-
 Agree-to-Disagree
674Quotes from an article by Heather du Plessis-Allan
Agree-to-Disagree
674Quotes from an article by Heather du Plessis-Allan
The plant-based food craze is over
February 2020, I basically said fake meat is not a thing, it's not going to catch on. And that is when I met the woman from Sunfed, who actually tried to change my mind.
Shama Sukul Lee came into the studio with some meat-free bacon, and it was actually delicious. Credit to her, she had a great product. And she had money behind it, she has $10 million worth of investment, which included some pretty high profile backers.
But she couldn't turn a profit. And she says it’s because the "plant-based bubble burst".
You know what the problem is, don't you? (this is the bit that is relevant to EVs)
It's the same problem I think the EVs have got. Consumers en masse will only switch if what you give them is better.
But plant-based food is not better than a steak. And frankly, not enough of us think about the climate deeply enough to do it for moral reasons.
There's a lot of this going on at the moment, there's hype about new products that we will switch to for moral reasons, EVs being the most obvious example right now.
But look what’s happening to the EV market, there's a massive slump. And why? Because they’re still not better than petrol and diesel vehicles, particularly over longer distances.
If there’s one lesson from this, it’s that moral motivation is not enough. The product you give us has got to be better. -
 Mikie
7.3kHere is a large report that explains some of the tipping points and what we might expect and what we ought to be doing about it politically. It's fairly up to date, and well researched. Seems mightily optimistic to me about the ability/possibility for human society to find its own transformative positive tipping points in terms of world governance and mitigating technologies and lifestyle adaptation. But hope springs 'til the last minute. — unenlightened
Mikie
7.3kHere is a large report that explains some of the tipping points and what we might expect and what we ought to be doing about it politically. It's fairly up to date, and well researched. Seems mightily optimistic to me about the ability/possibility for human society to find its own transformative positive tipping points in terms of world governance and mitigating technologies and lifestyle adaptation. But hope springs 'til the last minute. — unenlightened
Thanks for the reference. Very interesting. -
 AmadeusD
4.2k
AmadeusD
4.2k -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674
Agree-to-Disagree
674 -
 AmadeusD
4.2kI haven't even read your posting, just saw the name and ears pricked up.
AmadeusD
4.2kI haven't even read your posting, just saw the name and ears pricked up.
Always good to see locals about :)
I agree with the final line. But i think there are ways around it - much less cynical than Du Plessis-Allan. -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674much less cynical than Du Plessis-Allan — AmadeusD
Agree-to-Disagree
674much less cynical than Du Plessis-Allan — AmadeusD
I am a cynical and skeptical person.
Heather du Plessis-Allan's comments seem reasonable to me. Not enough people think about the climate deeply enough to make major changes for moral reasons. Many people don't like change, and most people don't want to give up the things that they enjoy.
What is being done to fight climate change at the moment is like rearranging the deck chairs on the Titanic. :roll: -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674I'm neither as cynical, or as bothered, it seems — AmadeusD
Agree-to-Disagree
674I'm neither as cynical, or as bothered, it seems — AmadeusD
I am not particularly bothered about climate change. But there are a number of things that annoy me.
-- :naughty: -- science seems to have sold its soul to the devil
-- :down: -- science is being controlled by bureaucracy
-- :scream: -- many things are exaggerated (scaremongering)
-- :zip: -- the public is not told the full story about many things
-- :roll: -- people are doing the wrong things to fight climate change
There are many other things about climate change that annoy me, but it is time for my afternoon nap. :yawn:
The good thing is that I will probably be long dead by the time the shit hits the fan. :grin: -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674Where would you rather live, location A or location B ?
Agree-to-Disagree
674Where would you rather live, location A or location B ?
The graphs below show a compact characterization of the entire year of hourly average temperatures. The horizontal axis is the day of the year, the vertical axis is the hour of the day, and the color is the average temperature for that hour and day.
Based only on these average temperature graphs, where would you rather live, location A or location B ?
Note that location A and location B are real locations on the earth. I will reveal where the locations are after people have answered the question. Location A and location B are very close to being on the same line of longitude, and the straight line distance from location A to location B is about 490 kilometers.
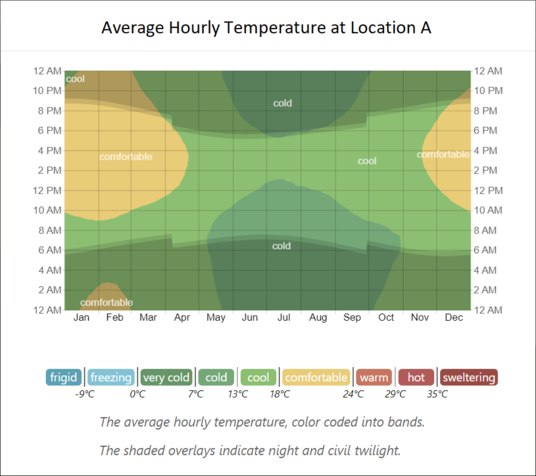
© WeatherSpark.com
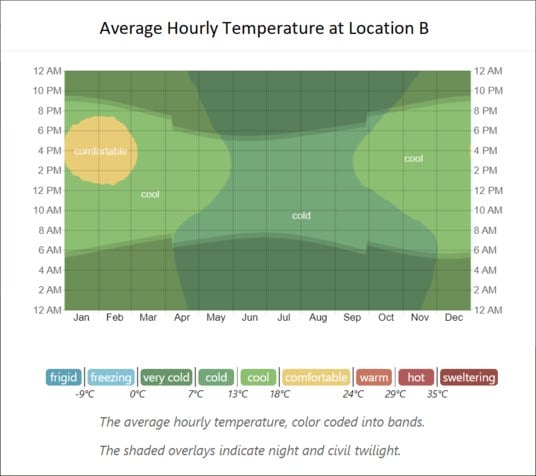
© WeatherSpark.com -
 javi2541997
7.2k-- :down: -- science is being controlled by bureaucracy — Agree-to-Disagree
javi2541997
7.2k-- :down: -- science is being controlled by bureaucracy — Agree-to-Disagree
Do you mind if science is being controlled overall or just by the bureaucracy? It seems you want to set science and scientists free. -
 Mikie
7.3kMany of us realize climate change is a threat to our well being. But what we have not yet grasped is that the devastation wreaked by climate change is often just as much about headline-grabbing catastrophes as it is about the subtler accumulation of innumerable slow and unequal burns that are already underway — the nearly invisible costs that may not raise the same alarm but that, in their pervasiveness and inequality, may be much more harmful than commonly realized. Recognizing these hidden costs will be essential as we prepare ourselves for the warming that we have ahead of us.
Mikie
7.3kMany of us realize climate change is a threat to our well being. But what we have not yet grasped is that the devastation wreaked by climate change is often just as much about headline-grabbing catastrophes as it is about the subtler accumulation of innumerable slow and unequal burns that are already underway — the nearly invisible costs that may not raise the same alarm but that, in their pervasiveness and inequality, may be much more harmful than commonly realized. Recognizing these hidden costs will be essential as we prepare ourselves for the warming that we have ahead of us.
Let’s start with heat, which is killing more people than most other natural disasters combined. Research shows that record-breaking heat waves are only part of the story. Instead, it may be the far more numerous unremarkably hot days that cause the bulk of societal destruction, including through their complex and often unnoticed effects on human health and productivity. In the United States, even moderately elevated temperatures — days in the 80s or 90s — are responsible for just as many excess deaths as the record triple-digit heat waves, if not more, according to my calculations based on a recent analysis of Medicare records.
In some highly exposed and physically demanding industries, like mining, a day in the 90s can increase injury risk by over 65 percent relative to a day in the 60s. While some of these incidents involve clear cases of heat illness, my colleagues and I have found that a vast majority appear to come from ostensibly unrelated accidents, like a construction worker falling off a ladder, or a manufacturing worker mishandling hazardous machinery. In California, our research shows that heat may have routinely caused 20,000 workplace injuries per year, only a tiny fraction of which were officially recorded as heat-related.
Unseen Ways Climate Change Effects Us -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674
Agree-to-Disagree
674
Mikie, you really need to improve your "cut and paste" skills. Some of the text in your post has mysteriously changed from the original text in the article.
Original article text:
the devastation wreaked by climate change comes not just from headline-grabbing catastrophes but also from the...
Mikie's text:
the devastation wreaked by climate change is often just as much about headline-grabbing catastrophes as it is about the...
Why did the text change Mikie?
Did you make the change? -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674
Agree-to-Disagree
674
Mikie, thank you for making this post. It is a good example of the sort of climate stupidity that is making the public distrust climate science and climate scientists.
.Instead, it may be the far more numerous unremarkably hot days that cause the bulk of societal destruction, including through their complex and often unnoticed effects on human health and productivity. In the United States, even moderately elevated temperatures — days in the 80s or 90s Fahrenheit — are responsible for just as many excess deaths as the record triple-digit heat waves, if not more, according to my calculations based on a recent analysis of Medicare records — We Don’t See What Climate Change Is Doing to Us
Consider the different states in America. Some of the states are hotter than others (e.g. Texas, Florida, Louisiana) and some of the states are colder than others (e.g. North Dakota, Minnesota, Montana).
This article implies that the hotter states should have more societal destruction, and more effects on human health and productivity, than the colder states. Is that true?
The article also implies that the hotter states should have a greater number of excess deaths caused by moderately elevated temperatures than the colder states. Is that true?
A growing body of literature links temperature to cognitive performance and decision making. Research shows that hotter days lead to more mistakes, including among professional athletes; more local crime; and more violence in prisons, according to working papers. They also correspond with more use of profanity on social media, suggesting that even an incrementally hotter world is likely to be a nontrivially more irritable, error-prone and conflictual one. — We Don’t See What Climate Change Is Doing to Us
Do people from hotter states have worse cognitive performance and decision making than people from the colder states? Do people from hotter states make more mistakes and have more local crime than people from the colder states? Do people from hotter states use more profanity on social media than people from the colder states. Mikie, do you live in a hotter state or a colder state?
Children are not immune. In other research, my colleagues Joshua Goodman, Michael Hurwitz and Jonathan Smith and I found that across the country, hotter school years led to slower gains on standardized exams like the Preliminary SAT exams. It may not seem a huge effect, on average: roughly 1 percent of learning lost per one-degree-hotter school year temperatures. Probably hardly noticeable in any given year. But because these learning effects are cumulative, they may have significant consequences. — We Don’t See What Climate Change Is Doing to Us
Did hotter states have slower gains on standardized exams like the Preliminary SAT exams than colder states?
If 1 percent of learning is lost per one-degree-hotter school year temperatures, and the effects are cumulative, then the children from the hotter states must be slowly but surely becoming stupider than the children from the colder states. Mikie, do you live in a hotter state or a colder state? -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674Do you mind if science is being controlled overall or just by the bureaucracy? It seems you want to set science and scientists free. — javi2541997
Agree-to-Disagree
674Do you mind if science is being controlled overall or just by the bureaucracy? It seems you want to set science and scientists free. — javi2541997
Science needs to be controlled in some way. So some degree of bureaucracy is required. But it should not be strongly biased towards one view.
To paraphrase Judith Curry:
Bureaucracy influences research funding priorities, the scientific questions that are asked, how the findings are interpreted, what is cited, and what gets canonized. Factual statements are filtered in assessment reports and by the media with an eye to downstream political use.
Here is a good description of academic life from Sabine Hossenfelder, who has many videos on YouTube:
It made me realize that this institute wasn’t about knowledge discovery.
It was about money making.
And the more I saw of academia, the more I realized it wasn’t just this particular
institute and this particular professor.
It was generally the case.
The moment you put people into big institutions the goal shifts from knowledge discovery to
money making.
You have to work on topics that are mainstream enough but not too mainstream.
You want them to be a little bit edgy.
But not too edgy.
it needs to be something that fits into the existing machinery. -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674Every time you blame cows for climate change, an oil executive laughs
Agree-to-Disagree
674Every time you blame cows for climate change, an oil executive laughs
Of all the climate solutions out there, maybe we should concentrate on the 97% of industrial emissions that come from fossil fuels, and leave the cows out of it, Eurof Uppington writes.
Given the press, you’d be forgiven for thinking that reducing cattle numbers and moving to a plant-based diet is a climate solution up there with electric vehicles and offshore wind.
Billions of dollars and euros and celebrity endorsements have been invested in plant-based and alternative protein startups. “Cows create global warming” is a truism of our time, shared by almost all right-thinking people.
The emerging truth appears different. Not only is the climate impact of cattle confused and overblown — properly managed, grazing cows and sheep can be a climate and biodiversity solution. — Eurof Uppington (euronews) -
 Mikie
7.3kNew study calculates climate change’s economic bite will hit about $38 trillion a year by 2049
Mikie
7.3kNew study calculates climate change’s economic bite will hit about $38 trillion a year by 2049
Probably a huge underestimate, but hilarious that they have to put a dollar amount on it so the corporate masters can actually understand.
Also, this is a good summary by Michael Mann of what we’re dealing with these days from the newest form of industry propaganda/ denialism:
“Delayers.” Examples of individuals occupying that niche in the media today are folks like Judith Curry of the Georgia Tech School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences, former UC Berkeley astrophysicist Richard Muller, and “skeptical environmentalist” Bjorn Lomborg. Rather than flat-out denying the existence of human-caused climate change, delayers claim to accept the science, but downplay the seriousness of the threat or the need to act. The end result is an assertion that we should delay or resist entirely any efforts to mitigate the climate change threat through a reduction of fossil fuel burning and carbon emissions. Despite claiming to assent to the scientific evidence, delayers tend to downplay the climate change threat by assuming unrealistic, low-end projections of climate change, denying the reality of key climate change effects, and employing lowball estimates of the costs of those impacts. When the cost-benefit analysis of taking action is skewed by a downwardly biased estimate of the cost of inaction, it is far easier to make the Pollyanna-ish argument that technology and the free market will simply solve the problem on their own. It is a backdoor way of saying that we do not need to pursue clean, non-fossil fuel energy sources, which are arguably the only real ways to avoid locking in dangerous climate change.
Spot on. Best not to pay them any attention. -
 jorndoe
4.2kWildfire season roars to life in parts of central B.C.
jorndoe
4.2kWildfire season roars to life in parts of central B.C.
— Rhythm Reet · The Weather Network · Apr 21, 2024
Bit early? Last year was bad enough. -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674Best not to pay them any attention. — Mikie
Agree-to-Disagree
674Best not to pay them any attention. — Mikie
You seem to constantly repeat this advice Mikie. Doesn't that prove that they are getting attention?
And Mikie, you seem to be giving them a lot of attention. Otherwise why would you need to give this advice constantly? -
 AmadeusD
4.2kRather than flat-out denying the existence of human-caused climate change, delayers claim to accept the science, but downplay the seriousness of the threat or the need to act. The end result is an assertion that we should delay or resist entirely any efforts to mitigate the climate change threat through a reduction of fossil fuel burning and carbon emissions. Despite claiming to assent to the scientific evidence, delayers tend to downplay the climate change threat by assuming unrealistic, low-end projections of climate change, denying the reality of key climate change effects, and employing lowball estimates of the costs of those impacts.
AmadeusD
4.2kRather than flat-out denying the existence of human-caused climate change, delayers claim to accept the science, but downplay the seriousness of the threat or the need to act. The end result is an assertion that we should delay or resist entirely any efforts to mitigate the climate change threat through a reduction of fossil fuel burning and carbon emissions. Despite claiming to assent to the scientific evidence, delayers tend to downplay the climate change threat by assuming unrealistic, low-end projections of climate change, denying the reality of key climate change effects, and employing lowball estimates of the costs of those impacts.
This is a really smart way to make it quite clear that you have no patience for disagreement, and prefer alarmist 'I'm right' type arguments to enforce actions that make you personally feel better.
Weird way to approach science. -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674Net zero has become unhelpful slogan, says outgoing head of UK climate watchdog
Agree-to-Disagree
674Net zero has become unhelpful slogan, says outgoing head of UK climate watchdog
The concept of “net zero” has become a political slogan used to start a “dangerous” culture war over the climate, and may be better dropped, the outgoing head of the UK’s climate watchdog has warned.
But it was not just those who were against climate action who were causing the problem, according to Stark. Climate activists were also alarming people, he warned, and creating “quite a serious barrier to large parts of the political spectrum to support climate action” by forceful protests, and presenting environmental policies as radical.
“It would be more helpful if they were less divisive,” he said. “I don’t think it is radical. It’s really important that we stop using words like that, as it is understandably frightening.” — The Guardian -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674South Korean court hears children's climate change case against government
Agree-to-Disagree
674South Korean court hears children's climate change case against government
SEOUL, April 23 (Reuters) - South Korea's Constitutional Court began hearing on Tuesday a case that accuses the government of having failed to protect 200 people, including dozens of young environmental activists and children, by not tackling climate change.
The proceeding is Asia's first such climate-related litigation, the plaintiffs said, which includes four petitions by children and infants among others dating from 2020, as well as one from a foetus at the time, nicknamed Woodpecker. — Reuters
How did Woodpecker (a foetus) sign the petition? :chin: -
 javi2541997
7.2kHow did Woodpecker (a foetus) sign the petition? — Agree-to-Disagree
javi2541997
7.2kHow did Woodpecker (a foetus) sign the petition? — Agree-to-Disagree
An administrator, guardian or legal care taker can sign documents, petitions, papers, etc. in the name of a foetus. -
 Mikie
7.3kThree Places Changing Quickly to Fight Climate Change
Mikie
7.3kThree Places Changing Quickly to Fight Climate Change
Uruguay, a nation of 3.4 million people wedged between Argentina and Brazil, generates nearly all its electricity from renewable sources. In 2008, the government set a goal of transforming the electric grid, which had come to depend on imported oil.
The country had a lot of hydropower, but years of drought in the 1990s and 2000s slashed the dams’ output. Uruguay was forced to import oil instead, at volatile prices, and faced shortages and blackouts. Officials noted the increasing cost competitiveness of renewables, especially wind, and set out to build a local wind industry nearly from scratch.
Between 2013 and 2018, wind generation grew sharply from almost nothing to about a quarter of Uruguay’s electricity mix. By the end of 2022, the most recent year data is available, Uruguay generated more than 90 percent of its power from renewables, with wind and solar growing even as hydropower declined.
Often said that these smaller countries can’t compare to a leading polluter like the US. But it can compare to states— like NH, VT, MA, NC or SC, etc. Enough states do it, there will be a turning point. The question, as always, is how quickly.
Should have started 30 years ago. Then there’d be room for more optimism. We’ve already shot past the Paris target of 1.5 however. That’s dunzo. There will be massive damage caused by this, and we may reach tipping points because of our delay.
But this and other examples shows it can certainly be done. The people are there, the technology is there— the dying fossil fuel industry, their lobbyists, and their lackies in congress, still in denial. So given our anti-majoritarian system, short term thinking, and general science ignorance, stupidity will most likely put prevail. -
 Agree-to-Disagree
674Hydropower may be renewable and clean, but it destroys the surrounding ecosystem. A small price to pay perhaps, but there is that. — Lionino
Agree-to-Disagree
674Hydropower may be renewable and clean, but it destroys the surrounding ecosystem. A small price to pay perhaps, but there is that. — Lionino
This song was written by John Hanlon and was adopted by the opponents of the Lake Manapouri dam.
It is called "Damn The Dam".
Leaf falls to kiss the image of a mountain
The early morning mist has ceased to play
Birds dancing lightly on the branches by a fountain
Of a waterfall which dazzles with its spray
Tall and strong and aged, contented and serene
The kauri tree surveys this grand domain
For miles and miles around him, a sea of rolling green
Tomorrow all this beauty won't remain
Damn the dam cried the fantail
As he flew into as he flew into the sky
To give power to the people
All this beauty has to die
Rain falls from above and splashes on the ground
Goes running down the mountain to the sea
And leaping over pebbles makes such a joyful sound
Such as Mother Nature's meant to be
I have grave reflection, reflection of a grave
Trees that once lived green now dead and brown
The homes of tiny animals and little birds as well
For the sake of man's progression have been drowned
Damn the dam cried the fantail
As he flew into as he flew into the sky
To give power to the people
All this beauty has to die -
 Mikie
7.3kThe meat industry’s war on wildlife
Mikie
7.3kThe meat industry’s war on wildlife
Your taxes fund an obscure government program that kills millions of wild animals to benefit Big Ag. -
 unenlightened
10kThis is rather long. But I think it is worth plodding through, and thinking about. For instance, the simple notion that the largest waste product of modern human society currently by tonnage is... CO2.
unenlightened
10kThis is rather long. But I think it is worth plodding through, and thinking about. For instance, the simple notion that the largest waste product of modern human society currently by tonnage is... CO2.
In general, it is a great introduction to ecological theory and the comparison with economic theory is particularly cogent and revealing. But you might need to keep your happy pills handy.
Welcome to The Philosophy Forum!
Get involved in philosophical discussions about knowledge, truth, language, consciousness, science, politics, religion, logic and mathematics, art, history, and lots more. No ads, no clutter, and very little agreement — just fascinating conversations.
Categories
- Guest category
- Phil. Writing Challenge - June 2025
- The Lounge
- General Philosophy
- Metaphysics & Epistemology
- Philosophy of Mind
- Ethics
- Political Philosophy
- Philosophy of Art
- Logic & Philosophy of Mathematics
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Interesting Stuff
- Politics and Current Affairs
- Humanities and Social Sciences
- Science and Technology
- Non-English Discussion
- German Discussion
- Spanish Discussion
- Learning Centre
- Resources
- Books and Papers
- Reading groups
- Questions
- Guest Speakers
- David Pearce
- Massimo Pigliucci
- Debates
- Debate Proposals
- Debate Discussion
- Feedback
- Article submissions
- About TPF
- Help
More Discussions
- Other sites we like
- Social media
- Terms of Service
- Sign In
- Created with PlushForums
- © 2026 The Philosophy Forum








