-
Semiotics and Information TheoryThe hyper nominalism and relativism of some post-structuralist might be an example of what it would be good to avoid. These theories often invoke semiotics, but it's Sausser's brand, which ends up leaving the sign and its interpretation floating free of the signified.
Information can be seen as ultimately arbitrary only when it is divorced from its source however. E.g., a random text generator might produce all sorts of texts for us, but ultimately all it reveals to us is information about the randomization process used to output the text. Even if a random text generator were to spit out a plausible explanation of a cure for cancer, we should have no reason to think it is telling us anything useful, since there are very many more ways to fail to describe a proper medical treatment than ways to describe a proper one.
Hence, the "information source" cannot be divorced from the message if we want to understand the message (nor can we ignore the recipient). But often it seems the source and recipient are ignored, abstracted away. I think one assumption at work here is the idea that processes can always be reduced to understand them better, that facts about complex things can always be explained in terms of "parts," and that parts are always more fundemental. -
Semiotics and Information Theory
Information theory really is anti-semiotic in its impact. Interpretance is left hanging as messages are reduced to the statistical properties of bit strings. They are a way to count differences rather than Bateson’s differences that make a difference.
I think that's a fair interpretation of how IT is generally interpreted. Popular interpretations of the extreme usefulness of information theory often try to explain everything in terms of "limits on knowledge" for some agent/physical system. That is, information is useful as a concept but lacks "mind-independant existence." Perspective isn't "fully real" in a sense, and the true distribution for any variable vis-á-vis any physical system receiving a signal is just the very interactions that actually occur. The appearance of probability on the scene is just an artifact of our limitations, something that doesn't exist in the pristine "view from nowhere."
But it does seem that some views leave the door open for a more radical reinterpretation of the dominant mechanistic, dyadic paradigm. Relational quantum mechanics for instance looks at QM through the lens of Nagarjuna's concept of relations, not things, being primary. And there are a few other examples I can think of where a sort of "perspective" exists in physical interactions "all the way down."
I've also seen semiotic accounts of computation, but this has always focused on the computing devices designed by humans, rather than biological or physical computation writ large. Because computation can also be described as communication, it seems like there is an opening here for a triadic account, although I've yet to find one.
In his collected papers, Peirce remarks at one point about his despair over getting people to realize that the "interpretant" need not be an "interpreter." I've seen some explanations of information that try to get at this same sort of idea (e.g. Scott Mueller's Asymmetry: The Foundation of Information). The core insight is that "which differences make a difference," is contextual. When one thing is linked to something else via mediation, the nature of the interpretant matters. I'll agree that this is more obvious when it comes to organisms and their specific umwelts, but it seems true "all the way down," as well.
But I have searched in vain so far for anything that attempts to really fit these together. One big thing that semiotics would help overcome is the nominalism implicit in seeing information just in terms of numbers and probability. The idea that certain signals play a role in making the recipient think of one thing over anything else gets washed out when information appears as sheer probability. -
10k Philosophy challenge
Money is just used as a proxy for opportunity costs. Money is a good proxy because society is, in an important sense, organized around it. Moreover, we have lots of data on it. Yet it isn't a perfect proxy.
Ultimately, what you "pay" for any experience or thing is what you give up to get it—the "opportunity cost." For instance, walking with your sister at the park doesn't cost money, but it does mean giving up everything else you could have done during that time period (including earning money).
Wealth itself has decreasing marginal utility. Going from earning $20,000 a year to $120,000 is life changing, huge. Going from $120,000 to $220,000 is still a big deal, but it doesn't totally shift your options in the way the first move does. Whereas moving from $1,120,000 to $1,220,000 is not going to be super noticable and for the very rich an extra $100,000 is a rounding error they won't notice (even if they do care a lot about it due to the vice of pleonexia, "grasping.")
You see this in the backbending labor curve. As people make more money per hour they want to work more to get that high pay. But at a certain high level of pay they will start wanting to work less, to have time to enjoy what that money can give them.
This also helps fix the problem of inequality, in the money is "worth more" (in terms of utility) for those who have less of it.
As to the second point, I am not sure if this necessarily leads to democratization. People who aren't directly affected by something like a cure for blindness don't really participate in that market. There is a sort of aggregation here, but it is, at least according to most economists' assumptions, the aggregation of rational agent's choices based on their opportunity costs.
Obviously, I think this is open to critique at the level of how freedom is defined and the assumption that people are automatically "rational agents," making choices in an unconflicted manner. On the standard economic account, we end up assuming the heroin addict has simply made a rational calculation based on how much utility heroin is worth to him, versus other opportunity costs. This seems to be a bad assumption to me, but it is common (or at least we assume this is unproblematic in the aggregate, that movement away from rationality is just random noise that still tends to some mean).
Right, but mastering circumstances towards what end? Presumably we want to take control of circumstances to direct them towards some end we find good, else why bother trying to shape them at all?
Why do we find such ends good in the first place? Instinct? Passion? Taste? It seems to me that we will be most free when we fully understand why we pursue the ends we pursue and when we understand these ends to be good ends through a rational process.
Perhaps the natural end our behavior tends towards is survival, but once survival is assured how are new ends chosen? If it's not via a process involving some sort of rational reflection, in which ends are chosen based on what truly best, it seems like the problem of arbitrariness creeps back in. For example, to be determined by instinct alone, without any understanding of why the way one acts is choiceworthy, seems to be a less than fully free action. To be ruled over by instinct is to be ruled over by a mere part of oneself, to not fully fathom why one is acting. For it seems totally possible that we might judge the ends the passions and appetites drive us towards as inferior ends, as not truly choiceworthy.
And it seems to me that survival can be superceded as an end—that we can recognize higher ends (e.g. Socrates, St. Paul, Boethius, Origen, etc.) -
US Election 2024 (All general discussion)
I forget how she did in the debates. It seems like it should be easy to bait and trigger Trump into a meltdown. I would just pull out all the quotes from his own cabinet members calling him incompetent. Then when he called them "RINOs" point out that he was the one who appointed them and promised to "pick the greatest people."
He even whiffed his core issue, illegal border crossings hit a 13 year high under his administration and he didn't get his party to old even one vote on migration the whole time he had the House, Senate, and Court, showing how the GOP just uses the issue for votes. Oh, and almost quadrupling government borrowing during an economic expansion.
Virtually any Democrat would have won in 2008. Bush was historically unpopular and the GOP had just overseen a military disaster and the entire economy imploding. Dems had the House handily and a super majority in the Senate, no way they lose up ticket. Obama won both his elections so handily they were called almost as soon as polls closed and almost certainly would have won handily again in 2016. Aside from Reagan, who had dementia issues, he's the only guy who could have realistically been confident in getting a third term since term limits became a thing. -
Semiotics and Information Theory
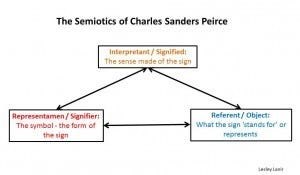
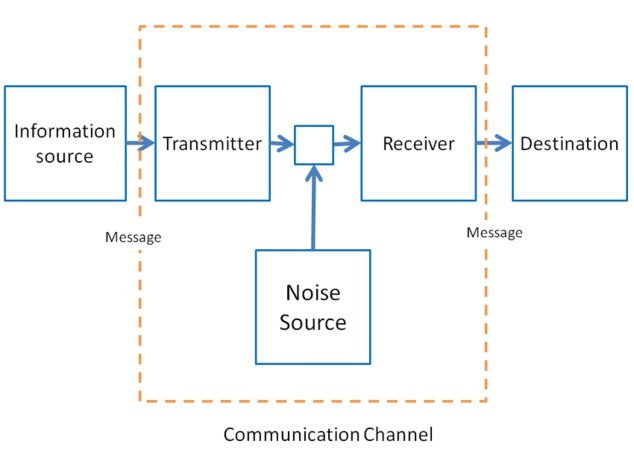
At a superficial level, it's easy to see how in the Shannon-Weaver model in IT the information source could be the object and the destination the interpretant. -
Devil Species Rejoinder to Aristotelian Ethics
:up:
It makes no sense from a naturalized view either. Predators don't benefit from the suffering of their prey, nor from their deaths; at least not in any direct sense. What the predator benefits from is calories, energy stored in the prey; any suffering is ancillary. Indeed, predators who over reproduce end up facing starvation (and the same is true of prey who over reproduce in the absence of predators). In either case, the population collapses due to it outrunning its food supply. The good of the predator and prey are linked.
Even if a species was oriented towards thwarting human ends, it would nonetheless need humans around to fulfill its ends. But nature would never create such a straightforward negation. Creatures might be in competition but there is no way for them to evolve such that "whatever is bad for x is good for y." -
Is the real world fair and just?IDK, the thing-in-itself seems to do some heavy lifting, e.g. securing human freedom at the end of the Prolegomena.
Personally, I think it's just bad metaphysics. I already shared the critique of "things-in-themselves" in the nominalism thread, from the Thomistic, Hegelian, Patristic, and process philosophy schools.
https://thephilosophyforum.com/discussion/comment/919006 (at the bottom of the comment where the quotes start). I find these arguments very compelling.
The semiotic view one gets from the Scholastics (Poinsot being a core example) or refined in the 20th century by Charles Sanders Peirce and John Deeley seem much more compelling to me.
In general, I think the types of "idealism" (if that is a useful title for them) that have no problem with Banno's three questions, e.g. Hegel, Plato, some interpretations of Aristotle, etc. avoid dealing with this Kantian false dichotomy. -
10k Philosophy challengeYou could always do what economists do and just use money as a proxy for freedom. The enhancement of freedom is to be valued at what people are willing to pay for it. The benefit here is that people's own decisions are helping determine the trade-offs.
Note, we are not talking about individuals' willingness to pay here but the aggregate willingness to pursue say "a cure for blindness," versus "a life extending treatment for such and such a disease." Here, the demand curve represents society's total willingness to pay (i.e. to forgo other goods and services) vis-á-vis a choice. This has the benefit of piggybacking off people's free choices in the market.
Now, there is the issue of inequality here but I feel this can be dealt with in a two-pronged fashion:
1. The theory in no way has to endorse current levels of inequality. It is perfectly consistent with much higher levels of redistribution, a strong safety net, inheritance tax, etc. In a more equal society, people's willingness to spend on enhancements of freedom will be a better proxy for goodness.
2. You can equalize individuals' willingness to pay by looking at it in terms of the % share of their total net worth and likely future income.
A third point might be that, all else equal, economic development has been key to securing freedom. It is a great proxy for life expectancy, lower crime, education, etc. In the aggregate, high wealth individuals tend to do much more to spur economic growth (or at least this is a common assumption). As such, the fact that they receive a higher weighting here is not necessarily a bug but rather a feature.
We need not say the invisible hand of the market is perfect here. We need only argue that it is the best measure, that emergent market dynamics direct us towards the greatest promotion of freedom.
And indeed this could also be used to make a strong moral case against oligopoly collusion, rent seeking, etc. while making a good argument for the regulation of monopolies and externalities.
This is only an outline. You could draw on a lot in welfare economics to make this case. It might make more sense to pair such an idea with the concept of a social welfare function so that inequality itself is dealt based on the free choices of members of the society. -
An Argument for Christianity from Prayer-Induced Experiences
That's certainly not an uncommon view in history. Consider I Peter 4:6
"For to this end it was announced-as-good-news even to the dead: that they might be judged according-to people in the flesh, but be living according to God in the spirit."
This has variously been interpreted as its straightforward meaning—"the Gospel is preached after death"— as being consistent with Ephesians 4:9 where St. Paul refers to Christ's descent into the Earth. It is also interpreted as referring to those who heard the Gospel and later died, which is a bit of a tortured reading, or as "dead" here being metaphorical (i.e."dead in sin), which seems at least more plausible.
Since every knee will bow, it is generally accepted that all of the dead will know the truth at some point anyhow.
But IMO, it is the highly individualistic and legalistic combination of readings that really transform the "Good News," into something quite the opposite, a desperate race for man to save man fromGod via a "loophole" of sorts. And this is also what transforms finite bad fortune into infinite bad fortune. -
Pragmatism Without GoodnessPlotinus could certainly have ideas that are incoherent or don't cash out well, although I don't think this is true. However, I would say Wayfarer's source also has a fairly standard summary on this issue (along with the admonition that Plotinus not be turned into a "proto-Hegel.") Plotinus does argue both sides of his case, pro and contra, but I don't think he's refused to lay down a position in any sense.
If a Neoplatonist slides towards proto-Hegelianism it is the Irish monk Eriugena.

St. Augustine's early attempts to reconcile Plotinus is an interest case of the evolution of Neoplatonism (although Augustine is far from the first to attempt this). He initially maps the three persons of the Trinity to the Plotinian hypostases. The Father is the unified One. The Son (Logos/Word) holds within itself the divine eidos/ideas/logoi as Nous. This allows the Father to have the Son as the object of its love and attention and for differentiation in the knowing relation. The role of Holy Spirit/Paraclete is less clear here. It is either logoi, the specific instantiating power of Nous in the world, or it is the World Soul, the ability of creatures to know. In a few cases it is reduced to simply that which allows creatures to know truth.
But Augustine eventually abandons this for two reasons. First, in the Plotinian cosmology the hypostases are in a clear hierarchy, but post-Nicean orthodoxy dictates that the three persons of the Trinity are co-equal. Second, it's a straightforward denial of divine simplicity.
Augustine turns away from strictly philosophical work by this point to theology and the practicalities of being an influential bishop in an area of the Empire riven by schism. Thus, all his later working out of this is buried in theological treasties like De Trinitate, which leads to philosophers ignoring them.
But I find his solution incredibly creative. It's a semiotic solution. Augustine realizes that for there to be any meaning at all (and thus any being) there must be a triadic relation of: object known/ground/Father, sign through which then object is known/Logos/Son, and that which knows/interpretant/Spirit. Thus, his later solution has the Godhead necessarily in a triadic semiotic relationship, one Augustine finds mirrored in the human soul itself, and in the interactions of the created world—a sort of pansemiosis. Although Augustine avoids the problem of an equivocity of the semiosis involved in inanimate non-living interactions, he does so at the cost of a sort of demotion of the relevance of the material world (and we might say plausibility as well). Material things are so just signs of their ultimate cause here; all things point up the Great Chain of Being (an idea that existed only in germ at the time)
Does this introduce multiplicity into divine unity? Or is the sign relation a unified gestalt that can nonetheless be analyzed by discursive reasoning without being truly reduced into parts (i.e. the whole is more fundemental than any parts)?
Jacob Böehem is another example of this issue. He has all of God's creativity and the Divine Persons springing from the undifferentiated Unground, which is nonetheless unstable because, existing alone and totally undifferentiated its being and non-being are identical. But Böehem's differentiations and process in the Divine Nature are to be thought of not as occuring in time but as a sort of logical implication. There is still unity, but the human mind can only know such unity through discursive reasoning (much like St. Thomas says). There is also Jan van Ruusbroec's conception of the Unground/Divine Darkness beyond all thought continually breaking forth out of itself in the Divine Utterance before returning to itself in Spirit, where the process is a dynamic unity.
I have always found the attempts to grapple with this very fascinating. The personalist idea that persons, not mere thought, are ontological bedrock is another relevant shift here. -
10k Philosophy challenge
It is not "the inability to choose anything", it is a case of willfully not choosing anything. The ability to choose remains, therefore choice is not impossible as you claim, it's simply a matter of none of the possible choices appearing to warrant being chosen at the present time.
Perhaps I should have spelled it out a bit more, it is not that action is physically impossible. Rather the issue is that at it is impossible for any determinant thought or action not to make someone less free. I would maintain though that a vision of freedom where maintaining one's freedom requires a flight from all definiteness is contradictory, for the reasons I have stated. Here, the exercise of freedom itself makes one less free.
Like I just explained, it is not a matter of arbitrariness, because the circumstances we find ourselves in are not arbitrary. The circumstances are however, to a large degree, unpredictable and often dangerous. This necessitates that the agent must have maximum freedom of choice to be able to best deal with whatever comes one's way. Your conclusion of "arbitrariness" is completely unfounded because you completely ignore the natural constraints of circumstances.
I'm not ignoring constraints, although I was speaking in abstract terms. Being determined by circumstance seems like a definite limit on freedom however.
I am not really sure how this is supposed to be a rebuttal. Freedom seeks no determinant end, but that's ok because the free individual will be prompted along by circumstances outside of their control?
And to the extent that we try to control our circumstances it seems we will have to have some end in mind, no? But if our ends are not determined rationally, but rather as a coping response to circumstance, then it seems to me they are less than fully free.
Right, this is the exact nature of "freedom", there is no specific end toward which the agent "ought" to be inclined. This allows the agent maximum capacity to act according to the circumstances, not being constrained by any sense of "ought". What's wrong with that? That is what survival requires, the maximum capacity to act according to the circumstances. So if survival is important to the agent, then freedom from "the Good" is justified.
It seems like "survival" is functioning as the overarching end here. But sometimes it seems like some ends trump survival, e.g. Socrates' acceptance of death. If we are always oriented towards survival rather than what we think is truly best, that will be a constraint on freedom of action. We could consider here the case where Socrates succumbs to cowardice and flees even though he knew he ought not do so. Here, he is not free to do what he thinks is best, but is rather ruled over by circumstance and fear.
If an agent is "oriented towards no specific end," but rather the ends are "determined by circumstance," then how is it not circumstance in the driver's seat? No doubt, we have to deal with the circumstances we face, but freedom would seem to come from mastering them to the extent possible.
I think Plato has a very good argument for why reason has to guide free action. We can't very well be fully free if we don't understand why we are acting or why it is good to do so. But the "rule of the rational part of the soul," would seem to require determinant aims. -
Do (A implies B) and (A implies notB) contradict each other?
Yes, given an "infinite amount of time," or an "eternal realm," it might make sense to think of these relations as eternal. Computation is inheritly stepwise though, so I am not sure this is particularly helpful to do. At any rate, no physical system computes in "no time at all." Human beings stop being able to see expressions as "other names" for their solutions at remarkably low levels of complexity.
Consider: 6X = 1929.121⁸ — (118 + 2/3) 1/918
The value of X is specified here. Is it obvious to you what it is? But surely you know what all the operators are and how to solve for X.
I don't think most people will even be able to glance at 175+39 and instantly tell what number it corresponds to. Hence our intuition that computation is informative
Anyhow, I think the Stroop Test (mentioned earlier) is a better illustration of the way in which cognition relies on communication. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
:up:
This is a perfect example of what I mean by a solid investigation of the "form of life."
Would that question not be simply what produces clouds and how do they in turn produce rain— a scientific question? I can't think of any other way to coherently frame the question. I mean you could feel a sense of great wonder that there are clouds and rain, and indeed a world at all, but I don't see any coherent question that sense of wonder could be transformed into other than the scientific ones.
Certainly. And this could likely be true for language to some extent. I personally think that the hard dividing line between "science" and "philosophy" is just an artifact of a specific and not particularly fruitful brand of philosophy of science that became dominant in the 20th century. The "anti-metaphysical movement," would be a key example, and I think it did real damage to scientific inquiry.
The reality is that theoretical work, particularly paradigm defining work, always has a lot of philosophy involved in it. The line between "philosophy of physics," and "philosophy of biology," and physics and biology is very blurry. I think we would be well served to returning to thinking of science as the systematic and rigorous study of a topic, rather than a sort of discrete discipline cut off from other forms of inquiry. -
Pragmatism Without Goodness
Modes of knowledge are tricky as are final causes. I don't think it makes sense to talk of the "God of the philosophers" "creating the world with a purpose," in the way man creates hammers "for the sake of driving in nails." The late Scholastic distinction between intrinsic/extrinsic final causes and exemplary/objective causes is helpful here. Deely's work on Poinsot and some other Scholastics and C.S. Peirce is a good example here. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
I think the answer is one that you seem to reject - convention. Given our species nature the rules from one group to another will have much in common based on our needs and characteristics as a species.
I don't reject it. It's a fine answer. It's just incomplete. It's like if someone asked for an explanation of rain and stopping at "it falls from the clouds."
"Clouds" is a fine answer, although perhaps trivial. The interpretation I dislike is the one that says that to ask "why are their clouds and why do they produce rain?" is to have become bewitched or fallen into incoherence. -
10k Philosophy challenge
yes I think perfectly rational agents can plausibly all want and choose different things. This need not be arbitrary, it might be instead related to what those agents want
Right, I don't mean to deny all particularity here. There are relative goods and these will be assessed by different people based on their own unique context. In the real world people also operate under significant constraints: imperfect information and finite reasoning capabilities.
However, look at your last sentence. If people's choosing what they choose is "based on what they want," and this is to fix the problem of arbitrariness, then what people desire—the good they seek in action—has to be something determined rationally. Such "wants" have to follow from something, to be grounded in "reasons."
To say that there is nothing they "should" choose is different. They should choose what is morally right. Not because that is what rationality dictates but because that is what it means for something to be morally right. Morality is the categorical imperative, the thing we should do regardless of our desires. Why should we do what's right? Because that is what "should" means
People should choose to do what is right because "right" means "you should choose this?" IDK, this is precisely the sort of thing that makes people say contemporary ethics just collapses into emotivism. "It just is," sounds unconvincing.
Plus, I'd tend to side with Aristotle on the intuition that the virtuous person should enjoy their virtue, or even Plato's view that the good person loves being good. If the good is not desirable then goodness is a limit on freedom. Goodness ends up being an unpleasant thing that constrains our freedom to the extent that we find it binding—which is strange if goodness also just is maximizing freedom. This is especially odd if we think one of the good things about freedom is precisely that it lets us avoid what we dislike and attain what we find good. -
Do (A implies B) and (A implies notB) contradict each other?
I'm not sure what your getting at here. It's not an approximate solution, in the example the program spits out the shortest path between all the nodes, not an approximation. The computation is deterministic. It can only be completed in polynomial time by a non-Nondeterministic Turing Machine, but a deterministic Turing Machine can churn through checking every path, it just takes forever if the input is large.
And the NTM doesn't spit out approximations either, it's just able to take many branching paths through the computation, doing multiple actions based on a single instruction (I was always told to think of this as splitting the NTM into copies in a sort of branching process). People use estimates for these sorts of problems, but that's because they take too long to solve. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
I do not think he is a skeptic with regard to rule following. There is, for example, a right way of following the rules of addition. If someone does not add correctly they are corrected. If someone makes a move in chess that violates the rules they are corrected. It does not matter what they might or might not understand as long as what they do follows the established rules. But it would be quite odd if someone did not understand the rules and yet consistently acted in accordance with them.
This is almost certainly correct. His entire later philosophy would collapse if we couldn't follow rules.
The problem as I see it is that his arguments (if they can be called that) for rejecting private rule following don't seem to limit the problems he identified to private rule following. They apply equally to public rule following.
Of course we can say: "but this is no issue. It would be a total violation of common sense to say we can't follow public rules. When someone violates a rule in chess we can see it and point it out to them."
But of course this is entirely true of private rule following too. Private rules are pretty common sensical. We can make up our own rules, write them down, try to follow them, and when we break them we seem to be able to determine when this has occured.
Now some Wittgenstein commentators might have it that all that is required is that we learn "what a rule is," in a social context. This seems much more agreeable to me, but I don't think it's what Wittgenstein is saying.
There is a difference between human beings acting in compliance with established rules and the question of whether nature obeys rules. It makes sense to say that if someone does not follow the rules of a game she may be playing a different game, but does it make sense to say that if the sun does not rise tomorrow it is playing a different game?
Right, but the questions I think his philosophy points to is: "from whence rules? Why are they useful? How do we come to understand them? Why are they natural to human behavior?"
Presumably, if nature "follows rules" it is in a way that is at best analogous to how we follow them.
Are you claiming that there are transcendent, fixed, eternal laws that human beings should follow that Wittgenstein fails to account for?
No, what can't be accounted for is "why do we have the rules we do? Why do they evolve the way they do? Why do disparate cultures that developed in relative isolation often develop similar rules? What is the relationship between our preferences, the world, and how we change our rules?"
Since the rules are presumably not springing forth from our heads like Athena from Zeus it seems like an explanation is wanting here as a sort of obvious "next steps for inquiry."
Wittgenstein believes that every interpretation must bottom out in some unjustifiable immediate reaction in order to escape the infinite regress of interpretive rule-following, so demanding an overt justification for the correct recognition of sensations even to be conceivable seems odd.
Indeed. Although the question: "where do rules come from?" would seem to offer another route away from the infinite regress. -
US Election 2024 (All general discussion)
Fine. My standards are pretty low by this point.
I do not think she will be a strong candidate though. I think she would be a significantly stronger candidate if she hadn't been VP, because Biden's administration is not particularly popular.
There are several people who make better candidates, Dems who have won in deep red states.
If she wants it she can probably get it though because this is the Democratic Party so who is going to want to say: "we need to pass over the Black woman candidate?" All the speculation I've read sort of centers around this.
I think the only way she isn't the nominee is if she pulls herself out.
There are a handful of very moderate Republicans who have won is very Democrat-leaning states who would be good to throw on the ticket to offset the "California liberal" vibes she gives off, but I don't know if either side would be willing to do that. It would be a brilliant move IMHO though. These folks are already exiles for failing to say the election was stolen though, so they might go along with it. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
Well, I would accept that if there is social agreement on how a rule applies in a new situation, that's how it applies. Rules of etiquette, for example. Linguistic rules.
Right, but you see the problem here right? How does any individual ever know that they are properly chastising someone for following a rule wrong? Per Wittgenstein, they can't be sure that they ever understand a rule.
Also how do people let someone know that they are following a rule wrong? For a person to know that they are being told that they are in error they must already be following at least enough of the rules to be able to get the message. More importantly, how can the individual be sure that they are being corrected, and that they are being correctly corrected instead of being corrected in error?
Wittgenstein has left the door open on a new sort of radical skepticism, one where a member in a language community can never be sure if they are really following a rule or just think they are. After all, for any rule someone thinks they are following there are infinitely many other rules that would dictate the same exact behaviors. Rule following is always underdetermined. But this is true for every member of the community, both as a whole and as individuals. People can never be sure if others are actually agreeing with them, if they are misinterpreting the rules, or if others are misinterpreting the rules. Everything is underdetermined in the private case, but the public case doesn't actually resolve the issues brought up to indict private rule following.
I personally think Wittgenstein never fully got away from Russell and Hume's influence re causation. That is, the influence that made him write:
5.1361 The events of the future cannot be inferred from those of the present. Superstition is the belief in the causal nexus.
Part of what helps cement rules though is causal consequence. Bad applied math results in bad consequences regardless of what the majority thinks for instance.
Hence he could never really pin down rules outside of "custom," which in turn leaves them floating free from the world in an infinite sea of "possible rules." He thinks he can rely on a sort of "democratization" to fix this problem and it isn't clear that it can do the job. And when it comes to cognitive relativism, he seems to have just recreated Cartesian skepticism with extra steps.
The "form of life," might be able to solve this issue, but not if people can be skeptical about which forms of life they belong to. -
10k Philosophy challenge
What you are showing is that perhaps freedom ought not be the measure of value.
What I was hoping to show is that freedom can't be thought of purely in terms of a power/potency. Nor can it be thought of something standing over and against the good. What you describe isn't just counter intuitive, it is contradictory.
A freedom defined in purely negative terms, as "freedom from any constraint," collapses into its opposite, a "total inability to choose anything." Any determinancy in thought or action becomes a constraint on freedom. In this way, "absolute freedom," the "freest we could possibly be," turns out to be a state where choice is impossible since any determinant choice is a fall from absolute freedom as pure potency.
Yet "the inability to choose anything," is the exact opposite of what is meant by "freedom." The term has collapsed into its own negation. Hence, the concept must negate its negation. We need a synthesis, a conception of freedom in terms of the self-determining capacity to actualize determinant ends.
However, total self-determination reveals its own contradictions. For we can imagine an individual with preternatural self-control and self-knowledge and still rightly ask, "but what will they choose to do?"
If freedom is defined without any reference to the Good, then there is no determinant end to which the "perfectly rational and self-determining agent," should tend. Why do one thing over any other? If this question can be answered with reason, there is no issue. But what if we claim that it cannot be answered by reason, that the (practical and moral) Good is unrelated to freedom? Then it seems that our perfectly self-determining agent must, in the end, be determined by what is wholly arbitrary. Their judgements of "what is truly best," do not flow from reason, but from "nowhere at all." Perfectly rational agents will all tend towards different goals because their goals are ultimately undetermined. But arbitrariness is the opposite of self-determining freedom.
Again, freedom has become its own negation.
Thus, in the end, perfected freedom must tend towards the Good, towards a determinant end, towards what is considered "truly best," and not towards what is chosen for "no reason at all."
We have here skipped over the issue of social freedom. Since any agent can deprive others of their freedom, or the chance to develop their freedom, there must also be some degree to which the freedom of agents is harmonized for freedom to be perfected. And this sort of social freedom must tend towards some determinant end as well. A society that organizes itself based on no determinant end would ultimately be ordered by arbitrariness. A society organized around "maximizing freedom," will be a society oriented towards arbitrariness when freedom is conceptualized as mere "freedom from constraint/determinancy."
This is a fairly Hegelian presentation of the problem, but the vision of freedom is widely consistent with Plato, Aristotle, Plotinus, St. Augustine, St. Thomas, St. Bonaventure, etc. as well as the Eastern and Oriental Orthodox/Coptic conceptions of freedom one finds in the Philokalia.
It is really more with Locke and other early moderns that we see the collapse of conceptions of freedom towards arbitrariness, and this sort of view became dominant by the 20th century. I consider this to be a major part of the "crisis of ethics." -
10k Philosophy challenge
. To protect one's freedom of choice requires that the person resists the formation of habits in one's thinking. To be inclined this way, i.e. to resist habitual thinking, requires that freedom be promoted, because choosing not to choose is an intentional skill requiring will power to develop, and the desire for freedom is the required intention. This is where consequentialism really fails us. It does not properly provide for the value of will power.
If freedom is conceived of as a pure power/potency, then even good habits are deleterious to freedom since they still constrain possibilities of action.
But the virtues were generally thought to perfect freedom precisely because they allow one to act in accordance with what they think is "truly best," not because they allow someone to act "in any way at all." This would amount to mere arbitrariness, which is sort of the inverse of freedom.
So long as the person is able to understand and make their own choices, then there is nothing that, as it were, "needs doing". Whether the person has constrained their own choices in some fashion is (in most cases) morally irrelevant.
The assumption that most adults understand their own choices transparently, or that they understand the likely consequences of their actions, seems problematic.
People who are intoxicated, suffering from head injuries, or dealing with age related cognitive decline might show an increasing inability to meet these conditions, but it is in no way a binary distinction. Yet if we can be more or less able to meet the conditions for freedom, it seems like this should make us more or less free.
I suppose this assumption is what allows manipulation to be a non-issue. However, someone indoctrinated into a cult from birth seems to be facing some constraints on their freedom even when they aren't actively being threatened. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
I've always found invocations of the private language argument strange because it's hardly clear that there is one coherent argument on this topic or what its conclusion is supposed to be.
I don't think I'm alone in this though. From the SEP article on "the argument:"
Even among those who accept that there is a reasonably self-contained and straightforward private language argument to be discussed, there has been fundamental and widespread disagreement over its details, its significance and even its intended conclusion, let alone over its soundness. The result is that every reading of the argument (including that which follows) is controversial. Some of this disagreement has arisen because of the notorious difficulty and occasional elusiveness of Wittgenstein’s own text (sometimes augmented by problems of translation).But much derives from the tendency of philosophers to read into the text their own preconceptions without making them explicit and asking themselves whether its author shared them. Some commentators, for instance, supposing it obvious that sensations are private, have interpreted the argument as intended to show they cannot be talked about; some, supposing the argument to be an obvious but unsustainable attempt to wrest special advantage from scepticism about memory, have maintained it to be unsound because it self-defeatingly implies the impossibility of public discourse as well as private; some have assumed it to be a direct attack on the problem of other minds; some have claimed it to commit Wittgenstein to behaviourism or verificationism; some have thought it to imply that language is, of necessity, not merely potentially but actually social (this has come to be called the ‘community view’ of the argument).
So I'm always a bit of a loss on that one, especially when "violating the private language argument," gets invoked as if it is the same thing as being contradictory (something one sees not uncommonly).
I had a thread a while back that no one was interested in on the idea of "mentalese" or "the language of thought," and the private language argument. I don't think the private language argument even rules mentalese out, nor does it really give us much to go on with claims like Chomsky's, that the primary function of language is to organize our own thoughts (as opposed to communication). On the view that mentalese underpins all "public language," it wouldn't seem to count as "private" under some definitions
My personal view is that thought is syntactical and combinatorial in the way that language is. Thought emerges from communication between different specialized areas of the brain. I think there is a lot of evidence from people with brain injuries to suggest something like this is true. Language can, and often is used to structure and present these communications within phenomenal awareness. High level functions, like language processing and production, reach down into lower level functions and color them, and everything ends up very interconnected. Rule following behaviors, or at least "rule-like" behavior (if we assume "rule" → social), underpins these relations.
I would take the private language to be at its strongest when it is a straightforward rejection of Cartesian absolute privacy. There are always outward signs of any "inner" experience. These can be more or less obscured for any outside observer, but in practice there are very many ways in which other people's experiences are present to us, even when they attempt to obscure them. At the limit, on pain of dualism, there should be no "inner difference," without some, in principle, observable outer difference. This jives with a broadly enactivist view.
But then the private language argument(s) are not a great way to make this point. If a stronger formulation is taken, e.g. that private rule following is impossible because of the possibility of unknown error, this seems to actually follow on for social rule following too, and at any rate it simply doesn't jive with experience.
So, with the lion, it seems clear we should know what "please bring more zebra steaks sir," means if the lion says it. However, there also seems to be a sense in which the lion's inner experience, which corresponds to outward signs, is more hidden from us because we do not share the same "form of life." Yet per the topic of this thread, I do think mammals might be said to share some sort of "form of life;" we can recognize each other's emotional states decently after all.
This would be the last chapter of his "Wittgenstein: A Very Short Introduction."
I'm afraid few decent philosophical arguments can easily be refuted by counter-example. Someone else can read the note, so it doesn't count as private language - even if it's in cipher.
And this seems true for any thought to me. Suppose in the far future it would be possible to equip a person with an extremely high resolution fMRI, CAT, PET, etc. type scan set up to continually monitor them from before birth. We also record this person's surroundings. We then use an AI to correlate inner state changes with outer state changes.
In theory, it seems possible that given enough observations we might be able to determine to some degree "what a person is thinking about." But then the person's body is itself a sign of inner changes, which of course Wittgenstein seems to suggest. The body is just an imperfect sign in this respect, in part because we have a useful capacity for deception.
This is in line with Augustinian semiotics. The body is sacramental, an outward sign of inner/higher realities. -
10k Philosophy challenge
It seems to me someone might care about something more than what is morally good, or perhaps not care about it at all. That seems imaginable.
Yes, if we divide practical and moral reasoning into two discrete things. I see no reason to do this though.
When someone cares more about something other than "moral good," it seems to me that they are simply seeking one good over another. The thief prefers the good of what they can get from stealing. The parent who neglects their child prefers the good they derive from going to the bar, playing video games, etc. Yet in all these actions people are still motivated by a good they seek to attain through their actions.
Part of what makes contemporary ethics intractable is denuding "moral goodness" into some sort of esoteric property cut off from the rest of existence. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
Exactly lol.
That's one way of framing it in the "Tarzan Versus Crusoe," discussion at least, but there is also the idea that Crusoe cannot make new rules so long as he is alone, and any continued rule following can only be judged by an absent community.
But one might consider that, if we are incapable of judging our own rule following, what qualifies us to judge others? -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
In his own metaphorical terms, I think when Wittgenstein says that his spade is turned when he hits the bedrock of "forms of life," many would simply suggest that he buy himself a shovel or a pick axe.
As to logical form, one glaring example is that TLP has no example of actually mapping the logic of a proposition to the world. The claim about the relationship is never demonstrated, and it turns out to be impossible to demonstrate, even for simple statements.
I still think that TLP might end up being more valuable than PI. It has a number of very good insights that I think relate very well to the paradigm shift across the sciences brought on by information theory and complexity studies. It's too bad Wittgenstein didn't live to see the rise of these techniques and how they can unify the sciences, because I think he would have had very interesting ideas about it all. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
That isn't Wittgenstein though. Wittgensteinians often make claims that are the opposite of "common sense." For example, the claim that a man who washes ashore on desert Island loses his ability to make and follow rules, but then regains this capacity when a second person washes ashore later. Obviously, a great many Wittgensteinians (as well as people generally) find this to be somewhat absurd.
The common sense points I could think of were just the ones I pointed to. The ancients were well aware that language shifts over time. For example, parts of the Tanakh are written in extremely archaic Hebrew (and exist in a sort of proto-Hebraic in their earliest known forms), and this comes up in interpretation. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
Language and mathematics are social practices.
Language and mathematics are things we learn how to do through social interactions. Children raised in isolation will learn neither and children learn the language they grow up with.
Language and mathematics are rule governed. Games are also rule governed.
These rules are developed socially and change over time.
Language and mathematics are abilities we develop.
Language and mathematics are activities. They are behaviors we engage in.
People are able to understand each other because they share things in common.
If people are following a rule incorrectly, but they think they are following it correctly, they will not know they are following the rules incorrectly (this one is a tautology).
Use determines what a word means over time. If all people started using "cat" to refer to "dogs" and "dog" to refer to "cats" the words would swap meanings.
---
I can see how these can all seem pretty common sense, and I can't think of anyone who ever denied them. The philosophy of language of Wittgenstein's era wasn't challenging these assumptions. However, it was sometimes getting so far into theory that it seemed to forget them at times.
There are, of course, deeper things to draw on in Wittgenstein, but sometimes these get served up as if they are full explanations. E.g.:
"What is logic?"
"It's something humans engage in, an activity."
Well, respiration is also an activity, but we can probably go a bit further than that. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
More "give your own opinion," because discussions about "what Wittgenstein really meant," are interminable.
If it's a misrepresentation it's not Grayling's, since he is commenting on efforts by some "Wittgensteinians," to clarify what Wittgenstein's philosophy entails. It seems to me that the relativist camp tends to draw from On Certainty more than PI. At any rate, they have their own extensive sets of "scriptures," to justify their position.
My personal opinion is that Wittgenstein's work is too vague to decide this issue. The tendency to give give aphorisms and metaphors instead of arguments, and the tendency to assert rather than try to demonstrate (which applies to TLP too) makes the work a sort of rorschach test, and more so than works of most philosophers (the vast diversity of Hegel interpretations would be a kindred example).
I agree that there must be some commonality that allows us to move between games. Obviously people can become fluent in new languages and cultures.
This is why I considered the idea of overlapping, and perhaps somewhat hierarchical "forms of life." Pace Wittgenstein, I think we can often understand Chinese gestures quite well. Hell, we can understand when a dog, lion, or badger is upset because mammals signal aggression in similar ways. The reason "reptilian" and "insect-like," have the negative connotations they do is because these animals don't signal their "emotions" to us in the same way, leading to them seeming unpredictable and alien.
I imagine coming to understand extraterrestrial or synthetic lifeforms capable of language would end up being a good deal more difficult than learning a new human language, although perhaps not impossible. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
:up:
I agree with all of that and I think it's a problem for Wittgenstein's philosophy, at least in how it is often interpreted. I do wonder how he would respond to modern AI or the Chinese Room thought experiment.
Robert Sokolowski's concept of vagueness, grounded in phenomenology and Aristotle, seems applicable to the case where words are used correctly without users understanding their meaning. It often seems possible for people to learn how to comment on complex scientific or philosophical theories, e.g. quantum mechanics, while seemingly following all the rules of those discipline's discourse, yet not really understanding what they mean. It seems very possible to me to be able to "speak of something correctly," and not to really understand it. Dogmatic theology is another excellent example here.
I am confident that you yourself disagree with that idea to some extent.
Of course; it seems demonstrably false. Half a century + on, neither ordinary language philosophy nor Wittgensteinianism have convinced many people that these issues are dissolved. Even most practitioners in these camps don't tend to assert that. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
It seems relevant to the claim that meaning is use, which is of course different from the claim that use helps to fix our determine meaning.
And this relates to the idea that all manner of philosophical problems might be dissolved if one pays close attention to how words are used. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"
That's a tough call. The form of life "human" seems like it should wrap around the others, but there does seem to be some potential for fuzziness. French(Punk Rock) seems like it should be different from Japanese(Punk Rock), but the inner form shares a commonality across the categories of the outer term. -
10k Philosophy challenge
Right. It's conditioned on expectations about the future in many forms.
If I press an elevator button not knowing someone is stuck in the shaft (and having no good reason to think this is the case), and this kills someone, I have hardly committed murder. I have performed a trivial act that couldn't possibly have been known to result in someone's death; it's a mistake a saint could make.
Now as suggests, we might divorce goodness and praiseworthyness and solve this problem, although this seems somewhat counterintuitive to the extent that we tend to praise people precisely for attempting to do good, and even more for actually achieving it. We praise the virtues because they help to achieve good, not because they involve intending good for instance. -
10k Philosophy challenge
Yes, this is the problem I mentioned vis-á-vis defining freedom purely in terms of potency.
Negative Freedom - Hegel begins his analysis of freedom in the Philosophy of Right where many modern theorists have ended, with a conception of freedom as defined in purely negative terms—freedom as lack of constraint or unrestricted potency. In its absolute form, such freedom must become “pure indeterminacy,” since all determination is ultimately a form of constraint. To illustrate this, let us imagine an infinite blank canvas before us. We can draw upon it anything we’d like; we have absolute freedom within this two dimensional space. Yet if we draw a triangle, we are not free to have drawn a square. If we erase our triangle, we are not free to have kept it. Any choice must bring with it some limiting form of determinacy.
At the level of the individual, Hegel identifies the move towards this sort of negative freedom in the religious pursuit of “pure contemplation,” a retreat into wholly contentless thought., At the social level, the desire to recoil from all definiteness manifested itself in the destructive anarchism of the French Revolution’s sans-culottes. For these revolutionaries, any definite form of government became an intolerable retreat from the liberty offered by the pure indeterminate potency of revolutionary spirit.
Such freedom is ultimately contradictory. One can never choose anything without compromising one’s freedom. The ascetic can think of nothing without giving up on “pure contemplation.” The revolutionary cannot advance any concrete policy without abandoning absolute liberty. Thus, negative freedom collapses into a total lack of freedom, the “inability to choose anything.” At the same time, any action proceeding from pure potency would appear to be wholly arbitrary, a choice “made for no reason at all.” Yet if our choices are wholly undetermined then they can hardly be said to be ours.
Reflexive Freedom - As we have seen, negative freedom collapses into its opposite. Thus, freedom must sublate its own negation, resulting in a modified conception of freedom where agents positively and determinately "choose between” known options., For such choices to be ours, they must emerge from a process of self-conscious self-determination. Thus, reflexive freedom is defined by subjects’ freedom relative to themselves. “Individuals are [reflexively] free if their actions are solely guided by their own intentions.” Thus, “man is a free being [when he] is in a position not to let himself be determined by natural drives,” or circumstance; i.e., when his actions are not subject to “contingency,” but instead arise from rational, self-conscious decision-making.
Self-control alone is not enough here. We often need self-control to get what we desire, but we also sometimes desire things that we do not want to desire. Someone who shows tremendous self control in covering up an adulterous relationship they do not want to have begun is not fully free. To be perfected, reflexive freedom requires something like Harry Frankfurt's concept of "second order volitions," the ability to successfully align our desires towards what reason has determined to be “truly good.”, However, it is the issue of what is “truly good” that brings us to the consideration of authenticity as a form of freedom.
Etc. The contradictions continue up to a level of social freedom, because someone who possesses the lower sorts of freedom can always choose to deprive others of their freedom. This is where, for Hegel, institutions come in to shape people's identities and incentives such that they want to promote the freedom of their fellow citizens.
This lies in contrast to this theory, which doesn't seem to offer any reason for why people should be good or why they might decide to be good under various differing conditions. -
Wittgenstein, Cognitive Relativism, and "Nested Forms of Life"Ancillary point from Grayling:
We can understand the meaning of a word, say the German word for "village" and have not the first clue how to use it in a sentence.
Yet we can also know how to use words without knowing what they mean. For example, plenty of people use "e.g." "QED," "i.e.," or "amen," correctly without knowing what they mean.
This to me suggests a meta knowledge of rules and language which must sit outside individual language games. Or, more reasonably, that meaning is related to use but that the two are in no way identical. -
How do you interpret nominalism?
imperceptible difference. This exit from the identical into the same remains very slight, weighs nothing itself..it is not necessary to imagine the death of the sender or of the receiver, to put the shopping list in one's pocket, or even to raise the pen above the paper in order to interrupt oneself for a moment. The break intervenes from the moment that there is a mark, at once. It is iterability itself, ..passing between the re- of the repeated and the re- of the repeating, traversing and transforming repetition... Pure repetition, were it to change neither thing nor sign, carries with it an unlimited power of perversion and subversion.”
Interestingly, even on a reductive physicalist account, the general notion here should be true. Sign relations involving human cognition are incredibly complex and dynamic, and will never repeat in exactly the same way. But then again they will not be entirely different either. Commonalities will probably defined in terms morphisms between some set of processes, and then these could potentially be given the status of "abstract objects."
I don't know if physical reality being inherently processual should be a problem for realism. On the face of it, they don't seem to match up, but you can turn any 3D process into a 4D static abstraction.
Yes, as commonly interpreted. Although Aristotle is often still interpreted in fairly "idealist" terms, which makes eidos (form/pattern) and universals quite a bit different than a sort of immanent realism that tries to work with most modern forms of physicalism. For Aristotle eidos is what is "most real," while matter is simply what explains what stays the same when eidos changes—and there is no matter without eidos since this would entail being of which nothing can be said (Parmenides' "speaking nothing").
We can think of how eidos comes from the Greek iden, "to see." In Latin and then English these evolve into "idea," which is obviously now taken to be quite different from "to see" or "image." Now we might think of "what is seen," as studying arbitrarily far from "what is," but for Aristotle the eidos both makes a thing what it is and gives us grounds to say anything about it at all.
I had wondered if we also get "identity" from eidos, which would be instructive since identity, what a thing is, comes from eidos, but this is actually from the Old French "idem et idem," "same and same," and idem comes from Latin and develops from proto-Italiac not the Greek.
Consider that things can only be what they are in virtue of relation and process. This idea has been embraced in a number of disparate schools and the reasoning seems impeccable to me:
To be a substance (thing-unit) is to function as a thing-unit in various situations. And to have a property is to exhibit this property in various contexts. ('The only fully independent substances are those which-like people-self-consciously take themselves to be units.)
As far as process philosophy is concerned, things can be conceptualized as clusters of actual and potential processes. With Kant, the process philosopher wants to identify what a thing is with what it does (or, at any rate, can do). After all, even on the basis of an ontology of substance and property, processes are epistemologically fundamental. Without them, a thing is inert, undetectable, disconnected from the world's causal commerce, and inherently unknowable. Our only epistemic access to the absolute properties of things is through inferential triangulation from their modus operandi-from the processes through which these manifest themselves. In sum, processes without substantial entities are perfectly feasible in the conceptual order of things, but substances without processes are effectively inconceivable.
Things as traditionally conceived can no more dispense with dispositions than they can dispense with properties. Accordingly, a substance ontologist cannot get by without processes. If his things are totally inert - if they do nothing - they are pointless. Without processes there is no access to dispositions, and without dispositional properties, substance lie outside our cognitive reach. One can only observe what things do, via their discernible effects; what they are, over and above this, is something that always involves the element of conjectural imputation. And here process ontology takes a straight-forward line: In its sight, things simply are what they do rather, what they dispositionally can do and normally would do.
The fact is that all we can ever detect about "things" relates to how they act upon and interact with one another - a substance has no discernible, and thus no justifiably attributable, properties save those that represent responses elicited from it in interaction with others. And so a substance metaphysics of the traditional sort paints itself into the embarrassing comer of having to treat substances ·as bare (propertyless) particulars [substratum] because there is no nonspeculative way to say what concrete properties a substance ever has in and of itself. But a process metaphysics is spared this embarrassment because processes are, by their very nature, interrelated and interactive. A process-unlike a substance -can simply be what it does. And the idea of process enters into our experience directly and as such.
Nicholas Rescher - "Process Metaphysics: An Introduction to Process Philosophy"
It is through action, and only through action, that real beings manifest or “unveil” their being, their presence, to each other and to me. All the beings that make up the world of my experience thus reveal themselves as not just present, standing out of nothingness, but actively presenting themselves to others and vice versa by interacting with each other. Meditating on this leads us to the metaphysical conclusion that it is the very nature of real being, existential being, to pour over into action that is self-revealing and self-communicative. In a word, existential being is intrinsically dynamic, not
static.
...by metaphysical reflection I come to realize that this is not just a brute fact but an intrinsic property belonging to the very nature of every real being as such, if it is to count at all in the community of existents. For let us suppose (a metaphysical thought experiment) that there were a real existing being that had no action at all. First of all, no other being could know it (unless it had created it), since it is only by some action that it could manifest or reveal its presence and nature; secondly, it would make no difference whatever to any other being, since it is totally unmanifested, locked in its own being and could not even react to anything done to it. And if it had no action within itself, it would not make a difference even to itself....To be real is to make a difference.
---
One of the central flaws in Kant’s theory of knowledge is that he has blown up the bridge of action by which real beings manifest their natures to our cognitive receiving sets. He admits that things in themselves act on us, on our senses; but he insists that such action reveals nothing intelligible about these beings, nothing about their natures in themselves, only an unordered, unstructured sense manifold that we have to order and structure from within ourselves. But action that is completely indeterminate, that reveals nothing meaningful about the agent from which it comes, is incoherent, not really action at all.
The whole key to a realist epistemology like that of St. Thomas is that action is the “self revelation of being,” that it reveals a being as this kind of actor on me, which is equivalent to saying it really exists and has this kind of nature = an abiding center of acting and being acted on. This does not deliver a complete knowledge of the being acting, but it does deliver an authentic knowledge of the real world as a community of interacting agents—which is after all what we need to know most about the world so that we may learn how to cope with it and its effects on us as well as our effects upon it. This is a modest but effective relational realism, not the unrealistic ideal of the only thing Kant will accept as genuine knowledge of real beings, i.e., knowledge of them as they are in themselves independent of any action on us—which he admits can only be attained by a perfect creative knower. He will allow no medium between the two extremes: either perfect knowledge with no mediation of action, or no knowledge of the real at all.
W. Norris Clarke - "The One and the Many: A Contemporary Thomistic Metaphysics"
For the maker is always existent Being, but they exist in potentiality before they exist in actuality It is impossible for the infinite to exist on the same level of being as finite things, and no argument will ever be capable of demonstrating that being and what is beyond being are the same, nor that the measured and immeasurable can be put in the same class, nor that the absolute can be ranked with that which exists in relation to other things, nor that that which has nothing predicated of it and that which is constituted by predication belong together. For all created things are defined, in their essence and in their way of developing, by their own logoi and by the logoi of the beings that provide their external context. Through these logoi they find their defining limits.
-St. Maximus - Ambiguum 7
Hegel's basic demarche in both versions [of the Logic] is to trade on the incoherencies of the notions of the thing derived from this modern epistemology, very much as in the PhG. The Ding-an-sich is first considered: it is the unity which is reflected into a multiplicity of properties in its relation to other things, principally the knowing mind. But its properties cannot be separated from the thing in itself, for without properties it is indistinguishable from all the others. We might therefore say that there is only one thing in itself, but then it has nothing with which to interact, and it was this interaction with others, which gave rise to the multiplicity of properties. If there is only one thing-in-itself, it must of itself go over into the multiplicity of external properties. If we retain the notion of many, however, we reach the same result, for the many can only be distinguished by some difference of properties, hence the properties of each cannot be separated from it, it cannot be seen as simple identity.
Thus the notion of a Ding-an-sich as unknowable, simple substrate, separate from the visible properties which only arise in its interaction with others, cannot be sustained. The properties are essential to the thing, whether we look at it as one or many. And so Hegel goes over to consider the view which makes the thing nothing but these properties, which sees it as the simple coexistence of the properties. Here is where the theories of reality as made up of ' matters' naturally figure in Hegel's discussion.
But the particular thing cannot just be reduced to reduced to a mere coexistence of properties. For each of these properties exists in many things. In order to single out a particular instance of any property, we have to invoke another property dimension. If we want to single out this blue we have to distinguish it from others, identify it by its shape, or its position in time and space, or its relation to other things. But to do this is to introduce the notion of the multipropertied particular, for we have something now which is blue and round, or blue and to the left of the grey, or blue and occurring today, or something of the sort.
-Charles Taylor - Hegel
There is also the more science-based arguments for the primacy of process and relation: https://thephilosophyforum.com/discussion/comment/826619
Here we might also consider Roveli's relational quantum mechanics as an example. Then there is Jaegwon Kim's convincing arguments that any sort of strong emergence is impossible under a building block metaphysics where "things are the thing-units they are made of," which in turn seems to lead to either panpsychism or the denial of conciousness. https://thephilosophyforum.com/discussion/comment/837241 -
10k Philosophy challenge
I mean, it is consequentialism, so people's motivations for their actions don't really come into it, just the consequences.
IDK, it seems like some consequentialists consider the intended consequences of acts. To totally ignore them makes our marauding soldier a hero so long as he is killed before carrying out his assault, while a doctor offering to treat the poor for free becomes equivalent with a murderer if he accidentally kills a patient.
I'm afraid I haven't read it, so I can't comment with certainty.
You might be interested. It's quite short and not very dense, so it would probably make for a good audio book for driving too. I bring it up because its society is a stunning success if it is judged by the common metrics of public policy studies, economics, medicine, or many contemporary ethical theories. There is no crime or poverty, people are largely allowed to "do what they want." But it's intended to be entirely abhorrent, devoid of substantial freedom or beauty, and most readers agree that it's very successful in this respect.
Putting weakness of will to one side, do you think it's possible for people to choose evil over good intentionally?
It depends on how evil is defined, but generally I would say no, at least in as much as the person is a "rational agent," is not ignorant of what is good, and is confident in their knowledge vis-á-vis the good. Why would someone knowingly choose the worse over the better?
I have no idea. I'm not sure if I have met any rational persons
Well, the question of people's rationality is a different issue. I don't know if I've ever come across "the rational agent"—homo economicus—in the wild. That said, people aren't entirely irrational either, so the limit case is instructive. -
10k Philosophy challenge
Suppose no weakness of will, a person is able to make themselves so whatever they deem to be choiceworthy (e.g., no "I really shouldn't eat that donut, but it looks too tempting," type situation).
Suppose no ignorance about what is truly best.
Why does the rational person choose the worse over the better in this situation? Imagine their internal monologue: "yes, this is most choiceworthy. I know this and am confident of that knowledge. I will now go choose something worse when I could choose something better."
Of course these conditions are never met, but we can come more or less close to them. -
10k Philosophy challenge
the saving and the raping are two separate actions though. One is good, the other bad
This still seems to have it that a marauding soldier who rescues a girl for the sole purpose of raping her would have performed a good act. And supposing he gets killed by a stray artillery shell as soon as he is done pulling her out of the building he has only been "good."
And if coercion is only problematic if it involves violence and threats against property that seems to allow a whole host of troubling manipulative behaviors to be morally neutral. Yet if the goal is something like a mathematical equation the edge cases seem troubling.
Let me ask, would Aldous Huxley's "A Brave New World" be a utopia on this view? What if we ignore intentionally cognitively impairing the Gammas?
You don't think that someone can understand what's good or right and choose against it? That someone can intentionally do what they know is wrong?
No, weakness of will and incontinence exist. Also relative gradations of ignorance about what is truly good. -
10k Philosophy challenge
There is a link in the first post to a detailed write up. It's on the word "here."
I would suggest you may be making some moral assumptions unknowingly.
I'm making them knowingly. I would tend to sum up the vision of freedom common in Western philosophy before the early-modern period as "the self-determining ability to actualize the good," (act over potency). This leaves open the problem of "what is goodness?" but avoids the collapse into emotivism that seems to plague modern ethics.
But, to answer your question, a rational agent may not care about others freedom. There's a longer discussion to be had there, but suffice to say that I wouldn't assume that moral facts are motivating to others, and if people fail to care about what is moral, then so much the worse for them.
Seems so much the worse for an "objective theory of goodness," if people can look at it, understand it, and reasonably say "but that goodness isn't good for me."
Anyhow, it seems like a serious issue to me if goodness is defined in terms of freedom but then freedom is left vague. Perhaps you have addressed this elsewhere. You allow that coercion limits freedom but there is a lot of coercion that falls short of pointing a gun in someone's face. When a family holds an intervention for an alcoholic they are being coercive, but it's unclear to me that they are limiting freedom. When someone reminds us to do our duties and fulfill our obligations it is a sort of coercion, but it seems that can be good. Children and spouses have a lot of leverage when it comes to softer forms of coercion, but it has always seemed strange to me when theories of freedom would have it that our careers and families—what makes us who we are—is a limit of freedom.
The trade off thing seems like it could lead to some unpleasant conclusions too. If a man has a chance to save a girl from a fire, then he is better off doing that than "vanishing as a moral agent." But this seems true even if he saves her from a fire only so he can rape her afterwards. On the mathematics of "maximizing freedom," his act still ends up at a net positive, but calling this "good" seems absurd to me.
My solution would be that the problem is best solved by abandoning the idea of a "mathematics of morality." I imagine that's not prize material though :rofl:
Count Timothy von Icarus

Start FollowingSend a Message
- Other sites we like
- Social media
- Terms of Service
- Sign In
- Created with PlushForums
- © 2026 The Philosophy Forum


