The Yin/Yang principle gave people the BothAnd idea of harmony of opposites, to offset the destructive dualistic belief in Either/Or, us-versus-them, and my-way-or-the-highway. And the Tao-concept served as a unifying principle of balance upon which to build a harmonious society. Today, universal & ubiquitous Tao-like Information could serve as the fulcrum upon which to balance our divisive modern world. If only enough people were aware of its role in every facet of life. Enformationism is also practical advice for avoiding the Matter vs Mind estrangement of vulgar Materialism. :nerd:
PS__But what is "information"? En-Form-Action. Stay tuned.
WHAT’S THE PROBLEM? :
Historically, the dominant worldview of civilizations and cultures has swung between the two poles of practical Materialism and theoretical Idealism. Idealist societies, such as medieval Europe, tend to focus their intellectual energy and attention on otherworldly matters, hence material progress stagnates. In their more worldly materialistic phases, cultures such as modern Europe prefer to emphasize the here and now, accelerating technical (reductive) progress to the detriment of spiritual (holistic) development. Eastern cultures, that have been traditionally more Idealistic, are now attempting to catch-up with pragmatic Western nations in technical prowess and materialistic goods. Consequently, the internal struggles between Body and Soul, Part and Whole create tension and friction for those on both sides of the moral/material balance point.
Materialists often object to the intrusion of idealistic, meta-physical religious and philosophical concepts into the pragmatic, scientific search for understanding of the world around us. But it is my contention that it was materialistic Science itself, following the evidence where it led, that accidentally stumbled into the forbidden realm of Idealism. If they could turn back the clock to the golden age of science–-before the unexpected and unwanted intrusions of Einstein and the Quantum Theorists into regions of the universe beyond the limited scope of man’s physical senses–-Materialism would still reign supreme. Since Einstein showed the practical impossibility of going backward in time, I guess we will just have to move forward, and deal with the perplexing paradoxes of pre-cosmic and sub-atomic reality in the scientific spirit of open-minded skepticism. And let the facts fall where they may.
I’m not so idealistic that I could believe we are on the verge of a final resolution of this long-standing philosophical debate. But I do see a glimmer of light ahead of us in the tunnel of life. If humanity can come to see that the duality of this world is natural, necessary, and inherent in material Reality, but not in metaphysical Ideality, then perhaps a detente can be negotiated so we can work together toward common goals in both realms. Conflict is an unavoidable effect of Duality, but those opposing forces can be resolved in Ideality.
The Enformationism paradigm envisions a convergence of scientific knowledge and philosophical wisdom; matter & mind; real & ideal; body & soul. But like any paradigm shift, it may take a long time to take hold. This thesis is just a beginning.
Enformationism website -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
You are comparing empirical Science with theoretical Philosophy. But they are different approaches to a> practical knowledge or b> meaningful wisdom. Materialistic Science limits its reductive analysis to questions that are inherently amenable to empirical evidence. But Philosophy was left holding the bag of metaphysical questions that have no true/false answers, only more-or-less plausible.On the other hand, metaphysical matters (God, etc.) are mere possibilities, unproven/unverified; quite frankly, they maybe unprovable/unverifiable.
Now look at how the two stack up against each other: Imagination (metaphysics) vs. Facts (empirical science). Is this even a choice? Fantasy vs. Reality? Maybe it is, but daydreaming is frowned upon, oui? — Agent Smith
If you think we are doing Science on a Philosophy forum, you should take-up your scalpel and dissect the God question into its fundamental Atoms. For most of us, God is not a physical object, but a mental concept, defining the whole of which we humans are merely questioning particles. From that perspective, maybe you are an Atom of God. So, yes, you have a choice : to dissect material objects or to understand mental Models. This forum offers the latter. :smile: -
Deus Est Novacula Occami
The concept of a single theory, or even a single equation, to explain everything in the world, is a sort of Holy Grail for physics & cosmology. For a while it looked doable. But in recent years, they have tried & failed to reconcile Relativity/Gravity equations with Quantum/Non-local mathematics. If they ever do discover an algorithm to calculate every phenomenon, from smallest to largest scales, Hawking conjectured that "then we would know the mind of god". In other words, we would understand more than a complex pile of isolated facts, but the integrating force that holds the entire system together : i.e. Holism. So, you could say that the TOE is both simple (singular ; container), and complex (comprehensive ; contents).Why should a ToE be simpler? Shouldn't it be more complex?
Coming to your theory of Enformationism, do you have any specific reason why you settled on information rather than something else, assuming there's an alternative, to construct your own ToE? — Agent Smith
In the case of Enformationism, the singular element of the cosmos is Information, Not just in the Shannon definition of empty containers for meaning, but the actual ideas & images & feelings in the human mind. Back in the 1980s, physicist John A. Wheeler (nuclear fission, relativity, black hole as information sink) coined the phrase "it from bit". That summarized his conjecture that all real "its" (physical objects) were derived from non-physical "bits" of abstract Information. Speculating further from that inspired intuition, he developed the hypothesis of a Participatory Universe, in which Observers construct their own model of reality, and that interaction between real & ideal might even have physical effects on the objective world. I don't take that mind-over-matter (magical) notion literally, but it works metaphorically, as an explanation for the collapse of a particle's virtual (mathematical; mental) waveform, into a measurable physical object .
Then, in 1999, the Matrix movie popularized the sci-fi concept that humans are living in a computer simulation. And that novel notion was symbolized by the green "raining code" (bits of information) that dreaming pod-people interpreted as Reality. Possibly inspired by that fiction, cosmologist Max Tegmark proposed his "Mathematical Universe" theory : a speculative "theory of everything". Some years later, I was reading an article about recent developments in Quantum Theory. In it, the physicist noted that all we know about an electron is abstract attributes, such as charge, spin, & momentum, not the particle itself. So, he expressed amazement that "it's nothing but information!".
I was intrigued by that convergence of disparate views of the role of Information, in the real and ideal worlds. But, I only gradually realized the philosophical significance of all-purpose bits of mind-stuff. Eventually, I pulled all the various functions of abstract information, into a thesis I labeled as Enformationism. That coinage was intended to symbolize a new information-based worldview to replace the outdated paradigms of Spiritualism & Materialism & Idealism. Shape-shifting Information is the common denominator (organizing principle) of all those worldviews. So, you could say that, in keeping with Ockham's Razor, our perceived & conceived Reality all boils down to the symbolic Binary-Unity of the single continuum from 0-to-1; nothing to everything; the Holistic System of many parts. The thesis presents a plethora of "specific reasons" for accepting Mental Information (bits), instead of Physical Atoms (its), as the fundamental element of the world. :nerd:
PS__If you will message me, I'll give you a link to the Enformationism website.
Binary Nature of Reality :
Reality is what we take to be true,” pioneering physicist David Bohm asserted in 1977. “What we take to be true is what we believe… What we believe determines what we take to be true. What we take to be true is our reality.”
The question of what is true is, of course, invariably a binary one — in answering it, we must choose between true and false. Left or right, the red pill or the blue pill, the ultimate “To be, or not to be.” Information theory is built upon this binary mindset — the if this, then that logic of most programming languages is predicated on the true/false dichotomy in executing commands — and it was to thiselemental relationship between information and human consciousness that Bohm was speaking.
A little more than a decade later, the great theoretical physicist John Archibald Wheeler (July 9, 1911–April 13, 2008) enriched this idea in a concept he called It from Bit. More than thirty years after he popularized the term “black hole” — a term for the cosmic object which consumes most information into oblivion — Wheeler suggested that our experience of the objects, events, and phenomena that constitute reality is the result of binary decisions — true/false, yes/no, on/off — which we make in the process of observing them.
https://www.themarginalian.org/2016/09/02/it-from-bit-wheeler/


-
The 'New Atheism' : How May it Be Evaluated Philosophically?
I found an article that quoted a TV interview some time before Jung's controversial quote you mentioned. At that time he sounded certain of the existence of a god "who's nature is beyond human comprehension". Apparently, he was censured for making such a bold Gnostic assertion. However, he also acknowledged that what he "knew" was more emotional than intellectual. Yet, my own Agnostic belief is more intellectual than emotional. But, I suppose both of us fit somewhere in the middle of the range from Theism to Atheism.You present a good argument for agnosticism and one which counters Jung's argument, 'I don't believe, I know'. — Jack Cummins
So, a more positive label for my semi-belief is Deism, sometimes defined as "rationalistic theology". Intellectually, and based on general evidence from science*1, I believe there must be a First Cause with omni-potential for the full range of outcomes, both good & evil, which are manifested in the imperfect world that we inhabit. Hence, I label my have-it-both-ways non-committal philosophical worldview as BothAnd. That's how I deal with the theological "Problem of Evil" for monotheism, which describes God as goodness personified, yet sneaks in an evil deity through the back door.
Such a wishy-washy worldview is not sufficient to motivate a religious commitment. But, it's acceptable for philosophical humility, as a wise man once admonished his listeners to keep an open mind, by admitting paradoxically : "I know that I know nothing". :cool:
*1. e.g. Evidence from science that evolution is progressive & self-organizing (Enformy), instead of self-destructing (Entropy), as you would expect from a random or accidental reality. Hence, the implication of Teleological & Intentional Design. But, the Hegelian method of "progression" is bottom-up heuristic (trial & error) instead of top-down divine fiat. Even human-designed computer programs have adopted the trial & error method of reaching the best possible compromise solution : Evolutionary Programming.
Jung's need to know :
All that I have learned has led me step by step to an unshakable conviction of the existence of God. I only believe in what I know. And that eliminates believing. Therefore I do not take his existence on belief – I know that he exists (Sands 1955, p. 6) . . . .
In Jung’s view, the truth about God is complex because God is a mystery whose nature is beyond human comprehension. . . .
The God-image is the expression of an underlying experience of something which I cannot attain to by intellectual means…
https://steve.myers.co/jungs-regret-over-i-dont-need-to-believe-i-know/
Evolutionary Programming :
Special computer algorithms inspired by biological Natural Selection. It is similar to Genetic Programming in that it relies on internal competition between random alternative solutions to weed-out inferior results, and to pass-on superior answers to the next generation of algorithms. By means of such optimizing feedback loops, evolution is able to make progress toward the best possible solution – limited only by local restraints – to the original programmer’s goal or purpose. In Enformationism theory the Prime Programmer is portrayed as a creative principle (e.g. Logos), who uses bottom-up mechanisms, rather than top-down miracles, to produce a world with both freedom & determinism, order & meaning.
BothAnd Blog Glossary

-
The 'New Atheism' : How May it Be Evaluated Philosophically?
Yes. Both Atheists and Theists have some good arguments to support their polarized positions : magic vs matter. But they are both Gnostic, in the sense that they feel sure they know the true answer to the God Question. That's why I sometimes describe myself as an Agnostic Deist. Because I have concluded that logically there should be a First & Final Cause of our temporary universe, and a comprehensive holistic Aspect/Entity of our dynamic, many-minded world. But my limited mind can't wrap around an uncaused Cause or an unbounded Mind.It is all about interpretation and I do wonder if there is a middle ground rather than theism and atheism and I don't mean agnosticism because that is like a waiting area to make a choice — Jack Cummins
Therefore, all I know about everything-actual-&-possible is just-a-theory. And, as a mere speck in the cosmic whole -- a fleeting instant in eternity -- I know nothing for sure about such all-encompassing generalities, universals & absolutes. So I can only think in terms of philosophical principles & poetic metaphors & rational speculations. For example, Cosmologists viewing the universe from the inside -- and from a materialist perspective -- construct imaginary models of what it would look like from the outside. Those speculative constructs typically look like either bubbles of unspecified-something, or evolving horns of burgeoning plenty, or in some cases as topological toroid rings. Yet, they are all pictured floating in the black emptiness of the unknown. And, they are all imaginary materialistic metaphors for a mind-boggling mystery.
As an Agnostic, I am ignorant of the Mind of God. I have no direct revelation from the Source. And yet, I am motivated to know what can be known about my cosmic context. So, I tend to use a variety of symbolic concepts, in a feeble attempt to comprehend the all-encompassing features & functions of the Logical All, of which you and I are minor parts. An alternative way to think of the Cosmos, including Life & Mind, is not as a place in space or time, but as a universal state of consciousness. Like Plato's Forms, which are not “out there”, but everywhere, everywhen, all-at-once.
However, Atheists might say there's no such thing as Everything, outside space-time. And Theists could object that my skimpy theory has no place for Favored People, or for salvation from imperfect Reality. Also, in my incomplete Agnostic theory of Everything, the world does not revolve around me or my kind. It's just a way to know a little something about the vast unknowable, and to make sense of the "blooming buzzing confusion" of incoming signals. Meanwhile, I'm content to wait for omniscience to set-in, before I place my faith in a mystery, or abandon all hope. :cool:
PS__There are several ways to interpret the general idea of an intentional universe. For example a> Panpsychism/Pantheism/PanDeism/PanEnDeism ; b> universe as mathematical simulation (a la Matrix) ; c> gestation of a baby god (a la Omega Point) ; and so forth. But I try not to get too specific in my speculations into the dark realm of manifold Possibilities . . . or too fantastic.
MULTIVERSE : AN UNBOUNDED SPHERE OF MANY SPHERES
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/db/c4/dbc4cd8b-b4b3-4a28-b211-42bc49a87a11/42-46205410.jpg)
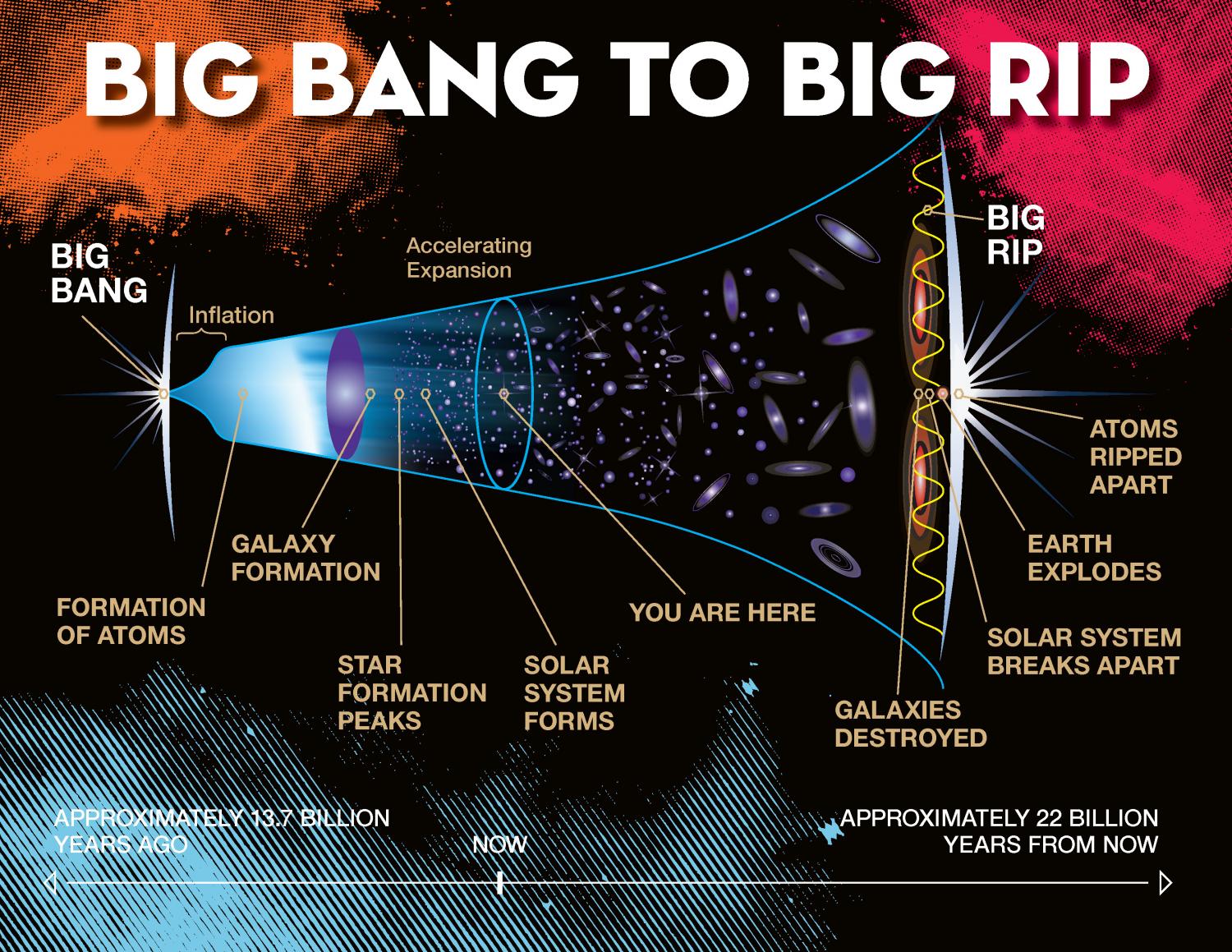
PROGRESSION FROM BIG BANG TO BIG RIP
COSMIC DONUT

-
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
So, there's no escape from the supremacy of Emperor Science?- First of all "Empirical Science" isn't a philosophical caprice but a Pragmatic Necessity and no "crawling out" is talking place. — Nickolasgaspar
Wow! Ten reply posts in a row. That must set some kind of record. And I salute your passion. To what do you attribute your emotional drive to drive a stake into the heart of God? And how do you characterize that heart-felt motivation? To purge pristine Science of all conjecture & speculation?
Again, I bow before the power of your relentless Logic. But, I hope you won't report me to the Emperor, for expressing my forbidden opinions in public. I thought I could get away with my watered-down god-concept. But now I see that I was wrong to think I could evade the moral census of Science. I hereby repent of my sins against Lord Logic, and promise to avoid any further transgressions of Official Doctrine --- on this thread. :joke:
Are you now, or have you ever been a member of the Philosophical conspiracy to subvert Science?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/McCarthyism -
Deus Est Novacula Occami
Hey! You raised the question of TOE & novacula occami. So, what was your motivation? Was it simply to ridicule the idealistic fantasy of ultimate non-redundant simplicity in a complex world? Or is your pessimism complicated by an itch you can't scratch, except philosophically?↪Gnomon
You maybe onto something. I, however, am not so optimistic, but don't let me, an agent of the system, dampen your spirits. Carry on. Do keep us posted on any interesting developments. — Agent Smith
Pragmatic sober scientists, a century ago, were surprised by evidence that our world was not eternal. Yet they were foolish enough to accept the crazy idea that all the zillions of things in the world emerged from a hypothetical Singularity, at a unique point-of-beginning, to create Space-Time from who-knows-what. How much simpler can it get? Except possibly to look for the Source of that fertile Cosmic Egg. Or the Programmer of the algorithm of Evolution? But, why complicate things with fruitless conjectures? Don't you have something better to do?
I agree that the concept of Monotheism was probably an exasperated attempt to simplify the confusing convoluted myths of Polytheism. At least, the notion of an eternal Potential, an Uncaused Cause, seemed to be an intellectual improvement on most bedtime-story explanations for the existence of the natural world, and its cultural questioners. But, that logical shot-in-the-dark has remained hypothetical down to this day. Are we getting any closer to the bottom of what we perceive as universal Reality?
Ancient philosophers sought to simplify the diversity of material things, by postulating an elementary smallest unit of matter : the Atom. And matter-chopping scientists continued to look for that basic building block of the real world, until the 20th century. Ironically, their newly-crowned "atom" was soon found to be made up of even smaller subatomic particles, right on down to the Trinitarian notion of multi-flavored hypothetical Quarks. But their quirky existence was easy to ridicule, due to the necessity to assume something even farther down the tower of turtles : hopefully labeled "preons" (non-dimensional points in four varieties). But its actual existence remains as unprovable as that of the ancient storm-gods.
Hence, the frustrating search for the ultimate "indivisible" element, was shifted from tiny material objects to amorphous invisible Fields of mathematical grids presumed to be made of potential energy. More recently though, the never-ending quest has turned to immaterial Information (mind stuff) as the foundational substance of reality. And that's where I picked-up the impossible dream, But, that seemingly silly notion may have been anticipated by Spinoza in his postulation of a Single (infinite) polymorphic Substance, that he equated with God or Nature. Were all those sages over the centuries barking up the wrong tree? Do we have to go completely out of this world to find the Ground of Being? :worry:
Is Information Fundamental? :
Could information be the fundamental "stuff" of the universe?
https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/article/is-information-fundamental/

-
Metaphors and validity
I think that's a primary distinction between pragmatic Science and theoretical Philosophy. Science tries to describe material reality in terms of physical attributes, while philosophy characterizes the invisible immaterial aspects of reality in terms of analogies, comparing mental concepts to material objects. Unfortunately, there is no objective validity in those symbolic figures of speech, because they are essentially subjective, and often culturally biased. However, a metaphor is just as valid as a pencil sketch of the defendant in a trial : to illustrate appearances from a limited perspective : not to prove innocence or guilt. :smile:Is it valid to use metaphors to illustrate certain attributes of an object, even though the objects being compared are not actually identical (although they are said to be)? — _db
Metaphor in philosophy :
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metaphor_in_philosophy -
Deus Est Novacula Occami
Only partly tongue-in-cheek, I call my own Enformationism thesis a "Theory of Everything", in the sense that it boils all Matter, Energy & Mind in the universe down to a single all-encompassing "entity" : Information. This is based on current extensions of basic Information Theory, from Shannon's 1s & 0s, to a wide variety of physical, mathematical, & mental applications. If you sum-up all those various Forms of information, the whole cosmic system could be viewed as "God", at least in Spinoza's notion of deus sive natura. As you suggested : "God is one entity and is the simplest explanation for everything". :smile:What could possibly be simplest explanation for all phenomena? A ToE (theory of everything)? One with just one entity obviously, oui? — Agent Smith
PS__Calling my thesis a TOE doesn't mean I personally know everything. It just implies that potentially every question in science & philosophy could be explained by reference to a single "entity". Some professional thinkers & researchers are already scratching the surface of that gold mine of knowledge. -
A Physical Explanation for Consciousness, the Reality Possibly
This is all way over my head, including its EM field aura. :wink:CEMI (conscious electromagnetic information) theory is a promising framework for explaining intentionality and the spectrum of arousal as EM field effects. — Enrique
To put your theory into context :
1. How does it differ from CEMI? Does it add or subtract certain features?
2. If this Mind-Field is physical, would it make mind-reading possible, via something like an EEG machine hooked-up to a computer to translate vibrations & excitations into human language?
3. What patterns of field activity would indicate Intention-to-act or to-express-thoughts-&-feelings?
4. Do you see some other practical applications of this theory in the near future?
Note : Self-publishing costs vary from $2000 to $4000 (not including marketing) for a non-technical publication. One low-cost alternative would be to create a WordPress website, which costs as low as $3 per month for shared hosting. Then, you could do your own "marketing" by posting links on other related technical or general interest websites & forums, including Quora. Be advised though, that some sites frown on free self-promotion. Links to the Abstract might provide enough information to elicit interest that might eventually result in being picked-up by a journal. -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Pardon me, but I only see an opportunity for Philosophy to crawl out from under the domination of Empirical Science, as Quantum Physics and Information Theory have elevated the importance of the mind-of-the-observer in both analytical (reductive) and synthetic (holistic) scrutiny of reality. I've heard that the Chinese word for "crisis" means "danger + opportunity".I don't know what you think you have heard but there is a crisis in Philosophy for so many years because humans use the field as a comforting pillow to rest their anxieties and seek validity by just stating "its philosophy". Things are not that simple. — Nickolasgaspar
Can you point to a post in this thread where someone justifies his premise with the appeal to authority of "its philosophy". I assume that's how it appears to you, since you seem to hold a dim view of traditional Philosophy as senseless wrangling about nonsense. That is the self-defeating view of the philosophical position known as Scientism, which was a response to a perceived "crisis" in philosophy. Since that minor branch of philosophy probably began with the Vienna School of the 20th century, it's hardly a current crisis. By contrast, on this forum, those defending a position aligned with Scientism often refer to the concept of capital "s" Science as the centralized & universal authority on all pertinent questions, including philosophical conundra.
For the record, I will gladly acknowledge that you and are more knowledgeable than me on 20th century science and philosophy. And perhaps smarter than me in general, as you seem to assume. But I have read few of the works of 20th century philosophers. of the 174 list in the link below, only Daniel Dennett and Thomas Nagel books are in my library. The others, I have either never heard of the others, or only from Wikipedia articles. I took basic college courses in the major divisions of Science, and have subscribed to Scientific American & Discovery & Skeptic & Skeptical Inquiry magazines for over 40 years. I suppose that pitiful summary pales beside your own curriculum vitae.
However, I came late to philosophy, only a few years ago. And my personal interests are primarily in leading-edge 21st century science, and philosophical investigations into Information & Consciousness & Metaphysical questions, that are still on the margins of scientific concern. So, I admit that most of your criticisms of my ignorance or idiocy fall on deaf ears. Fortunately, there are a few on this forum with similar interests, that I can dialogue with. Hence, I'm not motivated to seek your approval.
List of 20th century philosophers :
https://www.thefamouspeople.com/20th-century-philosophers.php
Thus the struggle between metaphysics and scientific world-conception is not only a struggle between different kinds of philosophies, but it is also—and perhaps primarily—a struggle between different political, social, and economical attitudes.
The rise and fall of scientific authority — and how to bring it back :
Preaching, denouncing or shouting ‘Science works!’ won’t help. Neither will throwing around statistics, graphs and charts.
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-019-00872-w -
The 'New Atheism' : How May it Be Evaluated Philosophically?
Somewhere in the middle. Spinoza's God/Nature may be too close to Pantheism for the comfort of Atheists. And it was dismissed by his contemporary Blaise Pascal as the impotent "god of philosophers", lacking an offer of salvation. But, the notion of identifying God & Nature could be acceptable to Deists, who believe in a Supreme Being or First Cause of some kind, but not one who violates natural laws with miracles. :smile:I wonder to what extent those who believe in Spinoza' s God may be considered to be theists or atheists? — Jack Cummins -
Psychology Evolved From Philosophy Apparently
Yes. But I think Psychology, Sociology, and the other "soft" sciences are still primarily theoretical & philosophical, with a scientific veneer of statistical probabilities. In the early 20th century, premature psychology was dismissed by scientists as "mere philosophy". So, Skinner proposed to make it a "hard" science by studying only objective behavior, instead of speculating on subjective ideas & feelings. That approach faded away after a while, since outward behavior is not a reliable indicator of inward thoughts & motives. What we now know is that humans evolved from apes, yet still have much in common with them. :smile:Psychology, the science of the mind and behavior, supposedly evolved from Philosophy. That was what I was taught when I was taking my psychology classes. I can see how that would be the case, they have much in common and overlap quite a bit. — HardWorker
Behaviorism :
Strictly speaking, behaviorism is a doctrine – a way of doing psychological or behavioral science itself.
https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/behaviorism/ -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Pardon me, but I only see an opportunity for Philosophy to crawl out from under the domination of Empirical Science, as Quantum Physics & Information Theory have elevated the importance of the mind-of-the-observer in both analytical (reductive) and synthetic (holistic) scrutiny of reality. I've heard that the Chinese word for "crisis" means "danger + opportunity".I don't know what you think you have heard but there is a crisis in Philosophy for so many years because humans use the field as a comforting pillow to rest their anxieties and seek validity by just stating "its philosophy". Things are not that simple. — Nickolasgaspar
Can you point to a post in this thread where someone justifies his premise with an appeal to authority of "its philosophy". I assume that's how it appears to you, since you seem to hold a dim view of traditional Philosophy as senseless wrangling about nonsense. That is the self-defeating view of the philosophical belief system known as Scientism, which was a response to a perceived "crisis" in philosophy. Since that minor branch of philosophy probably began with the Vienna School of the 20th century, it's hardly a current crisis. By contrast, on this forum, those defending a position aligned with Scientism often refer to the concept of capital "s" Science as-if it's the centralized & universal authority on all pertinent questions, including philosophical conundra. I have previously pointed-out some examples.
For the record, I will gladly acknowledge that you and are more knowledgeable than me on 20th century science & philosophy. And perhaps smarter than me in general, as you seem to assume. Admittedly, I have read few of the works of 20th century philosophers. Of the 174 listed in the link below, only Daniel Dennett & Thomas Nagel books are in my personal library. I have either never heard of the others, or only from Wikipedia articles. I took basic college courses in the major divisions of Science, and have subscribed to Scientific American & Discovery & Skeptic & Skeptical Inquiry magazines for over 40 years. I suppose that pitiful summary pales beside your own curriculum vitae.
However, I came late to philosophy, only a few years ago. And my personal interests are primarily in leading-edge 21st century science, including philosophical investigations into Information & Consciousness & Metaphysical questions, that are still on the margins of establishment scientific concern. I admit that, due to impertinence, most of your criticisms of my ignorance or idiocy fall on deaf ears. Fortunately, there are a few on this forum with similar interests, that I can dialogue with. So, I remain open to discourse, but not to argue "true science" with you. And, I'm not motivated to seek your approval. :cool:
List of 20th century philosophers :
https://www.thefamouspeople.com/20th-century-philosophers.php
Vienna Circle :
Thus the struggle between metaphysics and scientific world-conception is not only a struggle between different kinds of philosophies, but it is also—and perhaps primarily—a struggle between different political, social, and economical attitudes.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vienna_Circle
The rise and fall of scientific authority — and how to bring it back :
Preaching, denouncing or shouting ‘Science works!’ won’t help. Neither will throwing around statistics, graphs and charts.
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-019-00872-w -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Thanks. Since I have no formal training in philosophical argumentation, I'm using this forum as a "school of hard knocks". As a child, my opinion was seldom solicited, and it was expected to align with the rather conventional views of my father (with a sixth grade education & fundamentalist indoctrination). So, I reached adulthood with a scarcity of clear ideas of my own, and little confidence in those few I had mulled-over inwardly.↪Gnomon
:up: Your posts are definitely improving through time in my humble opinion. Just been reading this interview which I'm sure you will find relevant. — Wayfarer
Over the years my philosophical dialogues were primarily within myself. Even in college, anyone who I dared to suggest a non-standard idea to, would usually exhibit expressions of incomprehension. Consequently, at retirement age, when began to write my thesis, I didn't even know what I thought until I saw what I wrote. However, I still see my harmless-but-unconventional ideas reflected back at me, often with the same eye-glaze of incomprehension, or a grimace of acute disgust.
In my own mind, the general information-based thesis is clear & comprehensive. But then I'm viewing it from my own eccentric perspective, founded primarily on little-known "facts" of Quantum & Information theory. Which have turned the common-sense classical worldview upside down. So, I've had to learn the hard way, how to summarize a complex-but-inter-related system in words that convey novel ideas, without seeming to be deranged or dismissive of "settled science". Since the core concepts of Holism & Consciousness are similar those of Eastern religions, I'm forced to deny, A>implications that I've had the wool pulled over my eyes by pop-religion gurus, or B> accusations that I'm in science-denial.
BTW, your link to the Faggin interview, was right on time. It noted the overlooked aspect of reality in conventional Science : the mind of the observer. And, IMHO, that is where Philosophy still has a role to play in modern science. For example, I consider Psychology, Sociology, and the other "soft" sciences to be essentially inwardly-focused philosophical inquiries, with a statistical veneer of hard science. :smile: -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Exactly! Modern Science studies the physical aspects of Nature, by means of their innate "scope" of Consciousness (what we know with). But they take that inwardly focused "lens" for granted, because it is not a material object to be dissected into structural elements. Instead, Consciousness arises from complex systems as a holistic function. It seems to be "aware" of internal neural states, converting their physical patterns into metaphysical meanings.3. Metaphysics: Here we try to ask and answer questions about things science takes for granted: What is causality? What are space & time? What is existence? Etc. — Agent Smith
In the interview (below), linked by , a physicist suddenly realized that something important was being overlooked in the sciences he was studying : the mind doing the examining. Unfortunately, such subjective subjects were tossed out, along with the faith-stained bathwater, as Science emerged from under the yoke of autocratic Religion. :smile:
Consciousness as the Ground of Being :
I was studying neuroscience and biology, and I asked myself: ‘How come that all these books never mention consciousness?’ ___Physicist Federico Faggin ; inventor of the Intel 4004 chip
https://besharamagazine.org/science-technology/consciousness-as-the-ground-of-being/
MENTAL SUBJECT . . . . . . VIEWS . . . . . . . PHYSICAL OBJECT

Note -- the metaphysical Mind is a holistic function of physical neuronal systems in the brain -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Nick, I can save you a lot of time & effort to defend Atheism against Theism, or Physics vs Metaphysics, Science vs Philosophy -- however you frame your besieged belief system.Factually wrong statement by Gnomon. — Nickolasgaspar
Just copy & paste all the replies to me from . I've heard it all before. But his, and I assume your, Binary worldview has no place for my personal non-polarized worldview. So, what I'm saying does not compute And my terminology has no place in your vocabulary. Therefore, your castigations bounce off me and return to you. Have a nice day. :smile: -
The 'New Atheism' : How May it Be Evaluated Philosophically?
In your prejudicial imagination. :cool:-Obviously you aren't. You are not even making a philosophical case since you are arguing for the supernatural!!! — Nickolasgaspar
FWIW, see my reply to :
https://thephilosophyforum.com/discussion/comment/678622 -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
No. Metaphysics is specifically exempted from scientific analysis. So, scientific verification is out of the question. Yet, that's where Philosophy comes in. It picks up where Science leaves off. Science provides pragmatic knowledge about Nature, while Philosophy provides reasonable opinions about Culture (the human aspect of nature). By "reasonable", I don't mean absolutely true facts, but merely ideas, whose logic has been tested in the fires of well-informed disagreement, to remove the dross.I'll leave you with a question: Can metaphysical claims be verified/falsified? — Agent Smith
Being "well-informed" though, includes knowledge of how the physical world works, so you can tell the difference between a natural event, and a miracle. That's why Philosophers as far back as Plato & Aristotle doubted the actual existence of the metaphorically useful Greek gods. For example, Ari knew enough about the weather to understand that scary lightning occurred randomly, and not due to vengeful cloud-hopping storm-gods. But they still had to assume the "metaphysical existence" (being qua being) of natural-but-invisible causal principles. Yet, those postulated essences were not susceptible to direct observation, so they were placed in a sub-category, under Physics, of Meta-physics.
We no longer turn to his volume on Physics for information on physical questions. But 2500 years later, we still debate some of the non-physical topics -- such as substance, quality, quantity, and relation -- that he chewed-over in the second volume. He also classified four explanatory conditions — an object's form, matter, efficient cause, and teleology --- that are still applicable today. Nevertheless, philosophy is still not in the business of verifying natural facts. It can only use those ancient methods to separate reasonable beliefs from heart-felt opinions.
So, it's due to my own amateurish philosophical analysis, that I have let go of my childhood belief in the Abrahamic Yahweh-Jesus, and the human-edited & redacted scriptures that are presented as the inspired word of God. Yet, I have never been able to rationalize the existence of a contingent world without a First Cause of some kind. That primary, efficient, and final Cause is inherently Preter-natural, hence invulnerable to natural science, which must be satisfied with useful normal or natural facts. But meta-physical philosophy is not bound to physical facts, because it only seeks for logically necessary concepts. Those essential "truths" are Logically Verifiable, but not Physically Falsifiable.
So, no. Metaphysical claims cannot be "verified/falsified" by physical methods. But, they can be proven for logical soundness by rational methods. And prior assumptions, or degrees of belief, can be tested for probability via Bayesian statistics. But, yes. I do include a Creative Cause in my worldview, to at least theoretically explain the "something from nothing" (space-time from infinity-eternity?) issue raised by the scientifically plausible, but not physically provable, Big Bang theory. :nerd:
A contingent truth is one that is true, but could have been false. A necessary truth is one that must be true; a contingent truth is one that is true as it happens, or as things are, but that did not have to be true. In Leibniz's phrase, a necessary truth is true in all possible worlds.
https://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/oi/authority.20110803100226735
Preternatural : beyond what is normal or natural ; metaphysical
Note -- even Multiverse & Many Worlds theories are beyond the scope of physical verification.
The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Logical Verification :
A formal proof is a logical argument expressed in a logical formalism. . . .
In contrast, an informal proof is what a mathematician would normally call a proof. These are often carried out on a blackboard, and are also called “pen-and-paper proofs.”
https://cs.brown.edu/courses/cs1951x/static_files/main.pdf -
The 'New Atheism' : How May it Be Evaluated Philosophically?
I'll just point-out that I'm not making a scientific case. Besides, Atheism is a belief in Absentia. It is not based on scientific facts, but on the absence of physical evidence, which is literally & figuratively immaterial to a metaphysical concept. By "meta-physical" I refer to that which is non-physical (e.g. mental ; cultural), hence immaterial to scientific methods, which specifically eschews subjective phenomenology (personal experience).-Again posting poetic takes on metaphysics by scientists doesn't help your case. — Nickolasgaspar
BTW, my position is not anti-science, but pro-philosophy. I'm also not a Theist, so the typical anti-theism arguments miss their imaginary target. IMHO, Philosophy is more of an art than a science. So demanding reductive scientific evidence for a holistic concept is like, requiring Picasso to justify his odd imagery with empirical facts. Did he really see the world that way? It doesn't matter. :smile:
Legitimate Metaphysics :
Naturalized metaphysicians defend the thesis that science licenses meta-
physics, such that only metaphysical results that are based on the best science
are to be considered legitimate.
http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/11149/1/OMR_Does_Science_License_Metaphysics.pdf
Metaphysics as the Science of Essence :
the central task of metaphysics is to chart the possibilities of being, with a view to
articulating the structure of reality as a whole, at its most fundamental level.
http://ontology.buffalo.edu/06/Lowe/Lowe.pdf -
The 'New Atheism' : How May it Be Evaluated Philosophically?
The quote referred to "scientific method[s}" to contrast with "philosophical methods". Note, I added the "s" to improve the parallel, and to make you feel better. :joke:-Well the definition is wrong or vague at best. First of all there isn't such a thing as A scientific method. — Nickolasgaspar
On what basis do you make that factual claim?The fact is that the formation of the universe was not a creation act...at least we can not make that claim. — Nickolasgaspar
Yes, But I also see the acknowledgement that the BB could be construed as a creation event. Which is why Einstein, among others, resisted the idea. He had assumed that the universe was self-existent. But was forced to change his mind. Some scientists quibbled that the BB was not an "explosion in space" but an "expansion of space'. But even that clarification avoided the issue of how space came to be. Had it always existed somewhere in the Great Beyond, or was it "created" from nothing? Since I know nothing about the Great Before, like most non-specialists, I accept the BB philosophically & metaphorically as a "creation event". Besides, all other pre-BB explanations, such as Multiverses, are also Creation Myths. :smile:-Cherry picking on Stephen's poetic irony? You do see the irony in his words.....don't you??? — Nickolasgaspar
“The basic laws of the universe are simple, but because our senses are limited, we can't grasp them. There is a pattern in creation.”
___A. Einstein
https://www.azquotes.com/author/4399-Albert_Einstein/tag/creation
"The Big Bang Is Hard Science. It Is Also a Creation Story."
___Barry Powell
Apparently, you are going to place everything in this topic backwards. Are you just being contrarian? :cool:indeed, I placed them backwards. — Nickolasgaspar -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Yes. However, the concept of BothAnd didn't come from ancient philosophy, but from my research on ubiquitous Information. Like some pioneering scientists, I concluded that the fundamental substance of Reality is not Dualistic (energy + matter, or mind + matter), but Monistic (it's all Information in various forms : mind + energy + matter + everything else). So, the essence of BothAnd is Monism. The "BothAnd" label is simply an indicator that truth is not polarized, but a continuum. :smile:You want to, in a sense, incorporate the best of both (opposing) worlds, that's what we recognize as the aurea mediocritas (the golden mean), in your quest to gain a complete understanding of reality. You need both halves (the yin & the yang). — Agent Smith
The "excluded middle" and "non-contradiction" rules are presuming that you have access to absolute all-encompassing Truth. But the BothAnd rule assumes that we humans are all limited to small bits & pieces of perfect Platonic Truth. That's why I compare it to Einstein's Relativity : the truth you see depends on your "frame of reference", your limited perspective. So, for us earth-bound truth-seekers, it's all "middle ground". :cool:However, as I've always been concerned about, doesn't your Both/And Principle violate 2 laws of logic viz. the law of the excluded middle and the law of noncontradiction (given a proposition p, either p is true or ~p is true but not the case that both p and ~p are true/false at the same time). As an illustration, either theism is true or atheism is true, but both can't be true and both can't be false. There can be no middle ground betwixt theism and atheism. — Agent Smith
Since I consider Meta-Physics to be the sole purview of Philosophy, I wouldn't agree that we shouldn't discuss non-physical (e.g. mental) topics. What else are we going to talk about, the weather? Even so, we cannot make any absolute claims about non-verifiable or non-falsifiable bits of truth. Philosophy can only allow us to get "Closer to Truth". As the link below notes, despite our best efforts to "know the mind of god", philosophers, by "exploring the deepest questions" can only hope to improve their own personal understanding. Beware of prophets who claim to reveal the absolute Truth. However, the Enformationism thesis is intended to suggest a way to approximate a Theory of Everything.The point is we can't discuss metaphysics for it's impossible to justify any claims we make therein (pure speculation is all that we can manage). . . .
By the way, Nagarjuna's tetralemma is known as the middle way because it rejects/negates extremes. — Agent Smith
The rejection of extremes is definitely akin to the BothAnd view. However, it's statistically possible that the balance point of Harmony could be at one extreme. For, example, a rule against torturing babies may be as far as possible away from Sadism. But such clear (radical) oppositions are rare. :nerd:
Closer to Truth :
the greatest thinkers exploring the deepest questions
https://www.closertotruth.com/
What's the Point of Philosophy? :
“It is suggested that the intrinsic point of doing philosophy is to establish a rational consensus about what the answers to its main questions are. But it seems that this cannot be accomplished because philosophical arguments are bound to be inconclusive,”
https://qz.com/1313616/whats-the-point-of-philosophy-a-new-philosophy-paper-says-there-isnt-one/
The Mind of God is a 1992 non-fiction book by physicist Paul Davies. Subtitled The Scientific Basis for a Rational World, it is a whirlwind tour and explanation of theories, both physical and metaphysical, regarding ultimate causes. Its title comes from a quotation from Stephen Hawking: "If we do discover a theory of everything...it would be the ultimate triumph of human reason—for then we would truly know the mind of God."
The Enformationism thesis is a sort of Theory of Everything (TOE), in the sense that "X" is supposed to be the cosmic All, of which our world is a small part. But it is not a scientific model of reality, and it does not claim to be the absolute Truth. Instead, it is merely a framework for my personal under-standing of the enigmatic world I found myself wandering in, like a stranger in a strange land, as an unfledged babe. It's also a response to the babble of rival theories-of-ultimate-reality -- religious & scientific -- that only added to the mystery.
BothAnd Blog, post 11
Note -- "X" can be imagined as G*D, Logos, Programmer, Creator, The All, The One, etc. Sadly, as the part cannot know the whole, we may never know the mind of "X" for sure. But we can guess.
INFLUENCES ON PERSONAL FRAME OF REFERENCE
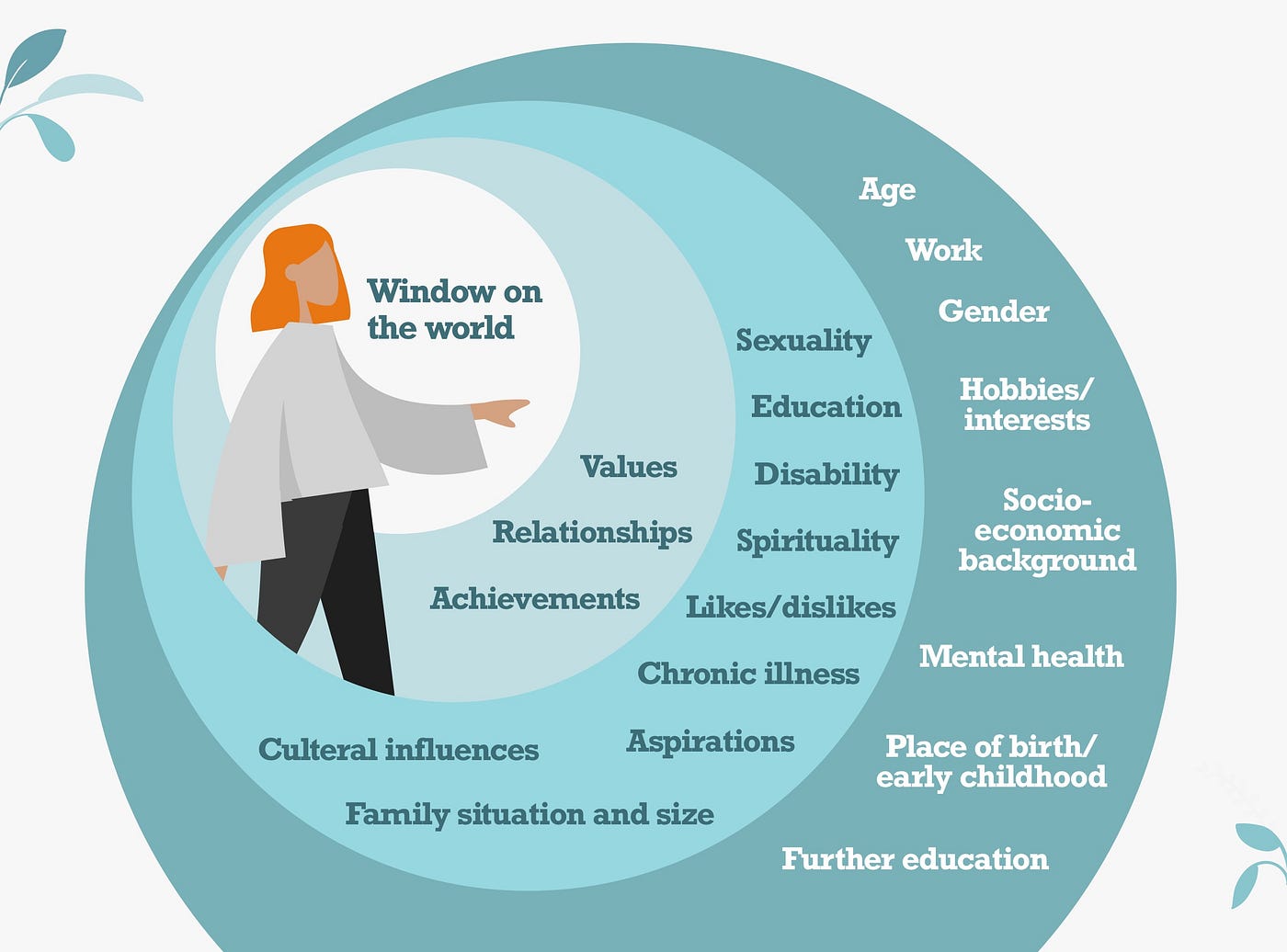
-
The 'New Atheism' : How May it Be Evaluated Philosophically?
Perhaps. But, since this is a philosophical forum, I'm referring to the position defined in the quote below. So, there's not much distinction between them. :smile:-Two issues. Naturalism is not one thing. Science is based on Methodological Naturalism..not Philosophical Naturalism. — Nickolasgaspar
Philosophical Naturalism :
naturalism, in philosophy, a theory that relates scientific method to philosophy by affirming that all beings and events in the universe (whatever their inherent character may be) are natural. Consequently, all knowledge of the universe falls within the pale of scientific investigation.
https://www.britannica.com/topic/naturalism-philosophy
I have been surprised at how many prominent scientists have referred to the BB as a "creation event". You can Google some of their quotes. :smile:Now, In science the big bang event is not labeled as "creation"
(since it would imply extra agencies) but as "formation" so there was no real shock caused by that observation. — Nickolasgaspar
"There is a strange ring of feeling and emotion in these reactions [of scientists to evidence that the universe had a sudden beginning]." ___ Robert Jastrow, astronomer, physicist
"An expanding universe does not preclude a creator, but it does place limits on when he might have carried out his job!" __ Stephen W. Hawking
I assume your comment got [1] & [2] backward. :wink:- [1] Anthropic principles and [2] statistical probabilities are not even in the same ball park. The first is a conclusion based on available facts and the second presupposes teleology and purpose behind a creation.(fallacy). — Nickolasgaspar
ANTHROPIC ASSUMPTIONS
A. We can identify which natural properties are necessary or compatible for life
B. Evolution follows natural laws and inherent limitations set by initial conditions & constants
C. The element Carbon, only produced in certain stars, is essential to life, but is rare (.025%) on Earth
D. The initial conditions of our universe were selected from all possible logical (mental) or actual (multiverse) combinations
E. The complex pathway to Life has a low statistical probability
F. An unlikely occurrence is not necessarily a miracle, but must have some ultimate Cause
Book Review of The Anthropic Cosmological Principle -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Apparently, you have misunderstood the point of the BothAnd philosophy. In practice, the BothAnd principle considers all possibilities between 0 & 1. But tries to find the point of balance & harmony. It is intended to be an alternative to the typical unbalanced binary all-or-nothing Either/Or posture. But it doesn't prescribe a position in the exact middle of the range of views. Each observer will have personal reasons for emphasizing certain aspects over others. However, it is generally aligned with Aristotle's Golden Mean, and Buddha's Middle Path, and Taoism's Yin/Yang. As a rule-of-thumb, it simply means "nothing to excess". :smile:Have you ever considered that you could be, by limiting yourself to a binary system (for vs. against), alloying the two belligerent sides on any issue, you could very well be committing the false dichotomy fallacy or the argumentum ad temperantiam fallacy. — Agent Smith
Both/And Principle :
* My coinage for the holistic principle of Complementarity, as illustrated in the Yin/Yang symbol. Opposing or contrasting concepts are always part of a greater whole. Conflicts between parts can be reconciled or harmonized by putting them into the context of a whole system.
* The Enformationism worldview entails the principles of Complementarity, Reciprocity & Holism, which are necessary to ofset the negative effects of Fragmentation, Isolation & Reductionism. Analysis into parts is necessary for knowledge of the mechanics of the world, but synthesis of those parts into a whole system is required for the wisdom to integrate the self into the larger system.
BothAnd Blog Glossary
Yes, The BothAnd principle does seek a third option, which is the balance point between excess & deficit. I'm not familiar with "terralemma", but having to juggle four alternatives, instead of two or three, may violate Ockham's Razor. The term "BothAnd" merely acknowledges that most philosophical debates tend to force participants to defend one extreme or the other. By contrast, "moderation in all things" advises us to compromise, so as to avoid mutual annihilation, or a Mexican stand-off. :joke:For instance, in the debate between atheism and theism, is it possible that, instead of trying to unify the two into a whole, you could reject both and contemplate on a third alternative which is neither theism nor atheism, and not some amalgamation of the two (the middle), but something else entirely. Have you come across Nagarjuna's terralemma? — Agent Smith
PS__This very thread illustrates the Either/Or policy. If someone proposes a moderate position, others will immediately attack it as-if it was a totalitarian rejection of their position. My stance on the god question is in the middle : Theism - Deism - Atheism. But a Theist would consider me to be an Atheist, and vice-versa.
Why Compromise? :
Like the philosophy of Pragmatism, the BothAnd principle, requiring accommodation to seemingly extraneous factors, could be dismissed as a weak policy of compromising eternal principles for temporary goals. But that sneer misses the point of taking the broader view, seeking harmony & balance instead of victory & triumph. So, the idea is to make practical concessions to the fact that each person, social group, nation, planet, and galaxy is but a small part of a greater whole.
BothAnd Blog, post 2
Deism :
An Enlightenment era response to the Roman Catholic version of Theism, in which the supernatural deity interacts and intervenes with humans via visions & miracles, and rules his people through a human dictator. Deists rejected most of the supernatural stuff, but retained an essential role for a First Cause creator, who must be respected as the quintessence of our world, but not worshiped like a tyrant. The point of Deism is not to seek salvation, but merely understanding.
BothAnd Blog Glossary -
The 'New Atheism' : How May it Be Evaluated Philosophically?
You will find Stenger very clear in his arguments, because he takes a firm stand on Naturalism. You could even call his inflexible position Dogmatism. If you agree with his Naturalist premises though, you must agree with the logic of his Atheist conclusions. But philosophers tend to be open to other interpretations of Nature, that may not be of interest to empirical scientists. Especially, regarding Ontology and questions about "something from nothing".I will look out for the writing of Dr Stenger because it is worth looking at the idea of the new atheism from a wider angle. — Jack Cummins
Naturalism takes the existence of this physical world for granted. So the scientific evidence for a specific "creation event" came as a shock. But, they have adapted their belief in eternal Nature, to imagine explanations for a time-before-time, when our knowable world didn't exist as we know it. Yet, Multiverse & Many Worlds theories are simply extensions of their original Naturalist premises across the Big Bang abyss into the unknowable what-if.
Ironically, the Wiki quote below says he also used a statistical probability argument, for which the data must be imagined, to prove that our world is nothing special. Hence, not created by an omniscient deity. However, other scientists have used similar anthropic logic to prove just the opposite. So, apparently, the Las Vegas odds are in favor of the "house", who determines the odds (premises) you will play with. So, are you going to play by house-always-wins rules, or your own personal reasoning? If you are a Theist, Stenger will challenge your assumptions. But, his own presumptions are also subject to philosophical questioning. :smile:
Stenger was an advocate of philosophical naturalism, skepticism, and atheism. He was a prominent critic of intelligent design and the aggressive use of the anthropic principle.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Victor_J._Stenger
The anthropic principle is the principle that there is a restrictive lower bound on how statistically probable our observations of the universe are, given that we could only exist in the particular type of universe capable of developing and sustaining sentient life. ___Wikipedia
Ever since Copernicus, scientists have continually adjusted their view of human nature, moving it further and further from its ancient position at the center of Creation. But in recent years, a startling new concept has evolved that places it more firmly than ever in a special position. Known as the Anthropic Cosmological Principle, this collection of ideas holds that the existence of intelligent observers determines the fundamental structure of the Universe.
https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/218097.The_Anthropic_Cosmological_Principle -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Yes, but. The hypothetical Singularity (non-dimensional point in non-space) is about as simple as it gets. It's essentially a mathematical concept, with no moving parts. Consequently, the philosophical question arises : how does real complexity arise from unreal (ideal) simplicity. I turn to Aristotle for the answer. He distinguished between Potential & Actual. But the problem is that a Potential thing is like a Platonic Form : it doesn't exist in the real physical world. So, in what sense does "Potential" exist?↪Gnomon
What I would like to stress on is if it's (genesis of the universe and life) is goimg to be, as you claim, bottom-up (for me this means going from the simple to the complex), there really is no need to posit an intelligence. It could proceed quite naturally, on its own accord, without the intervention of a "higher power". — Agent Smith
Based on the sub-quantum sciences and information theories, I have concluded that Potential exists in the same sense that mental Information (ideas ; thoughts ; meaning) exists : as Ideal Forms. And AFAIK, Meaning exists only in Minds. Although, probably to avoid confusion with humanoid Greek gods, Plato tended to avoid personal terms, such as "Mind", his "Ideal Forms" were clearly non-physical abstractions equivalent to ideas or definitions in a human mind. But he didn't specify whose mind, except to imply that his hypothetical impersonal Logos was the ultimate source of all mental attributes. Some, less scrupulous, later philosophers have interpreted his Ideal realm as the "Mind of God".
For the same reason, I refer to the Mind, in which the mathematical Singularity was conceived, by various descriptive but non-personal names -- beginning with Logos, which is indeed an imaginary "higher power". Materialists refer to the same hypothetical Ultimate Source of our orderly world with "invented" abstract models : Multiverse, Many Worlds. Yet, they are portrayed as mindless impersonal accidental systems of energy, matter, & laws. In which case, they have no explanation for the emergence of the non-physical non-things that are of highest importance to mortal humans : Life, Mind, Ideas, Meanings, Feelings, Reasons, Love, etc.
Our world does indeed seem to be self-organizing (bottom-up evolution), requiring no divine intervention to correct its course. Once the evolutionary process gets started, "it proceeds naturally". But, unlike pragmatic scientists, philosophers are also interested in Ontology (being). So, they ask impractical questions, such as "why is there something instead of nothing"? And Multiverse theories just take existence for granted, even though non-being is just as likely. So, the beginning of Being is an open question. Since my thesis is based on Information, I like to use computers as a metaphor for the real world. A computer program is self-organizing, and works from the bottom-up, from original algorithm to final output. And it requires an external Mind to build the computer, to input the algorithm, to define the problem to be solved, and to push the Start button.
So, like Plato, I try to avoid attributing personal attributes to an abstract concept, beyond my ken. I merely imagine a job description for the "Programmer" (the Intelligence, the Enformer), who input the Energy & Laws (the algorithm) to initiate the smooth-running & creative & progressive process that we call Evolution. :nerd:
Potentiality and actuality :
Aristotle describes potentiality and actuality, or potency and action, as one of several distinctions between things that exist or do not exist. In a sense, a thing that exists potentially does not exist, but the potential does exist.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potentiality_and_actuality
Note -- Potential exists as a mental concept, not a material object
What is the relation of Plato's Forms to things? :
For Plato, Forms or Ideals (eidos ; ideas) are essences or originals of qualities or things.
Because Plato managed to do something THAT NO BODY ELSE HAVE MANAGED TO ACCOMPLISH ON THIS PLANET at least in his scale. . . . . Namely He spoke about the invisible abstract world without the use of advanced technology or through Deamons(Magic). . . .He described something that only advanced technology today can some times prove that exists. He spoke about the blue prints of this universe. He described the world of IDEAS a world that is stable in contradiction to our world where everything are subjected to degradation and death.
https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-relation-of-Platos-form-to-things
Note -- empirical scientists don't do essences; that is left up to impractical philosophers.
BEING :
In my own theorizing there is one universal principle that subsumes all others, including Consciousness : essential Existence. Among those philosophical musings, I refer to the "unit of existence" with the absolute singular term "BEING" as contrasted with the plurality of contingent "beings" and things and properties. By BEING I mean the ultimate “ground of being”, which is simply the power to exist, and the power to create beings.
Note : Real & Ideal are modes of being. BEING, the power to exist, is the source & cause of Reality and Ideality. BEING is eternal, undivided and static, but once divided into Real/Ideal, it becomes our dynamic Reality.
BothAnd Blog Glossary
Programmer vs Creator vs Recycler :
Admittedly, the hypothetical Cosmic Creator or Prime Programmer of this thesis is nothing more than a job description, and we can imagine a variety of office-holders to fill the prescribed roles. For those who prefer a transcendent ultimate entity, an unimaginable deity like Allah or Brahman would fill the bill. For others, more modernistically & humanistically inclined, a clean-cut white-haired Architect, as in the Matrix movie, might suffice to symbolize the Designer. Or for those who prefer a more abstract and impersonal concept, a Multiverse of eternally cycling energy, creating a variety of material forms out of nothing more substantial than the power-to-enform, might sound more scientific. But it still must somehow explain the emergence of conscious minds. Moreover, any intervention from above by any of these role-models would have to work from the bottom up, in order to agree with the observed mechanisms of reality. Which of these role-models would best suit this new worldview for the 21st century, wherein Reality is founded upon immaterial yet potent information?
BothAnd Blog, post 4
Self‐organization is a core concept of Systems Science. It refers to the ability of a class of systems (self‐organizing systems (SOS)) to change their internal structure and/or their function in response to external circumstances.
https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-0-387-30440-3_475
Note -- SOS are able to evolve to suit changing environments. But they must be designed to do so. Self-organization doesn't happen accidentally. Presumably, what Darwin called "Natural Selection" is a programming function, like a "subroutine". -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Good point! That's why I have concluded that the potential for Life & Mind, must have been "programmed" into the evolutionary scheme that we now call the Singularity. Physicists define it as a mathematical point, with no extension in space or time. So, there was no room for actual Energy or Matter. Only the Logical "design concept" for those inherent properties of physical evolution would fit into a spaceless container. Logic & Math consist of abstract mental relationships, not actual material objects. For example : how big is the number "four"?Abiogenesis may lead to evolution but evolution does not lead to abiogenesis — Tom Storm
This notion of Causal Abstraction should be compatible with some hypothetical Mathematical Universe and Anthropic Principle conjectures. So, I assume the proponents must imagine that "abiogenesis" was originally an abstract mathematical-logical definition or algorithm of some kind. Of course, MUH is a controversial concept, and the only supporting evidence, so far, is logical consistency. So, I don't take it literally.
But something along those lines would answer some of the fundamental Origin-of-Everything questions. One of which is : how could any material object (not to mention any living thing) survive the holocaust of a Cosmic scale eruption of space-time-energy-laws?? Perhaps the big bomb was merely a mathematical abstraction itself. And we only imagine it in familiar terms of physical explosions, such as those in Ukraine. :smile:
Mathematical universe hypothesis :
Tegmark's MUH is: Our external physical reality is a mathematical structure. . . .
In any mathematical structure complex enough to contain such substructures, they "will subjectively perceive themselves as existing in a physically 'real' world". . . .
The MUH is based on the radical Platonist view that math is an external reality.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mathematical_universe_hypothesis
Note -- the virtual reality of the Matrix was a mathematical structure (simulation), that its inhabitants accepted as real. -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Actually, he did speculate on how life began in terms of his evolutionary theory : the warm puddle hypothesis. And other biologists have attempted to find hard evidence to support that notion. Even physicists have tried to expand the Darwinian theory back to the origin of everything. But, it was astronomers who found circumstantial evidence, in the expanding universe theory.Darwin's theory (to my knowledge) has never attempted to explain life on earth. — Tom Storm
Yet even that evolutionary cosmology ran into mathematical infinities in the minuscule Planck Time, near the creation event we now call the Big Bang. Even so, theorists like Allan Guth & Andrei Linde subdivided the BB era into even tinier fractions of a second. Yet, they still haven't reached the Holy Grail of explaining "something from nothing". All theories to-date stop short of the beginning-of-the-beginning : asymptotic to infinity.
So, the field remains open, even for philosophical conjectures. Such as where did the initial energy & laws originate? FWIW, my amateur summary of the phases of evolution is pasted below. And Life emerged in the middle, at step seven. Presumably, because the potential for Life was already programmed in the First Cause. But, by whom? :nerd:
Charles Darwin's hunch about early life :
Darwin was proposing that life began, not in the open ocean, but in a smaller body of water on land, which was rich in chemicals. This is in essence the primordial soup idea, but with one advantage: in a pool, any dissolved chemicals would become concentrated when water evaporated in the heat of the day.
https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20201110-charles-darwin-early-life-theory
Is The Inflationary Universe A Scientific Theory? Not Anymore :
The problem with inflation isn't the idea per se, but the overproduction of useless inflationary models. ___Sabine Hossenfelder, theoretical physicist
https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2017/09/28/is-the-inflationary-universe-a-scientific-theory-not-anymore/?sh=7df51ea1b45e
Phases of Evolution :
0. Omega Point :
Who knows?
9. Reiterate
Ongoing Emergences
8. Artificial Forms :
Machines, Computers
8. Metaphysical Forms
Reasoning & Designing
7. Organic Forms :
Life, Minds, Societies (consciousness)
6. Physical Forms :
Stars, Galaxies, Planets
5. Matter :
Primitive Particles
4. Energy :
Unformed Plasma
3. Quantum Field :
Statistical Possibilities
2. Big Bang :
Start the computation
Start the clock of Time
Set initial conditions
1. Singularity :
Design, Codes, Laws (the evolutionary Program)
0. Infinity :
Omni-potence, Omni-science,?
Note --- Hume : "like causes like"
nothing in the effect that was not potentially in the cause
e.g Life from Life & Mind from Mind -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
To give a prominent scientist his due, I suspect that Dawkin's bold assertion was expressed in frustration with the antagonistic Creationism movement, which often belittled Darwin's insight into the mechanism of speciation as "just a theory". After a century & a half of research, his theory is supported by lots of data-points of Fact. And there's little evidence to contradict Darwin's general description of the process of emergence, in which new "forms" originate (branch off) from old forms.Evolution is a fact.--Richard Dawkins, 2005 (3) — Gnomon
This is exactly the kind of misleading rhetoric that we should be worried about in my humble opinion. It encourages scientism (science as an absolute infallible authority). It is, in a sense, a betrayal of those who kicked off the scientific revolution which was a painful and sometimes deadly struggle against religious dogmatism. — Agent Smith
However, the presumption that Darwin's theory explains the origin of Life on Earth is still open to dispute. And that is the point the Creationists hammer on. Some modern theologians have given-up the outdated notion of special creation of each "kind", as described in Genesis. But, they still discern the necessity for an "intelligence", of some kind, to "design" the program of creative evolutionary progression. I'm no longer a theist, but I too, infer a logical role for a Programmer to map-out a scheme, whereby an almost infinite universe could be produced from the DNA-like information in a tiny, Planck scale, bit of potential energy & instructions for causing Matter & Mind to evolve over time, from almost nothing, in-the-beginning. The odds of that happening by Chance, seem more than infinite-to-one.
I understand that defenders of Scientism may feel justified, by Darwin's "Fact", in their dogged struggle against dogmatic Religious Creationism. But, my position is somewhere in the middle, between Cosmic Accident and Special Creation. The only way to know for sure how & why the world began & developed as it did, would require direct revelation from the Originator. I assume that's why various prophets, over the centuries, have claimed to be conduits for divine inspiration. But, I find their diverse & contradictory stories to be unbelievable, as the word of God. So, I have been forced to develop my own patchwork theory of creation & evolution, cobbled-together from bits & pieces of plausible information. It's a philosophical hypothesis, not a scientific fact or theory. Yet, it serves my personal need for a comprehensive worldview. And it all comes down to one simple fact of nature : Information (the power to enform) is fundamental & ubiquitous in the real world. :nerd:
Evolution as fact and theory :
Many scientists and philosophers of science have described evolution as fact and theory, a phrase which was used as the title of an article by paleontologist Stephen Jay Gould in 1981. He describes fact in science as meaning data, not known with absolute certainty but "confirmed to such a degree that it would be perverse to withhold provisional assent"
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evolution_as_fact_and_theory
Special Creation :
In creationism, special creation is a belief that the universe and all life in it originated in its present form by fiat or divine decree.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special_creation
Evolutionary Programming :
Special computer algorithms inspired by biological Natural Selection. It is similar to Genetic Programming in that it relies on internal competition between random alternative solutions to weed-out inferior results, and to pass-on superior answers to the next generation of algorithms. By means of such optimizing feedback loops, evolution is able to make progress toward the best possible solution – limited only by local restraints – to the original programmer’s goal or purpose. In Enformationism theory the Prime Programmer is portrayed as a creative principle (e.g. Logos), who uses bottom-up mechanisms, rather than top-down miracles, to produce a world with both freedom & determinism, order & meaning.
BothAnd Glossary
Is Information Fundamental? :
Could information be the most basic building block of reality?
https://www.closertotruth.com/series/information-fundamental -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
I agree. Science is about provisional facts. But some of us still feel the need for some ultimate arbiter of Truth. That feeling may be the same imperative need that motivated the ancient prophets, who tried to go over the head of irascible autocratic kings, by appealing to a King of Kings. In this case though, the Truth-giver is imagined as a sort of a collective hive-mind, composed of officially-frocked scientist priests. Anyway, for the prophets of Absolute Truth, there is no room for independent-minded, woo-mongering, uncertain, flakey philosophers. :joke:To cut the long story short, scientism, if it means science is about truths, is completely baseless. Science isn't about reality, it's about constructing best explanations of reality and that's a different story altogether. — Agent Smith
Why Science Is Not Final Arbiter of Truth :
For far too long, science has been shrouded in a cloak of unquestionable authority as the final arbiter of all knowledge (except, of course, when the research has been funded by business, which for some makes it necessarily suspect).
* What drives us onward in the work of science is precisely the sense that there are truths out there to be discovered, truths that once discovered will form a permanent part of human knowledge.--Steve Weinberg, 2001 (1)
* ...all scientific knowledge, however acquired, is inherently provisional.--Ian Tattersall, 2008 (2)
* It is a fact that we are cousins of gorillas, kangaroos, starfish, and bacteria. Evolution is as much a fact as the heat of the sun. It is not a theory, and for pity's sake, let's stop confusing the philosophically naive by calling it so. Evolution is a fact.--Richard Dawkins, 2005 (3)
* Science is not about final truth or "facts"; it is only about continually testing and trying to falsify our hypotheses, until they are extremely well-supported.--Donald P. Prothero, 2007 (4)
https://www.independent.org/news/article.asp?id=2681 -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Apparently, he was not questioning any particular god-concept, but merely the almost universal notion of some transcendent power over the world. Most of the world's religions hold that their supernatural authority (Lord) must be worshiped in order to receive blessings, or to avoid punishments. I suspect it's that intervening (blessing & cursing) Western (Abrahamic) god-model that the OP assumes may require some empirical evidence in a skeptical age. Almost all popular religions teach that their god, if properly motivated, can override Nature, and sometimes even human actions, on their behalf. That's the one I replied to in the negative. Empirical science has no evidence, one way or the other, about such extra-mundane beliefs.What is this concept of ‘god’? That is my starting question if the OP is asking about possible proof. — I like sushi
Before the advent of modern science, most people were mystified by the vagaries of Nature, which seemed as unpredictable, mercurial, & capricious as the behavior of their human leaders. But, there are other, more philosophical, and mostly Eastern (TAO), notions of transcendent power, that make no claims of placatable deities. In those cases, the deity or deities were presumed responsible for both the good and the bad events in the world (Good & Evil). Hence, a Stoic attitude was the best way to think about the inexplicable positive or negative effects of Nature on human welfare. Ironically, such apathy is almost indistinguishable from our modern concept of Nature as an automatic mechanism. Consequently, our scientists feel no qualms about tinkering with dangerous natural processes, in order to make them more agreeable to human wishes.
Unfortunately, Stoicism & Scientism, are not very attractive to the average human, who is more inclined to pray for instant & personal help, rather than to wait for human ingenuity to learn to control tornadoes, earthquakes, cancer, plagues, insurrections, civil wars, and so forth, with technology instead of magic. Those more philosophically inclined though, may still find the general notion of First Cause, or Cosmic Force, or Tao helpful to make sense of a bewildering world. From that cosmic perspective we are all parts of a universal Whole.
Since the Cosmos as-a-whole is "more than the sum of its parts: it is both Immanent & Transcendent. So, you can call it "GOD", or "TAO", or "LOGOS", or simply "Nature", as you please. However, there will still be no empirical evidence for that Holistic concept. The affirmation is merely philosophical, rational, & theoretical. So, the answer to the OP is still negative. :cool:
Conceptions of God in monotheist, pantheist, and panentheist religions – or of the supreme deity in henotheistic religions – can extend to various levels of abstraction: as a powerful, human-like,
___Wikipedia
Stoic physics :
The Stoics often identified the universe and God with Zeus, as the ruler and upholder, and at the same time the law, of the universe. The Stoic God is not a transcendent omniscient being standing outside nature, but rather it is immanent—the divine element is immersed in nature itself.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stoic_physics

-
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Yes. That's the theory. But, in practice, the core disagreement may be so wide & rigid that mutuality is impossible. When that happens, I call it a "political" dispute, instead of a "philosophical" dialogue. On this forum, the core issue seems to be focused on the authority of Science, envisioned as having monolithic dominion over certain kinds of questions, including "norms" & "values", but especially concerning Metaphysics.↪Gnomon
Thanks for the explanation. The two sides of a debate could thrash out the sticking points, identify where they disagree and come to a mutually acceptable agreement on how to settle their differences. — Agent Smith
For over a thousand years, the Catholic Church used Aristotle's & Ptolemy's physics & metaphysics as the final authority to settle dissension within its ranks. Today, Ari is out of favor, and Ptolemy is discredited. So capital "s" Science has taken their place as ultimate arbiter, at least for believers in doctrinaire Scientism. In general, that absolute trust in empirical Science, as opposed to theoretical Philosophy, was mandated by proponents of Logical Positivism (aka Logical Empiricism). Ironically, that movement has boldly crossed-over into the "Magisterium" of Religion. Hence, it seems to serve as a sort of religion-substitute for its adherents.
Although they may not realize that they have been indoctrinated with an anti-philosophy attitude, a few posters on this forum feel that their mission is to root-out heretics, who insist on defying the sovereignty of Science, by delving into Metaphysics, and by insisting that there is more to Reality (e.g. Mind) than just Matter & Physics. Therefore, it's that "sticking point" which blocks some attempts to reach "mutually acceptable agreements". Undaunted, some of us soldier on, buoyed by faith in FreeWill & Reason, to explore the meta-physical mysteries of our world, and especially the human Mind. :smile:
PS__Disclaimer : These are just my personal opinions, not those of The Philosophy Forum.
Scientism is the view that science and the scientific method are the best or only objective means by which people should determine normative and epistemological values. . . .
In the philosophy of science, the term scientism frequently implies a critique of the more extreme expressions of logical positivism
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scientism
Logical positivists denied the soundness of metaphysics and traditional philosophy; they asserted that many philosophical problems are indeed meaningless.
http://people.loyno.edu/~folse/logpos.htm -
Question regarding panpsychism
Good question! I assume that Panpsychists are probably trying to unify the traditional mind/matter dualisms, by assuming that both are merely emergent forms of a universal "substance" or "essence: Mind, which is best known in its manifestation as Consciousness. I agree with that motivation, but I personally take a slightly different track. A common retort to notions of universal Consciousness is to ridicule the idea of a conscious atom or grain of sand. Another problem, as you noted, is to make a distinction between Conscious & Subconscious mental processes.So I'm wondering what is gained by losing the distinction between conscious and not conscious. — Daemon
So, in my own attempts to understand how conscious Mind could evolve from mindless Matter, I merely reversed order of primacy. Many philosophers have found the notion a universal Mind reasonable. So, to present it as a philosophical principle instead of a religious doctrine, I substitute the more technical-sounding term "Information". The word originally referred to the contents of a human mind in the form of intangible Thoughts & Ideas & Feelings. But Claude Shannon stripped the word of its conscious connotations, and defined it as an empty container for any meaning you want to put into it. That abstract definition works well for the purposes of programming general-purpose computers, but not so good for the self-programming & self-conscious human mind.
My thesis tracks the evolution of the human mind back to the original Singularity (imagined as a creative evolutionary program), and even one step farther to a hypothetical "Programmer", traditionally known by philosophers as the generic "First Cause". And the common "substance" all the way up is generic "Information" (EnFormAction ; the power to enform). Which takes on many real forms along the way : Potential, Energy, Forces, Mass, Matter, and Mind. For those who are not familiar with cutting-edge Information theory -- in Physics & Philosophy -- that scenario will seem even more ridiculous than the mystical-sounding Panpsychism theory. But, I prefer to call it "Information Realism". It retains the distinction between Conscious Minds & insensible Matter, but unifies them as diverse forms of evolutionary emergence back to a common ancestor, the hypothetical Prime Mind. :nerd:
Physics Is Pointing Inexorably to Mind :
So-called “information realism” has some surprising implications
https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/observations/physics-is-pointing-inexorably-to-mind/
Consciousness : Emergent or Fundamental?
Most scientific and religious worldviews take the ontological status of Consciousness for granted. But when those belief systems are in conflict, their unstated presumptions are key to resolving the problem. Modern Science typically assumes, as an unproven axiom, that consciousness is an emergent property of physical processes. In other words, the human mind is a product of brain processes. And that hypothesis of mind as mechanical output makes sense from the the perspective of philosophical Materialism. But most religions are based on the principle of Divine Consciousness or Spirit or Will as the primordial creative force of the world. Unfortunately, centuries of debate have shown that it will never be easy to resolve such a stark black & white opposition of opinions.
Philosophy, though, is undaunted by irresistable forces and immovable objects. It thrives on head-knocking controversies. A recent post on the Quora Forum formulated this general topic as a technical question : " is consciousness a fundamental property of the universe like gravity . . . ?" In other words, is mind essential to reality instead of an accidental emergence? Or restated in religious terms, did God create the material world by simply imagining it? Put another way, the question may be posed as "What is the basis of reality, matter or consciousness?" Here, it sounds more like a functional distinction between shape-shifting intangible Energy and stable palpable Matter, or like the difference between Mind and Body.
BothAnd Blog, post 7 -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
This forum is supposed to be a meeting place for philosophical dialogue. and the Site Guidelines say : "Don't start a new discussion unless you are: a) Genuinely interested in the topic you've begun and are willing to engage those who engage you." No-one is trying to force "opposing sides to join hands". Instead, each side is allowed to present an argument, pro or con, regarding the topical question or comment. For an engagement to work though, it takes two to tango.You did mention in a previous post, adversarial collaboration but I'm not sure how much of that is just talk or hand waving. Instead of trying to make opposing sides join hands, isn't it better to let them go their separate ways and just wait & watch; whichever side gets it (the truth that is) is to be awarded a Nobel Prize. If both reach the finish line simulataneously, twice the fun, oui? — Agent Smith
Unfortunately, some posters get stuck on the "adversarial" step, and never make it to the "collaboration" station. So, they try to shut the door to further discussion, by demanding concession to a specified authority. But that tactic seldom works when there are strong motives on both sides. Some of the forum's longest-running threads are also the most contentious. So, the failure to communicate, or to "reach the finish line simultaneously" may be an indication of serious philosophical or political polarization. And "adversarial collaboration" requires identifying "diagnostic points of divergence", and a willingness to reach an agreement. The divergent topics are pretty clear, but the agreement stage may be a long time coming.
So, I'm not holding my breath, waiting for a break-through. After all, we are still debating some of the same topics that Plato & Aristotle raised 2500 years ago : "God", "Consciousness", "Free Will", etc. There's a common aphorism : "It's the journey, not the destination that matters.". Which acknowledges that you may never reach your desired destination. That's why I'm not trying to convert anyone to my personal worldview. Instead, by submitting my perspective to opposing views, I can learn it's deficiencies & weaknesses. As Nietszche said, "what doesn't kill you makes you stronger". :joke:
Philosophical dialogue is a mutual inquiry based on the principle that the more points of view there are, the better we understand what there is to understand. There are no winners and no losers - it is open, based on collaboration.
https://lepole.education/en/philosophy/32-practice-of-philosophy.html?start=4
adversarial collaboration rests on identifying the most diagnostic points of divergence
between competing theories, reaching agreement on precisely what they predict, and then designing
experiments that directly test those diverging predictions.
science.sciencemag.org/content/372/6545/911 -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Thanks, but I've already given my reply to the OP. Other, than that, I'm letting Voltaire and Einstein speak for me. Their personal opinions on the topic are not scientific facts, but philosophical inferences. :smile:↪Gnomon
The floor is yours. Say something. — I like sushi -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Are you not interested in a well-established philosophical concept, that was taken for granted by some of the smartest people on the planet for thousands of years? That list would include the "great skeptic" Voltaire.↪Gnomon
Asking why people believe in a ‘deity’ is not exactly defining what a ‘deity’ is in any reasonable manner. That is my point. It is like skipping the question ‘what happened before the bog bang’ and jumping straight into details of ‘before the big bang’. — I like sushi
Speaking of "smart people", is it not interesting that Albert Einstein often used the word "god" in reference to the unsolved mysteries of the world? Obviously, he is not referring to the various popular definitions of gods & God. Wouldn't you like to know what all the fuss is about, before you begin to dissect the general concept of deity into specific "details". Is the OP question a legitimate topic for discussion on a philosophy forum?
Once we have established that there is some reasonable basis for the plethora of religious ( celestial superheroes) & philosophical (First Cause) cosmologies, we can take those reasons seriously. What is common to all of them? Only then, can we treat the OP topic with respect. After all, it's asking about "scientific grounds", not "scriptural" or "emotional" grounds for the widespread god-concept among humanity. What is it about the real world that causes people to look beyond their physical senses for a universal Cause? :smile:
"I cannot imagine how the clockwork of the universe can exist without a clockmaker."
___Voltaire
"If God did not exist, it would be necessary to invent Him."
___Voltaire
"A knowledge of the existence of something we cannot penetrate, of the manifestations of the profoundest reason and the most radiant beauty - it is this knowledge and this emotion that constitute the truly religious attitude; in this sense, and in this alone, I am a deeply religious man."
___Albert Einstein
"I do not believe in a personal God and I have never denied this but have expressed it clearly. If something is in me which can be called religious then it is the unbounded admiration for the structure of the world so far as our science can reveal it."
___Albert Einstein
"I believe in Spinoza's God who reveals himself in the orderly harmony of what exists, not in a God who concerns himself with the fates and actions of human beings."
___Albert Einstein -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
Actually, it's not that simple. For the reductive methods of empirical science, there is no way to analyze a Holistic concept into its constituent parts. Because, by definition, a Whole is more than the sum of its parts. That's not really a "shortfall" for physical Science, though. But it's an opportunity for theoretical Philosophy to pick-up the slack. Actually, there is a new approach that some call "Holistic Science" (HS), but is better known as "Systems Science" (SS). Unfortunately, like Philosophical conjectures, the conclusions of HS & SS are unlikely to be conclusively proven by empirical evidence*1. Human beliefs will always remain beyond the scope of standard scientific methods.There are no methods full stop. It is not a case of science’s short falls. — I like sushi
Regrettably, non-reductive methods are often indiscriminately ridiculed as "pseudoscience". Nevertheless, SS remains a useful approach for the "soft" sciences, such as Psychology & Sociology, which seldom produce final "proven" Facts. What they do offer is rational insights into confusing complex systems. Ironically, the holistic systematic procedures used are almost indistinguishable from the traditional methods of philosophical "thought experiments". Therefore, they could conceivably be applied to such perennial stumper questions, such as "what existed before the Big Bang", or" why do people believe in an invisible deity". :smile:
Holism in science :
Holism in science, and holistic science, is an approach to research that emphasizes the study of complex systems. Systems are approached as coherent wholes whose component parts are best understood in context and in relation to one another and to the whole.
This practice is in contrast to a purely analytic tradition (sometimes called reductionism) . . .
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Holism_in_science
Systems science :
To systems scientists, the world can be understood as a system of systems. The field aims to develop interdisciplinary foundations that are applicable in a variety of areas, such as psychology, biology, medicine, communication, business management, technology, computer science, engineering, and social sciences. . . .
The best known research institute in the field is the Santa Fe Institute (SFI) located in Santa Fe, New Mexico, United States, dedicated to the study of complex systems.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systems_science
A Theory of Almost Everything :
Santa Fe Institute, the self-anointed headquarters of complexity. ... is our best means of distinguishing science from pseudo-science.
https://www.nytimes.com/1995/10/01/books/a-theory-of-almost-everything.html
*1. String Theory & Loop Quantum Gravity are usually considered legitimate Science, even though their conjectures are unlikely to yield any empirical confirmation in our lifetime. Perhaps the Santa Fe Institute, as it gains legitimacy, will be emboldened to take-on the ultimate Systems questions about the conditional existence of the universe. Until then, that job will fall to non-institutional philosophers. -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
When I first started posting on this forum I noticed that you seemed to know a lot more about the history of philosophy than I do. So, I thought I might learn something from you. But I eventually learned that most of your replies to my posts can be summed-up in two words : "boo" & "hiss". Apparently, there is something about my idiosyncratic personal worldview, or my way of expressing it, that offends you viscerally.A "restatement" of (Hegel's) dialectics https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dialectic or more generally dualistic monism https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dialectical_monism ... But why reinvent the wheel, Gnomon? How does your variation on this theme improve on Laozi, Anaximander, Heraclitus, Socrates/Plato ... Fichte, Hegel, Marx/Engels, Bookchin ...? Or the likes of Advaita Vendata? :chin:
Btw, your references to "Relativity" and "Superposition" are pseudo-scientistic non sequiturs which do not help make your case. — 180 Proof
I've never been able to understand exactly what the sore point is, except that perhaps I don't pay homage to some authoritative scientists & philosophers, as listed in your post. I'll admit that I can't help being ignorant of a lot of the history of philosophy. In college, I took basic courses in all the major disciplines of Science. Yet the only philosophy course I took was "Logic", and that was a Math requirement. Consequently, I have a better-than-average understanding of science-in-general. But the only philosophers that I'm somewhat familiar with, are Plato & Aristotle --- who basically wrote "the book" on philosophy for the next 2500 years. As some wit observed, about "variations on a theme", it's all "footnotes to Plato".
Anyway, I only dove into philosophy seriously after I retired -- just a few years ago --and began to construct a broad-but-coherent worldview, for my own personal use. The prompt for that on-going project was the conjunction of two paradigm-shifting innovations in 20th century science : Quantum & Information theories. So, I'm trying to weave those disparate scientific concepts into a holistic & consistent philosophical worldview, for my own personal application. Yet, there are plenty of practicing scientists, who are also exploring the philosophical implications of an Information-based universe. And, as you so astutely noted, my personal BothAnd philosophy is merely an update of ancient Golden Mean & Moderation principles for a philosophical life, updated for the current polarized context of adamant Either/Or positions..
Anyway, my general posting policy is to ignore your replies to my posts, because they seldom have anything positive to contribute. They seem to be mostly polarized shout-downs & heckles. However, I must thank you for the links to Dialectic articles. They do seem to be relevant to my thesis, but I assume you were actually trying to pigeonhole me into some easily ridiculed historical positions. Since, as a novice, I'm not well-read in the doctrines you listed above, I have been forced to "reinvent the wheel" to suit a 21st century worldview and context. My "variation" on a long-running philosophical theme was incidental to the thrust of a novel perspective that the venerable philosophers you listed were completely ignorant of. I'm just a layman working alone, while scientific & philosophical pioneers are forging new trails into the unknown territory of information-based Mind & Matter. :cool:
PS__Your dismissal of my references to "Relativity" & "Superposition", indicates that you have no idea what aspects of those concepts I'm talking about. FWIW, I make my case in more detail in the thesis and blog.
Philosophical Attitude :
Karl Jasper submits that “he who believes that he understands everything is no longer engaged in philosophical thought, he who takes scientific insight for knowledge of being itself and as a whole has succumbed to scientific superstition. He who has ceased to be astonished has ceased to question. He who acknowledges no mystery is no longer a seeker, because he humbly acknowledges the limit of possible knowledge. Karl jasper concluded that developing the philosophical attitude opens our mind to the unknowable that is revealed at those limits.”
https://medium.com/@TosinOlufeyimi/why-we-need-to-develop-the-philosophical-attitude-ea06f34bab94
The renowned British philosopher A.N Whitehead once commented on Plato's thought: “The safest general characterization of the European philosophical tradition is that it consists of a series of footnotes to Plato.
https://www.college.columbia.edu/core/content/whitehead-plato
A Universe Built of Information :
"In the long journey of the human mind attempting to decode the workings of reality, one trusted companion has to be abandoned: the materialistic and reductionistic scientific worldview."
___ James B. Glattfelder, physicist
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-03633-1_13 -
Are there any scientific grounds for god?
For the record, I don't think of the BothAnd Principle as a rhetorical device. Instead, it's a harmonious Holistic worldview. In some aspects, a BothAnd perspective is like the modern scientific concepts of "Relativity" & "Superposition". It allows you to see both sides of coin, or both sides of an argument, in order to reach a better understanding of a complex situation as a whole system of interacting parts. So, it's also the philosophical basis of scientific Systems Theory. :smile:For theists to maintain the Islamic position on God (there's nothing in us or in the world that could be used to get a handle on God hence Islam's hard-line iconoclasm) and also to claim knowledge of God, something quite clever needs to be done, oui? Apophasis (via negativa) + Cataphasis (BothAnd Gnomon) — Agent Smith
Cataphasis : noun. Rhetoric. the use of affirmative statements to discuss a subject; affirmation through positive statements.
Both/And Principle :
My coinage for the holistic principle of Complementarity, as illustrated in the Yin/Yang symbol. Opposing or contrasting concepts are always part of a greater whole. Conflicts between parts can be reconciled or harmonized by putting them into the context of a whole system.
* The Enformationism worldview entails the principles of Complementarity, Reciprocity & Holism, which are necessary to ofset the negative effects of Fragmentation, Isolation & Reductionism.
* Conceptually, the BothAnd principle is similar to Einstein's theory of Relativity, in that what you see ─ what’s true for you ─ depends on your perspective, and your frame of reference;
* This principle is also similar to the concept of Superposition in sub-atomic physics. In this ambiguous state a particle has no fixed identity until “observed” by an outside system. -
Question regarding panpsychism
Of course. But the suggestion was intended as a change of perspective, in order to adapt to a challenge to someone's religious worldview. From my own science-based philosophical worldview , I have concluded that what the ancients called "Spirit" (invisible agency), is what we now call "Energy" (invisible causation). The difference is that, thanks to Einstein, we can now equate invisible Energy & tangible Matter via the moderation of mathematical Mass. (E=MC^2)So, if you think of Matter as a tangible form of incorporeal Spirit, that might work — Gnomon
I think that's a reification. — Wayfarer
With that in mind, I could re-word my tongue-in-cheek proposal as : "think of Matter as a tangible form of intangible Energy". That's not the fallacy of Reification, but the realization that Energy is a mental model constructed to explain physical changes, that would otherwise seem mysterious. Energy may seem less mysterious (spiritual), if you view it as an active form of Generic Information, which I also call "EnFormAction", to denote its relationship to mundane Energy .
Why are most forms of energy invisible to the naked eyes :
"There is no manifestation of energy that is visible. Even light itself is not visible."
"Mostly because energy is a model we invented to make our physics easier. It doesn't physicially exist, it's just something we created to show how things behave"
https://www.quora.com/Why-are-most-forms-of-energy-invisible-to-the-naked-eyes-while-we-can-see-heat-as-fire-for-example-What-make-some-forms-seen-and-other-not.
Note -- we see the effects of Energy inputs as the physical changes in Matter
Information is Generic in the sense of generating all forms from a formless pool of possibility : the Platonic Forms.
BothAnd Blog, post 33
EnFormAction :
"En-" within : referring to essential changes of state
"Form-" to mold or give shape to : it's the structure of a thing that makes it what it is.
"Action-" causation : the suffix “-ation” denotes the product or result of an action.
* So the cosmic force of EnFormAction is the Cause of all Things in the world and of all Actions or changes of state. In physical terms, it is both the Energy and the Material, plus the Mental concept of things. It is the creative impulse of evolution.*
* Plato’s "Form"s were described, not as physical things, but as the idea or concept or design of things. The conceptual structure of a thing can be expressed as geometric ratios & relationships which allow matter to take-on a specific shape. So, in a sense, the ideal Form of a real Thing is the mathematical recipe for transforming its potential into actual.
BothAnd Blog, post 33
Gnomon

Start FollowingSend a Message
- Other sites we like
- Social media
- Terms of Service
- Sign In
- Created with PlushForums
- © 2026 The Philosophy Forum