-
A Deist Creation Myth
The 13th century Cosmological Argument, making a distinction between Necessity and Contingency, was scientifically supported by the Big Bang theory. On the space-time side of the Bang everthing real is temporary and dependent on prior causes. But on the infinite-eternal side of the equation, we can reasonably infer that only timeless/ideal essentials, fundamentals, and necessities existed : including Causal Power (energy) and Controling Power (laws). The only viable alternative to a deistic First Cause is the materialistic Multiverse Theory, which is just as un-falsifiable as the God Theory, and must assume, without explanation, that the Potential for Mind/Consciousness predated the Bang.I think the cosmological argument provides a very good proof that SOMETHING exists outside the realm of human understanding. — Brendan Golledge
Spinoza's 17th century Cosmological Argument*1 generally agreed with Aquinas' 13th century Natural Theology, but added the notion of Substance Monism. That "substance" was not mundane Matter, but Aristotle's "essence", which I update to the 21st century as Information/Energy (EnFormAction)*3 : the power to enform or to transform. What we now call "energy" is invisible and unknowable, except by its after-effects*2. And the ultimate pre-bang source of cosmic Energy/Law*3 may be "outside the realm of human understanding", but its instantiation in the real world is the basis of modern Science. :chin:
*1. Baruch Spinoza's cosmological argument for the existence of God is based on the idea that there must be a necessary being that all other beings depend on. . . . .
Spinoza's argument is based on his concept of substance monism, which is the idea that there is only one infinite substance, which is either God or Nature. Spinoza believed that God is the cause of everything, and that the universe is a mode of God. He also believed that thought and extension are attributes of God, and that the human mind and body are perfectly correlated.
___Google AI overview
*2. Yes, energy itself is invisible to the human eye; you cannot directly see energy, but you can observe its effects, like movement, heat, or light, which are manifestations of energy in different forms.
___Google AI overview
*3. EnFormAction :
Ententional Causation. A proposed metaphysical law of the universe that causes random interactions between forces and particles to produce novel & stable arrangements of matter & energy. It’s the creative force (aka : Divine Will) of the axiomatic eternal deity that, for unknown reasons, programmed a Singularity to suddenly burst into our reality from an infinite source of possibility. AKA : The creative power of Evolution; the power to enform; Logos; Change.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page8.html
Astronomers like to assume that the space-time universe may be infinite-eternal, but the observable evidence indicates that our knowable Cosmos*4, is finite . So, we have no way of knowing what exists on the outside of the manifest horizon of our contingent world. Nevertheless, the Big Bang couldn't have happened without a priori creative Potential, including Cause & Laws.if he contains an infinity of abstract potential, — Brendan Golledge
So I think your guess may be right, that the Creator/Programmer consists of unlimited potential. And, from the perspective of contingent & sentient beings, that absolute Power could have good or bad effects on contingent entities capable of suffering & dying. Yet, “infinite abstract Potential” could not be characterized as either Good or Evil. Such notions only apply in the sentiments of creatures who evolved with life-protecting senses capable of detecting positive & negative influences on their well-being.
Therefore, as you suggested, the First Cause may be like logical Mathematics, including the possibility of infinity, but also of innumerable instances of finitude. Our finite world cannot exist outside the scope of infinity. Therefore, I think of the God/World relationship in terms of PanEnDeism (all within god). In my thesis the common god/world substance is the creative potential for enforming : Energy/Information. :halo:
*4 In astronomy, the cosmic horizon is the boundary of the observable universe, similar to the horizon at sea. The cosmic horizon is a sphere that's 46.5 billion light years away from Earth.
___Google AI overview
Yes! The Big Bang theory implies that space-time began with high Energy/Law (low entropy)*5 and will eventually fade away to the high Entropy of Heat Death. But in the meantime, our world has evolved from formless Plasma to all the "endless forms most beautiful" that Darwin marveled about*6. Scientists have explained that mystery by postulating some constructive "force" that works in opposition to destructive Entropy. But their inappropriate name for that positive trend in evolution sounds negative*7. So, in my thesis, I coined a new term*8 that I think is more descriptive of an upward evolutionary trend. :grin:So, I think it's fair to say that the existence of entropy implies that the universe in its current form had a beginning. — Brendan Golledge
*5. The cosmic initial entropy problem (IEP) is the conflict between two views on the entropy of the universe. The past hypothesis states that the entropy of the universe has been increasing, while the standard model of cosmology states that the universe began with low entropy and then increased.
___Google AI overview
*6. Charles Darwin's quote about beauty from On the Origin of Species is, "from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being evolved".
___Google AI overview
*7. Negentropy is a concept that describes a system becoming more organized or less disordered, and is the opposite of entropy:
___Google AI overview
*8. Enformy :
In the Enformationism theory, Enformy is a hypothetical, holistic, metaphysical, natural trend or force, that counteracts Entropy & Randomness to produce complexity & progress. [ see post 63 for graph ]
# I'm not aware of any "supernatural force" in the world. But my Enformationism theory postulates that there is a meta-physical force behind Time's Arrow and the positive progress of evolution. Just as Entropy is sometimes referred to as a "force" causing energy to dissipate (negative effect), Enformy is the antithesis, which causes energy to agglomerate (additive effect).
# Of course, neither of those phenomena is a physical Force, or a direct Cause, in the usual sense. But the term "force" is applied to such holistic causes as a metaphor drawn from our experience with physics.
# "Entropy" and "Enformy" are scientific/technical terms that are equivalent to the religious/moralistic terms "Evil" and "Good". So, while those forces are completely natural, the ultimate source of the power behind them may be super-natural, in the sense that the First Cause logically existed before the Big Bang.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page8.html
Note --- Enformy is more like an initial programming algorithm than occasional divine meddling. -
A Deist Creation Myth
Rabbi Kushner wrote a book on that same subject : When Bad Things Happen to Good People*1. Generally, it advises us to look at the Big Picture --- when we personally experience the badness of life --- in order to see that the world as a whole is evolving as intended by the Creator, and that your personal problems are minor in the overall context. Would a theoretical theodicy make you feel better about your own suffering? :grin:As I have said before, I believe my psychological motive for creating this system was that I wanted to be able to see the good in situations where things were not going my way. — Brendan Golledge
*1. When Bad Things Happen to Good People is a 1981 book by Harold Kushner, a Conservative rabbi. Kushner addresses in the book one of the principal problems of theodicy, the conundrum of why, if the universe was created and is governed by a God who is of a good and loving nature, there is nonetheless so much suffering and pain in it. ___Wikipedia
Yes, you hit the nail on the head. When the Deus Project manifesto said it wanted to "fix what's wrong" with Deism, it wasn't casting aspersions on the deity. And it didn't imply that Deism "failed" as a philosophical worldview. It was simply noting that Deism had its "intellectual" heyday in the 18th century, but failed to appeal to the general public as an emotional "opiate"*2, hence failed to qualify as a popular religion.I am not aware that deism ever "failed" in the intellectual sense. Has anyone ever proven that it's impossible? It is merely not popular. I think the reason is probably that most people would rather believe in a god who is interested in their personal happiness. — Brendan Golledge
Personally, I'm not interested in a popular religion that panders to the emotions (dreams & fears) of the average human. Catholicism hit the jackpot 2000 years ago, and is still fulfilling the religious needs of millions of people : rituals & traditions to take the mind off the bad things, and myths to give them something better to look forward to. Do you think your Creation Myth has the "right stuff" to appeal to the six basic emotions*3 of homo sapiens? :smile: :sad: :gasp: :angry: :halo: :worry:
*2. "Opium of the masses” is a phrase that refers to religion and is derived from a quote by Karl Marx. The phrase is often used to describe religion as a way to soothe the suffering in society and the universe.
___Google AI overview
*3. The Six Basic Emotions :
A widely accepted theory of basic emotions and their expressions, developed Paul Ekman, suggests we have six basic emotions. They include sadness, happiness, fear, anger, surprise and disgust.
https://online.uwa.edu/infographics/basic-emotions/
PS___ I don't view the Deity (Programmer of Evolution) as "good and loving", but merely Logical and Causal. So, our best strategy for coping with the ups & downs of life, is to use our rational faculties to align our behavior with the laws of reality. Even might agree with that, as a philosophical policy, not a religious belief. -
A Deist Creation MythAccording to cosmological arguments, a first cause is one of the options for explaining existence, which implies something like a creator god. So, this part is at least plausible. Alternatives are an infinite regression of causes, or circular causality. — Brendan Golledge
I suppose you are contrasting an eternal transcendent Creator God with various versions of immanent or more-of-the-same-forever-and-ever-amen (linear-or-circular) physical explanations for Causation. All transcendent options are hypothetical & unprovable, hence philosophical & non-scientific. Therefore, says it makes more sense to him, to simply "substitute existence (laws of nature) . . . . for God". His preferred god-model is based on Spinoza's deus sive natura, which is similar to Deism, except no accounting for a contingent & temporary world. Transcendent Deism is one answer to "who lit the fire" questions.
Some form of divinity seems to be the original philosophy of inquisitive primitive humans, who imagined what we now call "laws of nature" as-if they were the arbitrary (whimsical) behavior of invisible humanoid beings in the sky : i.e. Nature Gods. As people became more civilized (e.g. Mesopotamia) they began to include in their pantheon of gods some abstracted functions of nature (e.g. Damu = healing & rebirth). Over time, the Hebrews developed an even more extremely spiritualized notion of their tribal god (who, by taboo, cannot be named). Eventually, the Jews abstracted their storm-&-war-god even further to a non-local, singular, eternal, omniscient, and omnipotent ruler of the whole world. This was still a sort of cosmic Nature God, except that it favored one tribe of humans over all others.
The notion of a partisan deity was always common, but unsurprisingly, for "stiff-necked" Jews, it triggered some enmity with the neighboring Gentiles. And the Christian version of Judaism exacerbated that religious hostility by emphasizing the necessity for voluntary Faith over accidental inheritance, with catastrophic consequences for disbelief. That may be one reason for the emergence of a less eternally-fatal alternative in cosmopolitan but non-soteriological Deism*1.
By contrast with the personalized primitive pantheons of Mesopotamia, and the inscrutable & un-nameable & timeless & spaceless Yahweh of Israel, in Hellenic Greece Plato & Aristotle advocated some further-abstracted mathematical & scientific concepts, such as First Cause and Prime Mover. You could even describe them as the (intentional or unintentional?) creators or causes or instantiators of what we now call "Natural Laws".
Yet, in view of the modern Big Bang beginning of space-time and cause-laws, the question remains : what were Cause & Laws doing before the Bang? Any postulated answers to such questions are, as you said, "working off speculation". So, is there any good reason to prefer extending what we now know into eternity, and an intentional entity, over attributing the Cause & Laws of our world to mere happenstance : it is what it is, for no particular reason?
As you mentioned before, your Deist worldview is intended to provide some foundation, or standard, for a stable universal Morality in a world of conflicting motives and opinions. But, without a valid revelation from the Lawmaker, how can we know what we humans ought to do? Most Deists would say to consult the Book of Nature (science), but moral interpretations tend to vary widely (e.g. homosexuality : natural or perversion?).
Also, as you said, "it is the people who believed in a creator god who came up with the scientific method". And the early Deists did indeed accept the world itself, as revealed by science, for the embodied intention (design) of G*D*2. Ironically, the natural world has been described as "red in tooth & claw" and its laws of Evolution (i.e. Natural Selection) denounced as resulting in suffering & death of apperceptive beings. Therefore, sentient suffering must be accounted for in order to answer Theodicy*3 questions. Does G*D care that I, or a worm, must suffer the slings & arrows of outrageous fortune?
Can we then supplement the objective facts of Science, with the subjective reasoning of Philosophy? Would you call that a Deist "religion", or simply a "natural philosophy"? Would an immanent Deity (the evolving Cosmos) suffice for your Deist morality, without speculating beyond the beginning of the space-time world for a super-natural higher authority? :smile:
PS___ My hypothetical transcendent deity (programmer) is imagined as amoral regarding how humans deal with each other. The ultimate design is for an evolving Cosmos, of which we humans are merely a willful cog of the system. Presumably, developing a workable morality is an essential part of the Game of Life in a real (not ideal) world.
*1. Deists have had different beliefs about rebirth, with some believing in reincarnation or resurrection.
___Google AI overview
*2. In Deism, the "word of God" is essentially understood as the natural world itself, meaning that God's existence and will are revealed through the observable laws and order of nature, rather than through any specific religious texts or pronouncements; essentially, God created the universe and set it in motion with natural laws, and that is how we can understand His design.
___Google AI overview
*3. In philosophy, the justification for a good God allowing evil to exist, often called a "theodicy" is typically based on the idea that permitting some evil is necessary to enable greater good, such as human free will, moral development, or the potential for deeper appreciation of good, even if it means suffering can occur; essentially arguing that a world with free choice, even if it leads to evil, is better than a world without it where everyone is always good by default.
___Google AI overview
PPS___ Regarding religion and science, here's a quote from a Sherlock Holmes story :
" What a lovely thing a rose is. There is nothing in which deduction is so necessary as in religion. It can be built up as an exact science by the reasoner. Our highest assurance of the goodness of Providence seems to me to rest in the flowers".
https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0506452/quotes/ -
A Deist Creation Myth↪Brendan Golledge
We wanted to fix what was wrong with Deism, ... by determining why it failed. — Gnomon
Afaik, deism is just 'the god of theism' on its day off (or on vacation), and so, if the latter is a fiction (e.g. ontologically separate – "transcendent" – from existence aka "nonexistent"), then the former must also be fictional. :chin:[/quote]
Brendan, is this how you view Deism : as a continuation of Theism without the bad parts (e.g. possibility of eternity in Hell)? If so, then may be justified in ridiculing it as a Pollyanna "fiction", based on non-empirical (transcendent) presumptions.
However, the alternative explanations for human existence (e.g. Multiverse) are also transcendent & non-empirical. Moreover, Spinoza's theory of immanent PanDeism or PanPsychism begs the Ontological question of our contingent temporal existence, when faced with empirical evidence for an inexplicable space-time beginning : a creation event. But, if you postulate an eternal Creator to play the role of First Cause, then, sans divine revelation, you are left with no further information upon which to build your philosophical god-model.
Which is why I make no assumptions about a Transcendent existence, apart from its logical necessity. For example, I have no good explanation for Why an eternal deity would create a temporal world, and then "take a day off". Or why an immanent deity would suddenly & inexplicably self-create in a burst of energy & laws. I simply imagine the Big Bang as the execution of a computer program, and Evolution as its ongoing implementation. Ironically, our world is a program with sentient beings, who question where they came from and where they are going*1. With only empirical information to go on, we can at best theorize & speculate about both ends of the time-cycle of physical existence. And that's what philosophers do, in order to intuit the Purpose behind the Program (if any). :smile:
*1. Setting aside such questions as why a loving god would choose to "create intelligent life through such a horrific process as natural selection". Philip Goff, in Philosophy Now Dec-Jan -
A Deist Creation Myth
Do you view yourself as the founder of a religious movement, as opposed to merely the author of a novel religious worldview/manifesto? Due in part to the confusing plethora of other religions, and in some cases, direct resistance to the competition, starting a new religion ain't easy.So, in writing this, I am creating my own religion. — Brendan Golledge
Years ago --- after the worldwide shock of 9/11/2001 --- I tentatively joined a local college student "club", that was originally called The Deus Project, and led by a pre-med student, who later became a doctor. Within a couple of years, the "club" became a website, and the name was changed to The Universist Movement. Due to its broadened appeal, it eventually attracted a variety of people who could be identified as "spiritual but not religious", yet even included some Atheists and Agnostics. Online members were located all around the world, but mostly in English speaking countries. In the Manifesto written by the student leader, it said "The Deus Project began by addressing Deism with the mission to make it into a 'religion of the future'. We wanted to fix what was wrong with Deism, and make it a satisfying replacement for faith, by determining why it failed. Our conclusion was that the opposite of faith, uncertainty, is the only satisfying antidote."
Unfortunately, as an online religion, I suspect that it never became as popular as Satanism. And due to internal philosophical divisions --- atheist vs agnostic ; materialist vs spiritualist ; etc --- the movement fizzled away into a footnote on failed religious movements. :sad:
Holiness and Sacredness are expansions on the ancient notion of Taboo, in which certain things (foods, weapons, etc,) were reserved exclusively for a hierarchy of gods & kings & nobles. Another aspect of Taboo was that certain proscribed things --- such a woman's menstruation --- were disgusting & repellent. I mention this because Holiness and Taboo are faith-based non-democratic notions, which eventually lead to a hierarchical priesthood, and a pantheon of saints. Do you envision your "religion" in such terms? Would it involve worship of the universe, or sacred trees? :smile:↪180 Proof
I'm used to thinking of God as being holy. So, if the universe is God, then it would follow that the universe is holy. — Brendan Golledge
Holy : dedicated or consecrated to God or a religious purpose; sacred.
___Oxford dictionary
Taboo : The English term taboo comes from tapu in Oceanic languages, particularly Polynesian languages, with such meanings as "prohibited" or "forbidden".
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taboo -
A Deist Creation Myth
's trite comparison of a metaphysical a priori concept, Original Cause, with our physical experience of the arbitrary designation of a navigational North Pole on a spherical planet, is completely missing the philosophical principle of how to explain the scientific Big Bang beginning of our space-time universe. The "true" North Pole is a human construct (idea), not a physical place, and the magnetic pole wanders*1. The Cause of our Cosmos is neither a place nor a time."Before the beginning" is not actually an arbitrary phrase. The matter we are familiar with only acts after it's first acted upon. So, it follows that if there was a first cause, it can't be anything at all like the matter we are familiar with. . . . . math might still have been true before the Big Bang. — Brendan Golledge
As you implied, alternatives to the god-postulate --- such as the Multiverse conjectures --- simply assume that the "before" was not a timeless First Cause principle, but a chain of mundane material causation without beginning or end. Yet I agree with you that our material world is a morphological effect --- something from Singularity --- and the Prime Mover must be more like a determining action (cosmic bang). Both Mathematics and Energy are defined in terms of logical & causal relationships*2*3. So I can agree that whatever caused the Big Bang must be more like logical Math & causal Energy than mundane malleable Matter. I call it EnFormAction : the power to cause form change. :smile:
*1. "True north" refers to the geographic North Pole, a fixed point on Earth's axis of rotation, while "magnetic north" is the direction a compass needle points to, which is influenced by the Earth's magnetic field and constantly shifts, meaning it is not a fixed point. ___Google AI overview
*2. Math is built on a foundation of logic, with each theorem, proof, and equation derived from logical rules. ___Google AI overview
*3. Yes, in the context of physics and science, "energy is logical" because it follows consistent and predictable laws, ___Google AI overview
The analogy of the Big Bang with an Egg or Fetus is a metaphor, not to be taken literally. Yet, I can't agree that the Creator "must be utterly unlike" anything in the Creation. I suppose your God-model is imagined as an immaterial Spirit. But I think the Creation must have something in common with the Creator, in order for us philosophers to even imagine what it's like. The word "like" implies a comparison.. . . disagree with the analogy of creation being like an egg or a fetus. Based on what I discussed immediately above, we have good reason to think that a creator god must be utterly unlike anything that we've ever experienced. — Brendan Golledge
The traditional notion of Spirit is more mind-like & energy-like than matter-like*4. My thesis observes that invisible relational causal Energy is more mind-like than anything else in the non-human world, and Creation is an Action. Therefore, I coined the term EnFormAction to combine Platonic (ideal) Form with Aristotelian (physical) Causation : Form + Action. :nerd:
*4. Mind :
In the Enformationism thesis, this common term is used in some uncommon senses. Ordinarily, Mind is equated with Consciousness, but I sometimes use it in a more general sense to include all kinds of information & energy processing.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page15.html
I agree that the pre-space-time Creator of the Cosmos should be more like timeless Logical Mathematics (ratios ; relationships) than like the time-bound entropy-destined material aspects of the world. But if the timeless Creator necessarily existed eternally prior to the creation event we call Big Bang, then it would not be identical to the space-time Creation (Pandeism)*5. Instead, the temporary Effect would exist as a momentary blip within the eternal existence of the Cause. That god-model is known as PanEnDeism*6*7. :halo:the deist creator god fits together more nicely with mathematics than the pandeist god. — Brendan Golledge
*5. A number of Christian writers have examined the concept of pandeism (a belief that God created and then became the universe and ceased to exist as a separate entity.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Christianity_and_pandeism
*6. There is something called PanEnDeism which perceives God or the Divine as being part of nature and somehow beyond the universe.
https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/panendeism
*7. PanEnDeism :
# Panendeism is an ontological position that explores the interrelationship between God (The Cosmic Mind) and the known attributes of the universe. Combining aspects of Panentheism and Deism, Panendeism proposes an idea of God that both embodies the universe and is transcendent of its observable physical properties.
https://panendeism.org/faq-and-questions/
# Note : PED is distinguished from general Deism, by its more specific notion of the G*D/Creation relationship; and from PanDeism by its understanding of G*D as supernatural creator rather than the emergent soul of Nature. Enformationism is a Panendeistic worldview.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page16.html
arbitrarily & "parsimoniously" limits his god-model to the immanent knowable things of Spinoza's space-time Natural world. But in order to accept that 17th century paradigm, he would have to ignore or deny the evidence of a point-of-beginning for Space-Time. Your god-model, and mine, are more like a meta-physical Idea than a physical Thing. But which is simpler : the Chicken or the Egg ; the Cause or the Effect? Some imagine that God must be infinitely complex, but that's a materialistic notion, not a philosophical principle. If the Creation has evolved sentient creatures, then the pre-conscious Creator of natural laws must have the Potential for Consciousness (ability to know), even though objectless thought might not be identical to our Actual experience of the material world. :cool:I briefly discussed in one of my earlier replies that I can't imagine a difference between an unconscious creator god and the laws of physics. — Brendan Golledge -
A Deist Creation Myth
I don't view Deism*1 as a religion, but simply a philosophical worldview that attempts to explain the contingent existence of our physical world, and its intelligent creatures, without resorting to magical thinking, or by putting words in the mouth of an anthropomorphic fascist-father-figure in the sky.Before the beginning, there was God. Nothing was before God, and neither does God depend on anything else. It is difficult to say much about God, because he is before logic and before matter. God has no body, and he exists neither in time nor space. Yet in God, in the abstract, exists all else that could be. — Brendan Golledge
Several years ago, I thought about writing a Deist Creation Myth that is consistent with modern science. But, unlike Spinoza in the 17th century, I couldn't just assume that our world (Natura sive Deus) is self-existent, because we now have evidence for a "big bang" beginning of space-time & matter-energy. And, since the bang did not instantly fizzle out like fireworks, I had to account for the Cause & Laws that reveal themselves in progressive Evolution, over far more than 6000 years. But I also could not give any credence to the pre-scientific scriptural myths of Judeo-Christian religions. So, my myth had to include a plausible First Cause & Law-Giver, that didn't resort to miracles to fix human problems. I guess you can see that it would have to be a provisional Deist myth instead of an absolute Theist Faith.
My approach is somewhat different than yours, in part because I can't imagine what an eternal-infinite "God" might do or think. As you said, "It is difficult to say much about God, because he is before logic and before matter. God has no body, and he exists neither in time nor space". So, the story only gives a cursory background, and focuses on the conditions related to the "birth" of our world. The rest. as they say, is history. However, since Intelligent beings, such as the posters on this forum, have emerged from eons of Cosmic evolution, I must assume that the anonymous First Cause must also be Intelligent & Intentional, instead of an infinite chain of rambling stumbling Chaotic un-aimed accidents.
In the essay linked below*2, I coined some new terminology, such as In-Form-Action, because our current language has no way to express the novel notion of Energy as a Causal program. In my blog, I now spell it EnFormAction. My neologisms, and other unorthodox terminology, are defined in the Blog Glossary*3. Do you see any commonality or overlap between your myth and mine? :smile:
*1. Deism :
An Enlightenment era response to the Roman Catholic version of Theism, in which the supernatural deity interacts and intervenes with humans via visions & miracles, and rules his people through a human dictator. Deists rejected most of the supernatural stuff, but retained an essential role for a First Cause creator, who must be respected as the quintessence of our world, but not worshipped like an imperial tyrant. The point of Deism is not to seek salvation, but merely understanding.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page12.html
*2. Intelligent Evolution :
A 21st Century Creation Myth
https://gnomon.enformationism.info/Essays/Intelligent%20Evolution%20Essay_Prego_120106.pdf
Note --- Yes, the essay agrees with Intelligent Design theory, except in the designation of the designer.
*3. BothAnd Blog Glossary :
Since they are based on an unconventional worldview, many traditional terms are used in unusual contexts, and some new terminology has been coined in order to convey their inter-connected meanings as clearly as possible.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page2.html -
The Mind-Created World
Quote from the link to : The Neural Binding Problem :However, the "hard question" remains : by what physical process does a brain construct a worldview? — Gnomon
Unknown — Wayfarer
" In Science, something is called “a problem” when there is no plausible model for its substrate. So we have the mind–body problem (Chalmers 1996), but not the color problem, although there is a great deal of ongoing color research."
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3538094/#Sec3
how does the brain create consciousness
"The brain creates consciousness through a complex interplay of billions of neurons, and there are multiple theories about how this happens"
"The creation of consciousness is one of the greatest remaining mysteries in science and philosophy"
___Google AI overview
Note --- "Multiple Theories", but none with a step-by-step process from Sensation to Meaning. -
The Mind-Created World
So, Schopenhauer is agreeing with Kant, that we can "not" know the true reality (ding an sich), and must make-do (improvise) with an imitation simulation : a virtual reality (immaterial experience)? But stubborn Materialists insist on getting true, authentic Reality, even if they have to take it on theory/faith? In that case, is natural Matter their substitute for belief in a super-natural Ideal realm?He's *not* saying that we have the idea of the object on one hand, and the actual object on the other - everything that appears to us, appears as 'idea'. Whereas materialism attempts to explain this unitary experience with reference to something else altogether, namely, 'matter', as a theoretical construct existing apart from or outside the experience of the object, and which is somehow more fundamental than the experience itself. — Wayfarer
I guess what Schopenhauer means by "given" is the knowledge (appearance) presented to us, effortlessly, by our understanding (interpreting) minds. Most of us take that mental experience for granted as real-enough (given), even though lacking in stuff with material properties. Yet some think it's the brain that does the "hard work" of bringing the exterior world inside the interior experience.
However, the "hard question" remains : by what physical process does a brain construct a worldview? What are the physical/material stages/steps between object and subject? I suppose the easy answer is to just take the experience as a "gift", given by the brain. But hard-to-please Materialists grudgingly accept the gift as an artificial substitute for the real object. Their policy is, "accept no substitutes" for the true ding. Hence, they rudely look a gift-horse in the mouth, to determine its true reality. :smile: :wink:
Note --- Quantum physicists constructed theoretical models of matter in empty space, that serve as place-holders for the ding an sich. Their theory of fields requires some "thing" to occupy each point in space, and to jump around (fluctuate) as they absorb virtual photons. Are such Fields real or ideal? Is that kind of matter True or Apparent?
A "virtual particle" is a temporary, theoretical particle that arises from the quantum field theory concept of "empty space" not being truly empty, . . . . ___ Google AI overview
Buddha's "Self"
His extraordinary insight was that appearances, properly understood as impermanent, interdependent, and unsatisfying, are also devoid of the ontological underpinnings we are used to ascribing to everything in our world. All of it, without exception, is utterly devoid of self.
https://tricycle.org/magazine/appearance-and-reality/
Note --- Is "self" the Buddhist version of matter or stuff or ding an sich? -
The Mind-Created World
Since I have no formal training in philosophical language and methods, some of Schopenhauer's argument against Materialism is lost on me. For example, the notion of "givenness", begs the question "by whom?". Are the ideas he calls "given" merely his personal preferences and assumptions, or Axioms generally accepted by experts in the field, or divine revelations?1. This grounds the connection between physical causation and logical necessity. . . . .
Hence, 'mind-created world'. — Wayfarer
Since unresolved debates between Materialism and Idealism are common on this forum, it might help to clarify our language, and the ideas that each side takes for granted. Will you take the time to summarize his argument in your own words? That might help me to resolve my own ambiguity about the obvious material/physical nature of nature, and the less obvious meta-physical essence of philosophical argumentation about Reality. Thanks. :smile:
Excerpts from the Schopenhauer quote :
# "Thus materialism is the attempt to explain what is immediately given us by what is given us indirectly."
# "materialism seeks to explain what is immediately given, the idea"
# "To the assertion that thought is a modification of matter we may always, with equal right, oppose the contrary assertion that all matter is merely the modification of the knowing subject, as its idea." -
"Potential" as a cosmological origin
I suppose that "nothing" is a mathematical concept encapsulated in the word : "Zero". But "nothingness" is a philosophical Qualia, a human experience of Lack, Void, Nihility. But, when says "nothing-ness" is a nonsense term only used in naive metaphysics", he seems to be speaking from the perspective of an empirical scientist. In which case, the assertion may be true. Yet, the concept of non-existence has been debated by feckless philosophers for millennia*1. Why is that? Why does the concept of negation even arise in a universe of substantiation?*2Is there a distinction in quantum theory between "nothing" and "nothing-ness?" — Count Timothy von Icarus
In a world of material things, the concept of Nothing appears to be a Paradox*3. And apparent paradoxes have been the fodder of philosophy since Socrates and Plato. So yes, Nothing might be a legitimate mathematical, hence scientific, concept. But the metaphysical idea of Nothingness was characterized by Martin Heidegger as the most fundamental issue of philosophy : "Why is there something rather than nothing?". And that question requires (necessitates) the complementary concept of Potential in order to formulate an answer. :smile:
*1. The concept of nothingness, or "nonbeing," has been a central topic of philosophical debate since ancient times.
___Google AI overview
*2. In Les Misérables, Victor Hugo contrasts universal negation with universal affirmation:
All roads are blocked to a philosophy which reduces everything to the word ‘no.’ To ‘no’ there is only one answer and that is ‘yes.’ Nihilism has no substance. There is no such thing as nothingness, and zero does not exist. Everything is something. Nothing is nothing. Man lives more by affirmation than by bread. (1862, 439).
https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/nothingness/
*3. Zero: The Biography of a Dangerous Idea
The book offers a comprehensive look at number 0 and its controverting role as one of the great paradoxes of human thought and history since its invention by the ancient Babylonians or the Indian people. Even though zero is a fundamental idea for the modern science, initially the notion of a complete absence got a largely negative, sometimes hostile, treatment by the Western world and Greco-Roman philosophy.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zero:_The_Biography_of_a_Dangerous_Idea
BEING AND NOTHINGNESS

-
"Potential" as a cosmological origin
By "not specific", I assume you are not making any religious claims of an ideal omnipotent Creator as the First Cause of the Real World. Just leaving the door open for discussion of Possibilities regarding the Potential-to-become behind the Big Bang burst of Actuality.Potential - not being anything specific but rather the ability to become a specific thing, need not be subject to the idea of presence or absence.. — Benj96
says, referring to the metaphysical notion of Creative Potential : This assumes that "beyond the Actual" – possibilism¹ – makes sense whereas beyond the merely "logically possible" – actualism² – is a much more reasonable and parsimonious metaphysical approach. He provides links to a discussion of the long-running Possible/Actual debate*1. If I was a professional physicist, I would have to agree that "actualism is more parsimonious". A pragmatic scientist seeks to "broaden his understanding of what actually exists", what is "present" in the real world. To do that, she limits her search to the material world. Materialism makes "sense", but does Potential make "meaning"?
Nevertheless, theoretical philosophers, especially amateurs on a philosophy forum, tend to seek "beyond what actually exists" in search of the ultimate ontological source of all that could possibly exist. And to do that, they extend the metaphysical chain of Causal Logic beyond the known Effects (Cosmos caused by?) into the unknown beyond Actuality. Unfortunately, the answer to ontological questions (the cause of being) is "absent" from the world of actual things. Which is why the debate has see-sawed back-and-forth for millennia. I suppose that some early scientists hoped that their Empirical methods might put an end to this foolishness about Potential vs Actual*1.
But in early 20th century those empirical methods raised even more questions about Reality and Actuality, when their experiments yielded only uncertain statistical results. For example, the Schrödinger equation includes the concept of Quantum Potential : "Q"*2. It's a combination of mathematical (statistical) Information and causal Energy. Ironically, one of the implications of statistical Possibility and philosophical Potential on the sub-atomic level is "non-locality", which could also translate into "non-actuality"*3.
Actualism is a good practical assumption for Physics (Science). But it would hobble the imagination of theoretical Meta-Physics (philosophy). For example, physicists --- frustrated by the whence & why implications of Big Bang theory --- have put on their philosopher hats, and speculated beyond the Actual evidence into the realm of Possibility. The Multiverse theory of some scientists is a metaphysical conjecture that "goes beyond what actually exists". 180's reference to Plantinga's Haecceitism (essence of a thing) is way too technical for my amateur abilities. But it sounds like a Latin word for the Greek concept of ideal Essence vs real Substance. So I'll let professional philosophers debate the never-ending Ontological question. For the purposes of this forum, you could just say we have differing opinions of the usefulness of the notions of Possibility & Potential. :smile:
*1. The Possibilism-Actualism Debate :
Possibilists claim that we can: we must simply broaden our understanding of reality, of what there is in the broadest sense, beyond the actual, beyond what actually exists, so that it also includes the merely possible. In particular, says the possibilist, there are merely possible people, things that are not, in fact, people but which could have been. So, for the possibilist, (4) is true after all so long as we acknowledge that reality also includes possibilia, things that are not in fact actual but which could have been; things that do not in fact exist alongside us in the concrete world but which could have. Actualism is (at the least) the denial of possibilism; to be an actualist is to deny that there are any possibilia. Put another way, for the actualist, there is no realm of reality, or being, beyond actual existence; to be is to exist, and to exist is to be actual. In this article, we will investigate the origins and nature of the debate between possibilists and actualists.
https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/possibilism-actualism/
Note --- Are theories, such as String Theory, Actual or Possible? Is a Multiverse logically possible? If possibilia are denied as valid for philosophical reasoning, why theorize at all?
*2. Quantum potential :
Initially presented under the name quantum-mechanical potential, subsequently quantum potential, it was later elaborated upon by Bohm and Basil Hiley in its interpretation as an information potential which acts on a quantum particle. . . . how the concept of a quantum potential leads to the notion of an "unbroken wholeness of the entire universe", proposing that the fundamental new quality introduced by quantum physics is nonlocality.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_potential
*3. Possibility vs Actuality :
The philosophy of possibility is concerned with the nature and existence of possible things, and how to determine if claims about possibility are true or false. It's a fundamental modality in logic and metaphysics, and is closely related to the concepts of necessity, contingency, and actuality. ___Goggle AI overview -
"Potential" as a cosmological origin
"Something from Nothing?" is a valid, ever-recurring philosophical/metaphysical question. But some posters will say that such a question is un-scientific or illogical, hence absurd. Ignore them.In conclusion, this is the argument as to why Potential stands as a better reasoning for existence than something coming from nothing. — Benj96
This is a philosophy forum, not a physics forum. If there was nothing, there would be no physics or physicists. But since there is something, some of those real "things" are thinkers who go beyond the obvious to inquire into the imperceptible. To go beyond the Actual (physical) to inquire into what's logically Possible (meta-physical).
To assume that Nothing can come from Nothing is a valid philosophical hypothesis. And in the real world we find no exceptions to that Law of Thermodynamics. Except when astrophysicists found evidence that our universe originated at Time Zero, and some curious minds logically wondered, "how is that possible?" One answer is that Cosmic Potential --- prior to space-time --- would include all possibilities. But only Cosmic Intention could narrow the list down to a single possibility, and then actualize it into a real instance.
Various philosophers and physicists have written books on that mystery. And the physical answer is usually some form of "our finite universe is just one instance of an (unknowable) infinity of universes". In other words, our some-thing came from some prior-thing. But that is an a priori*1 meta-physical guess presented as-if it's a physical fact. It's no more valid as a scientific answer, than your unstated implication of an unknowable a priori something that possessed the causal power (potential) to produce a Cosmos.
Even physicists must make use of the concept of Potential to explain such phenomena as Gravity & Electricity. For example, you can hold a AA battery in your hand without getting shocked, because the electric current is only Potential, not Actual. At sea level gravitational force on a body is moderate, but at the top of a mountain gravitational potential is higher. So the notion of Potential is not just some religious fantasy, it's a "theoretical deduction".
In scientific Big Bang & Multiverse & Many Worlds theories, the a priori Potential is assumed to be something akin to our physical Energy and Natural Laws*2. In religious myths of Origins, the a priori something is assumed to be similar to a human artist. We have experience of something new emerging due to the efforts of a creative mind. As when Da Vinci began with a blank canvas and bequeathed upon subsequent generations the Mona Lisa. Did that work of art come from nothing, or from the Potential we call Artistic Imagination?
Some posters think your notion of Something from Nothing is "logically impossible". Which is why the existence of our world is logically impossible, unless there was some a priori Potential. In any case, the minimum creative power would require both Causal (energy) and Logical (mind, law) operations. Hence, you could legitimately call it the Potential for Cosmo-Logical Origin. :smile:
*1. A Priori : relating to or denoting reasoning or knowledge which proceeds from theoretical deduction rather than from observation or experience. ___Oxford dictionary
*2. In physics, the concept "nothing can come from nothing" generally aligns with the idea that based on our current understanding of the laws of physics, something cannot spontaneously arise from a complete absence of matter, energy, or even space - essentially, a true "nothing" cannot create something; this is often linked to the principle of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
___ Google AI overview -
What is meant by the universe being non locally real?
I was kidding. But since you challenged the emptiness of matter, here's a couple of links. Does the notion that the "empty space" between and within atoms is full of "vacuum fluctuations of virtual particles" make you feel better about walking on solid ground? :joke:The 99% empty space isn't true, and that's also a misunderstanding of what is at work. The spooky stuff of QM isn't something to worry about since it doesn't happen at our level. — Darkneos
In quantum mechanics, "empty space" is not truly empty, but instead is filled with fluctuations of virtual particles that constantly appear and disappear, known as "quantum vacuum fluctuations";
___Google AI overview
Yes, indeed nearly everything is empty space including space between the electrons of an atom to its nucleus. 99.9999999% of Your Body Is Empty Space.
https://www.quora.com/If-atoms-are-99-99-empty-space-does-that-mean-we-re-99-99-empty-space-Is-everything-99-99-empty-space
Atoms are not the ultimate particle: they are nearly all empty space.
https://academic.oup.com/book/985/chapter-abstract/137840897?redirectedFrom=fulltext -
What is meant by the universe being non locally real?
True. Quantum Uncertainty is not a practical problem, it's a philosophical problem. For all practical purposes, the physical world still works the same way under 20th century Randomness, as it did under 17th century Determinism. Now that you know the ground under your feet is 99% empty space, are you afraid to take the next step over the quantum abyss? A stoic philosophical response to quantum scale indeterminism might be : "don't sweat the small stuff". :smile:Well it’s not much of a problem per se because this only applies to very small stuff, not our day to day. — Darkneos -
The Mind-Created World
Idealism or Deism would make no material difference in your life. But it might make a philosophical difference. What difference does your participation in a philosophical forum make in how you live your life? Personally, I have no ambition to change the world, just myself . . . . to change my mind, and the meaning of my life. :smile:What if Mind, not Matter, is the explanation for everything in the world? :smile: — Gnomon
Leaving aside the possibility that such a mind is an omniscient, omnipotent God who will judge us and accordingly determine the nature of our life after this one, what difference do you think it would make to how we live our lives? — Janus
Karl Marx
Philosophers have only interpreted the world, in various ways; the point, however, is to change it",
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theses_on_Feuerbach
Difference is understood to be constitutive of both meaning and identity.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Difference_(philosophy) -
What is meant by the universe being non locally real?
As I understood it, the question was "how can anything non-local (no measurable position) be real?" I guess it comes down to how you define "real". Some quantum physicists seemed to evade that real-vs-ideal question, by means of the "shut-up and calculate" approach. For example, Quantum Fields are defined as real because they have the potential for producing energy, even though the infinite "points" that make up the field are mathematical instead of material. Is Potential real, or ideal? :smile:As I understand it, the question of non-realism vs. non-locality is completely different and completely separate from the question of position vs. momentum, i.e. the uncertainty principle. — T Clark
Do Quantum fields describe reality or are reality?
https://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/769217/do-quantum-fields-describe-reality-or-are-reality
Nevertheless, quantum fields must be considered real, as they carry energy and have both calculable and measurable effects on the light and matter within the Universe.
https://bigthink.com/starts-with-a-bang/quantum-fields-energy/ -
What is meant by the universe being non locally real?
It seems to be a positive way to express the uncertainty of quantum physics. A particle can be either located in space (position), or measured for movement (momentum), but not both at the same time. Real things can be measured both ways, so what's wrong with quantum particles? Are they not things? Are they not real?I get conflicting accounts on how it says that reality can be real or local but not both. — Darkneos
The problem may be less problematic if you think of Quantum particles as Ideal instead of Real*1, in the sense of a mathematical Field with infinite possible local points, but none actual until frozen in place by the stone-turning eye of Medusa, i.e. an observation by a humorless scientist. :joke:
*1. Is the Mathematical World Real?
Philosophers cannot agree on whether mathematical objects exist or are pure fictions.
https://www.scientificamerican.com › article › is-the-mat...
DON'T LOOK INTO THE EYES OF A QUANTUM PHYSICIST

-
The Mind-Created World
In 's post above, he quotes from a talk on Buddhism :I wouldn't use that terminology, but I don't disagree with what I take to be the thrust of what you are saying. — Janus
What terminology would you use in place of "immaterial" or "non-physical" on a philosophy forum? Spiritual or Mental or Ideal or???? — Gnomon
"So in our understanding of the Universe we should recognize the existence of something other than matter. We can call that something spirit, but if we do we should remember that in Buddhism, the word "spirit" is a figurative expression for value or meaning. We do not say that spirit exists in reality; we use the concept only figuratively". — Three Philosophies, One Reality
Traditionally, in most world cultures, their philosophies & religions used terms like "spirit" to distinguish the material world from our mental models of it. Some of those models involve Ghosts as reified dead people, but for moderns the "spirit" is obviously a production of the observing mind (apparition or hallucination), not an actual person. That's why I try to avoid a term that is offensive to some on this forum, who have a low opinion of religion in particular, or philosophy in general. For example, I use "Self" in place of "Soul". But what substance is a Self made of?
The notion of walking spirits is based on the ancient philosophical concept of the Mind or Consciousness or Soul of a person, as something meta-physical (non-physical or mental) that can be known only by inference or imagination or sixth sense, not by physical senses. Therefore, the "something other" we call Spirit is our mental evaluation of material reality, in which Mind matters and Intellect makes sense. Reality as conceived by a Mind, not as perceived by the visual organ. :smile:
Note --- Even those who believe that there is life beyond the grave, are aware that this second life is immaterial or semi-material. That's why ghosts are portrayed as wispy or translucent. And they have even invented a semi-material substance, ectoplasm, to serve as a semi-scientific term for something that is real but not material. Would "Ideal" be a more philosophical term for that neither-fish-nor-fowl meaning? Do you have a better idea of term for a conceptual object?

-
The Mind-Created World
I was not familiar with those terms. But based on the definitions below*1, I assume that and I would generally agree with such inclusive concepts. However, there might still be some variation in how the role of Mind is conceived*2. Specifically, A> the notion that a human mind creates its own mental world (a worldview), or B> the more extreme possibility that our temporary cosmos (The World) was actually created from scratch by a pre-cosmic Mind. The latter idea could be food for further argumentation. Although, as you said, "we can't know what is the case"*3, as philosophers, not scientists, our job is to speculate & conjecture & rationalize about what might be the case. What if Mind, not Matter, is the explanation for everything in the world? :smile:He doesn't say that "physicalism is inconsistent" as a scientific approach. But that it is incomplete as a philosophical approach. — Gnomon
Non-reductive and/ or non-eliminative physicalism are not incomplete, any more than any metaphysical hypothesis is incomplete. The Churchlands argue consistently and extensively for eliminative physicalism, and they are professional philosophers, so it cannot be ruled out as a philosophical approach either. The reality is that we don't and can't know what the case is when it comes to metaphysics, — Janus
*1. Non-eliminative physicalism is a metaphysical view that all things are physical, but some aspects of the mental are not reducible to physical states. . . .
Non-eliminative physicalism is a way to preserve physicalism while still acknowledging that mental phenomena can't be reduced to physical phenomena by scientific laws. ___ Google AI overview
Note --- That all material objects (things) are physical is not controversial. But some eliminative-materialists (is that an actual position?) might disagree with the "not-reducible" part. I suppose, because non-reducible Mind could knock all-powerful Matter off the metaphysical throne as the creator of our world.
*2. Metaphysical materialism is a philosophical view that all mental, emotional, conscious, and philosophical states are a result of the physical or material world. This means that everything can be explained by looking at matter, or "the real world". ___ Google AI overview
*3. In philosophy, "the case" refers to a specific, detailed scenario or situation presented as a thought experiment to explore a particular philosophical concept or problem, often designed to elicit a judgment or reaction from the reader about the situation, thereby illuminating the underlying philosophical issue at hand; essentially, it's a hypothetical example used to analyze a philosophical idea. ___ Google AI overview
Note --- "The Case" is a hypothesis, not a verified fact. We can Believe, but not Know for sure, what is the absolute case. But when has that ever stopped philosophers from deducing from the available evidence what seems to be the all-inclusive Case/Truth? -
The Mind-Created World
I think you may mis-interpret 's arguments. He doesn't say that "physicalism is inconsistent" as a scientific approach. But that it is incomplete as a philosophical approach. For example in his quotation from "— Three Philosophies, One Reality", the point seems to be that the "something else", traditionally called "Spirit", is our mental evaluation of material reality : an Idea or mental model or mode of thought, or Reality as conceived by a Mind. This is the same observation that the Quantum Physics pioneers found strange-but-undeniable in their attempts to study the foundations of material reality*1*2*3. The "something else" or "missing element" in pre-quantum physics was the observing Mind : the "mental evaluation". :nerd:What I'm arguing against is the idea that the truth of idealism is obvious and that physicalism is inconsistent or incoherent. — Janus
*1. "What we observe is not nature itself, but nature exposed to our method of questioning".
___ Werner Heisenberg
*2. “Consciousness cannot be accounted for in physical terms. For consciousness is absolutely fundamental. It cannot be accounted for in terms of anything else.” ___ Erwin Schrödinger
*3. Dear Schrödinger, You are the only contemporary physicist, besides Laue, who sees that one cannot get around the assumption of reality—if only one is honest. Most of them simply do not see what sort of risky game they are playing with reality—reality as something independent of what is experimentally established. ___ A. Einstein
What terminology would you use in place of "immaterial" or "non-physical" on a philosophy forum? Spiritual or Mental or Ideal or???? I've been looking for a less-prejudicial term for years.Therefore, "if it cannot be directly observed and measured" I would say that the "activity" is immaterial, not non-physical. Hence, "neural activity" is a process-of-change in a material substrate, not a material object itself. — Gnomon
I wouldn't use that terminology, but I don't disagree with what I take to be the thrust of what you are saying. — Janus
How would you phrase the "thrust" of what I'm saying, regarding The Mind-Created World? :smile: -
Ontological status of ideas
I Googled "exist vs subsist" and got this link*1 to a philosophical definition. According to that authority, both "exist" and "subsist" are "modes", or mental models. But "exist" applies to our model of presumably real material objects, while ""subsist" applies to universal concepts, which are not real but ideal. For example, the Chair you are sitting in exists, but the notion of chairness, which is a mental definition of a kind of object, is merely a conventional model or "common understanding". The computer screen picture of a chair {image below}, subsists in an abstract artificial sense, but another realer mode of it may unfortunately exist in your child's room.The first statement refers to something which exists in some sense or other, even if we don't use the word "exist." I've seen the word "subsist" to refer to the referent of the first statement. So, chairs exists and numbers subsist? Is that a common understanding? — Art48
I suppose that Numbers persist only in conceiving Minds as modes or symbols or "persistent illusions"*2, but their rational relationships exist in the real world as the information patterns that cause your mind to conceive of counting real or imaginary objects. Absent a meaning-searching Mind, there would be no evaluated Numbers, but the geometric ratios would exist in the empty space between sensable objects. Think of Gravity as the geometry of reality. The natural/physical relationship is real, but the mental concept of gravity is ideal. As John Mayer sang : "gravity is working against me, gravity wants to bring me down". If gravity didn't exist, we'd have to blame our falling on some other imaginary agent. :smile:
*1. What's the difference between exist and subsist?
Existence, we find it said, is the mode of being proper to "particulars" or "substances," whereas subsistence is the mode of being proper to "universals," i.e. (on the usual view), "qualities" and "relations," as such, or considered apart from the particulars which they qualify or relate.
https://www.pdcnet.org/wcp6/content/wcp6_1927_0261_0271?file_type=pdf
*2. "People like us who believe in physics know that the distinction between past, present, and future is only a stubbornly persistent illusion." ___ A. Einstein

-
The Mind-Created World
For the purposes of my philosophical thesis, I make a distinction between "physical" (the study of nature as a system) and "material" (the study of matter as an object). So, measurements of "neural activity"*1 are observing the material effects of energy exchanges, not invisible Energy*2 per se. Therefore, "if it cannot be directly observed and measured" I would say that the "activity" is immaterial, not non-physical. Hence, "neural activity" is a process-of-change in a material substrate, not a material object itself.↪Patterner
What you say is not true. We can measure neural activity. Of course, you will say that isn't consciousness, but that is just an assumption—assuming what is to be proved.
Or think of energy itself—it can only be measured in terms of its effects. If it cannot be directly observed and measured, will you say it is non-physical? — Janus
That distinction is based on current scientific evidence that Energy is causal*3, not material ; the agent of change, not the substance being changed*4. When a sculptor (the causal agent) molds clay into a statue, his inputs are both intentional and energetic, and the output is a new material shape. :smile:
*1. Neural activity is the electrical and chemical signals that occur in neurons, the brain's primary cells, and is vital for brain function. ___Google AI overview
Note --- Signals (semiology) are communications between minds, not the material substrate that is used to make the signals sensable. For example, Indian smoke signals are the meaning, not the smoke.
*2. Yes, energy is invisible; you cannot see it directly because it is not a physical object, but rather a concept describing the ability to do work, and its presence is only observed through its effects like movement, heat, or light. ___Google AI overview
*3. Yes, in the context of physics, energy is considered causal, meaning that the transfer of energy between objects is generally seen as the mechanism behind a cause-and-effect relationship; where the "cause" is the application of energy, and the "effect" is the resulting change in the system due to that energy transfer. ___Google AI overview
*4. Energy is potential for form-change in Matter. The Matter/Energy Equivalence of E=MC^2 is a mathematical relationship, knowable by logical inference, not an object knowable by physical senses. Reference : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mass%E2%80%93energy_equivalence
AGENT AND EFFECT

-
The Mind-Created World
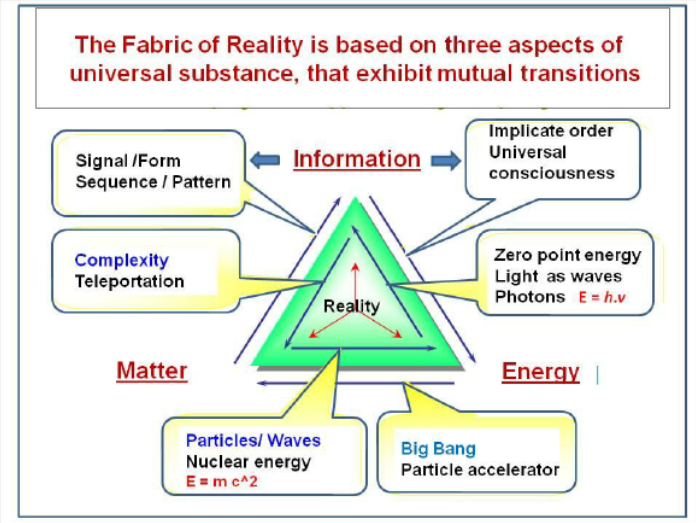
I too, prefer the label "Physicalism" (cause) to "Materialism" (effect) as the ultimate Reality. Matter is merely the clay that Energy shapes into the things that we perceive with the eye and conceive with the mind. Descartes imagined the material aspects of reality as one realm, and the mental aspects as a separate realm. But I view the world holistically, as one reality with several different departments. {see Triad illustration below}Physicalism is the claim that the fundamental nature of everything is energy. Physics understands matter and energy to be one and the same. What is the other alternative to the realm of the physical? I would say it is the realm of the mind. — Janus
FWIW, my personal worldview equates Energy (causation) with Mind (knowledge of forms), in order to explain how mental functions*1 could emerge from eons of material evolution. So, I agree that Energy (EnFormAction)*2 is the fundamental "nature" of everything. But, for human philosophers, Meaning is more important than Matter. My thesis and blog go into scientific details to support the conclusion that everything is EnFormAction. :smile:
*1. Mental Functions :
The most important cognitive functions are attention, orientation, memory, gnosis, executive functions, praxis, language, social cognition and visuospatial skills.
https://neuronup.us/areas-of-intervention/cognitive-functions/
Note --- "Gnosis" is the Greek word for the ability to know, to conceptualize what we sense. We know by informing the physical brain into a cognitive mind.
*2. Energy :
Scientists define “energy” as the ability to do work, but don't know what energy is. They assume it's an eternal causative force that existed prior to the Big Bang, along with mathematical laws. Energy is a positive or negative relationship between things, and physical Laws are limitations on the push & pull of those forces.
So, all they know is what Energy does, which is to transform material objects in various ways. Energy itself is amorphous & immaterial. So if you reduce Causation to its essence of information, it seems more akin to mind than matter & energy. Energy is Causation, and Form is Meaning. Together I call them : EnFormAction : the power to give meaningful/knowable form to malleable matter.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page8.html
*3. The fundamental triad of energy/matter/information :
This essay is based on the thesis that information is as fundamental as matter and energy in the fabric of reality,
https://www.researchgate.net/
Note --- The image below is just some scientist's illustration of how he conceives the interrelationships of Energy & Matter & Mind. Don't take it too literally. ResearchGate is a social network site for scientists and researchers. I may not agree with all of their publications. I have my own illustrations on my website.
-
The Mind-Created World
Speaking of BS. Your interpretation of my post was based on a Category Error. I was talking about Philosophy, not Science ; Meta-physics, not Physics.In philosophy, to equate mental with physical is a category error. — Gnomon
Brandolini's law : bullshit — wonderer1
The Category Error I referred to is not Descartes' notion of two different "substances"*1, but the relationship of a physical system and it's metaphysical function. A mathematical "function" is the output X that is dependent on the numerical values in the equation. None of those math values is physical, nor is the function. The function of your automobile is transportation, which is a concept, not a physical object. The function of your computer is Information Processing, not just displaying letters on a screen.
The function of a brain is control of "thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body". All of those are immaterial Functions, not material Organs. And a Process is a logical step by step procedure, not a substantial object. Yet, each function is typically associated with an organ : as Brain is associated with Thought, Emotion, Memory, etc. None of which is a substantial, tangible, massive material object. What is the mass of an Idea? To Associate : "connect (someone or something) with something else in one's mind."
In Aristotelian terms, the categories I refer to are "Substance" and "Essence or Form"*2. In this case, the Substance is matter (neural tissue of brain), and the Essence is the meaning or referent (rose), but the Form is the symbolic Idea (roseness), a Qualia that colors both Essence and Substance. The material Substance is tangible, but immaterial/intellectual Form & Essence are only inferrable & intelligible by reasoning minds. Are you familiar with those subtle philosophical distinctions? :smile:
*1. Cartesian Mind/Body distinction :
This means the “clear and distinct” ideas of mind and body, as mutually exclusive natures, must be false in order for mind-body causal interaction to occur. Hence, Descartes has not adequately established that mind and body are two really distinct substances.
https://iep.utm.edu/descartes-mind-body-distinction-dualism/
*2. Theory of Forms :
Essence is what makes a thing that particular thing. In other words, essence is what makes “that chair.”
Substance is what makes a thing a general thing.
Form is what makes the idea of a thing, without which the thing would not be intelligible. In other words, form is what makes “that idea of a/that chair.
https://o-g-rose-writing.medium.com/essence-substance-and-form-81c2b707c0d8 -
The Mind-Created World
Meaning in a brain emerges from systematic Holistic interactions, not linear Reductive operations. A more Holistic term for "arise" would be "emerge"*1. Your description sounds mechanical, but it doesn't answer Chalmers' Hard Question : how does a mechanical process convert physical inputs into mental outputs? In philosophy, to equate mental with physical is a category error. :smile:Arises from interactions within the brain which contains the neural networks trained to process written language, in response to the outputs of those neural networks signaling recognition of linguistic elements in the writing. — wonderer1
*1. Emergent properties are qualities of a system that are not present in its parts, and are a result of holism. Holism is the idea that the properties of a system are greater than the sum of its parts, and that the system as a whole determines how its parts behave.
___ Google AI overview
Note --- Ideas, feelings, concepts are not properties of Matter, but of Mind. By what means do they arise? What are the mechanical steps between Matter and Mind? Mind is a meta-physical function of Brain, not a physical organ or neuron. -
The Mind-Created World
I agree. What may be missing from the picture you see is the Interpretation or Understanding of its meaning. Your dog may see the same symbols on the computer screen, but they won't have the same "affect"*1 that they do on you. The effect is physical, but the affect is metaphysical (mental). Your dog may be emotionally affected by images of other dogs on the screen, but words in the English language will have no affect, because they are abstractions of intellectual ideas, not concrete objects.What ↪Wayfarer said is true, but what you interpreted is not what he meant. The "shapes" on a computer screen are indeed physical, but it's their meta-physical meaning (forms) that might affect you : — Gnomon
I am affected physically by what is said (sound) or what I read (light) and this causes changes in the body and the brain, and those changes are my interpretation of the meaning of what I have heard or seen.
You might not agree with this picture of what is happening, but nothing is missing, except of course complete understanding, which shouldn't be a surprise since we don't completely understand anything. — Janus
Your use of the word "affect" may reveal the "missing" element that distinguishes mental ideas or feelings from physical effects. For example, the letters on your computer screen have a physical effect (Percepts ; changes in Rhodopsin chemical) on the rods & cones in your eyes. But only the meaning of those abstract symbols --- how it relates to you personally --- can affect your mood or feelings or Concepts*2. The science of Semiology is focused on the meanings of signs --- how they are interpreted --- not just their physical shapes. The word "rose" refers to a flower ; but unless that textual symbol elicits a mental image in the mind, its meaning will be missing. :smile:
*1. Affect :
a. to put on a false appearance of (something) : to pretend to feel, have, or do (something) : feign affect indifference affect surprise.
b. Affect can be used as a noun in one particular situation: when referring to a display of emotion.
*2. Physics refers to the things we perceive with the eye of the body. Meta-physics refers to the things we conceive with the eye of the mind.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page14.html
A ROSE BY ANY OTHER NAME

-
The Mind-Created WorldI find it enjoyably ironic that it might be the case that we lack cognitive ability to determine why we have cognitive abilities. — Tom Storm
Indeed! :grin: One of my favorite sci-fi books is Neverness, by David Zindell. In it is a quote attributed to Lyall Watson (I don't know where it is in Watson's writings. Anyway:
If the brain were so simple we could understand it, we would be so simple we couldn't. — Lyall Watson — Patterner

-
The Mind-Created World
Some people --- writers, artists, designers --- will get more riled-up if someone steals their Intellectual Property*1 than some tangible physical property. Again, it's the meaning that matters to them. But lawyers have to be very creative to convince a jury, using materialistic language, that something of value has indeed been stolen. How do you think the (hypothetical ; intangible) creator of a Mind Created World would feel about h/er creatures denying the value of h/er most important creation : the human intellect? :joke:it has nothing to do with anything physical. It is only about the meaning. — Patterner
*1. Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. It's a reflection of someone's creativity and can be found in many things, including: computer games, films, cars, and miracle drugs. ___Google AI overview
Intellectual property rights are the rights given to persons over the creations of their minds.
https://www.wto.org/english/tratop_e/trips_e/intel1_e.htm -
The Mind-Created World
What said is true, but what you interpreted is not what he meant. The "shapes" on a computer screen are indeed physical, but it's their meta-physical*1 meaning (forms) that might affect you : first intellectually, and then emotionally, after the threat to your belief system registers in the brain, and causes a series of physical responses to combat the metaphysical threat. Wayfarer is not going to attack you physically, by sending bullets over the internet. Instead, he could affect you metaphysically, by causing you to believe that you have been psychically injured (offended).I could say something to you right now which would raise your blood pressue and affect your adrenal glands. And in so doing, nothing physical would have passed between us. — Wayfarer
That's just not true. If you are talking about what you write on the computer, then I would be looking at shapes (letters, words and sentences) on a screen which means the light from the screen enters my eyes and stimulates rods and cones, causing nerve impulses which travel to the brain and cause neuronal activity which in turn may or may not raise my blood pressure and affect my adrenal glands. — Janus
Of course, Wayfarer is much too genteel to resort to such underhanded tactics. Ironically, non-physical verbal attacks on odious beliefs are often used by the Physicalist trolls on this forum to counter-attack those who have offended their mentally-constructed non-ideal worldview. :smile:
*1. By "meta-physical" I don't mean the study of reality, but merely "non-physical" in the sense of "mental" Ideality*2. Ideas instead of Objects. Forms instead of Shapes.
*2. Ideality :
In Plato’s theory of Forms*3, he argues that non-physical forms (or ideas) represent the most accurate or perfect reality. Those Forms are not physical things, but merely definitions or recipes of possible things. What we call Reality consists of a few actualized potentials drawn from a realm of infinite possibilities.
# Materialists deny the existence of such immaterial ideals, but recent developments in Quantum theory have forced them to accept the concept of “virtual” particles in a mathematical “field”, that are not real, but only potential, until their unreal state is collapsed into reality by a measurement or observation. To measure is to extract meaning into a mind. [Measure, from L. Mensura, to know; from mens-, mind]
# Some modern idealists find that scenario to be intriguingly similar to Plato’s notion that ideal Forms can be realized, i.e. meaning extracted, by knowing minds. For the purposes of this blog, “Ideality” refers to an infinite pool of potential (equivalent to a quantum field), of which physical Reality is a small part.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page11.html
Note --- Quantum Fields are accepted by scientists as accurate depictions of reality (reified), even though they are immaterial mathematical constructs, and cannot be detected by human senses or instruments, but only known by philosophical inference. They seem to be a scientific version of Plato's Forms, or what I call Ideality.
*3. Theory of Forms :
a theory widely credited to the Classical Greek philosopher Plato. The theory suggests that the physical world is not as real or true as Forms.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theory_of_forms
Note --- Materialism is a belief system that rejects this theory of an immaterial Potential Source (or Field), from which our sensory perceptions of physical Shapes are constructed into the conception that we call Reality. Plato inferred that the intellectual Meaning (definition) of those Shapes is ultimately more important than their physical instantiation. This idealized notion may apply only to sentient creatures capable of inferring abstract meanings from concrete objects. For philosophers, the Potential Source of Forms is also merely an imaginary Idea, not a sensable thing. It's the meaning that matters, not the substance. -
The Mind-Created World
After I wrote the post above, I read this statement in a National Geographic magazine article about Artificial Intelligence. Under the title : Do we have to accept that machines are fallible?, it says "That's a big issue facing AI right now --- these evolving algorithms can hallucinate, a term for what happens when a learning model produces a statement that sounds plausible but has been made up. This is because generative AI applications . . . work functionally as a prediction program".↪Janus
, I'm not sure I understand what you think is redundant. I don't mean that in a smartass way. I mean I'm not sure what you're saying. — Patterner
Most definitions of AI "hallucinations" describe it as "false" data. But if you think of it as "anticipation", it could be useful information for entities that encounter rapid change, as in modern human cultures. The human brain seems to have adapted to deal with complex social networks, in which the ability to anticipate behaviors, or to read other minds would be beneficial.
I suspect that is critical of a crucial function of General Intelligence : that it goes beyond the facts, the raw data, to infer something that is not-yet-real ; maybe even ideal. An imaginary inference exists only as an immaterial idea. Even though it is embodied in a machine or brain, the idea (prediction ; conjecture) is not meaningful or useful except for another predictive intelligence. For a digital computer, not-yet-real data is erroneous information. For AI and human Intelligence, that data may be useful for anticipating future or possible situations. Yes, human brains are fallible, but they are also surprisingly adaptable to evolving realities. :smile: -
The Mind-Created WorldI think 'qualia' in its subjective sense as opposed to its 'sense data' sense is a kind of reification, and maybe the latter is too.
— Janus
I always thought that was the whole point, if qualia does not refer to something with its own ontology above and beyond the physical process of an experience there's really no use to the word at all. — goremand
This is my point. It is something with its own ontology above and beyond the physical process of an experience. It is our experience of hearing an A major chord, whereas a machine only detects vibrations of 440, 553.365, and 659.255 Hz.
↪Janus
, I'm not sure I understand what you think is redundant. I don't mean that in a smartass way. I mean I'm not sure what you're saying. — Patterner
I guess what they are saying is that ideas are redundant in a material world. Only the senses of vision, hearing, touch & smell are important for Materialists. Even a blind mindless mole can find a worm without imagining it.
What you experience subjectively in the Cartesian Theatre is immaterial, hence not useful (i.e. redundant). What they are implying is that you are mistaking your abstract mental feeling for a concrete material object. But I'm sure that's not how you feel about it. What is a Philosophy Forum for, it not for sharing subjective Ideas & Feelings encapsulated in artificial words? Do they have a mechanism for sharing Sense Data over the internet?
Since they view Qualia as non-existent, or even superfluous, I assume they don't have any use for the redness or the sweetness of a rose, as long as they can see & smell it. Those qualitative words (and their associated ideas) in our common languages are redundant in a physics lab. All they need is the data. So, when you insist that the rose smells sweet, it's as-if you are reifying an idea. But, really all you are doing is experiencing the sensation.
The bottom line here is that you are speaking a different language (Empirical vs Experiential) from the Materialists. But apparently your attempts at translation have fallen on deaf ears. :wink:
"Yes, "qualia" is a philosophical idea that refers to the subjective, qualitative aspects of conscious experience"
"Reifying an idea is the act of treating an abstract concept as if it were a concrete thing".
___Google AI overview -
Cosmology & evolution: theism vs deism vs accidentalism
Since most of the posts on this thread have been dismissive of the philosophical arguments presented in Return of the God Hypothesis, for an eternal, logical, intelligent, and intentional First Cause of the physical universe, I'm adding a Post Script to summarize Stephen Meyer's Epilogue, in which he responds to "scientific objections to its arguments" with scientific counter-arguments.
# Anthropomorphic Fine Tuning
"Lawrence Krauss challenged the idea that the physical parameters of our universe were fine-tuned to make life possible". Instead, he argued that "life on earth is fine-tuned to the universe".
Meyer : "the precise fine tuning of many critical factors needed to arise first before any conceivable form of life could have begun to evolve . . . "
Note --- Hence, a nursery world compatible with Life was a necessary prerequisite for fragile life to emerge from thermodynamic processes that produce only Entropy. In my thesis, I labeled that Vital Force (Negentropy) as positive Enformy*1*2.
*1. A Theory of Enformed Systems :
"Under TES, enformy, the capacity to organize, is essential to morphogenesis"
https://vxm.com/2.CompTheory.html
*2. Enformy vs Entropy :
Entropy is a property of the universe modeled as a thermodynamic system. Energy always flows from Hot (high energy density) to Cold (low density) -- except when it doesn't. On rare occasions, energy lingers in a moderate state that we know as Matter, and sometimes even reveals new qualities and states of material stuff .
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that, in a closed system, Entropy always increases until it reaches equilibrium at a temperature of absolute zero. But some glitch in that system allows stable forms to emerge that can recycle energy in the form of qualities we call Life & Mind. That glitch is what I call Enformy : the tendency to create new forms of matter (morphogenesis).
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page8.html
# Eternally Cycling Multiverse
"Several cosmological models have appeared . . . . to portray the universe as infinitely old". "Roger Penrose's conformal cyclic cosmology*3 and Paul Steinhardt's cyclic cosmology . . . . oscillating universe".
Meyer : "This model was subject to the problem of steadily increasing entropy . . . . with each cycle". "To address this problem, Penroses's model invokes a hypothetical Phantom Field with powers associated with no known physical field (but instead, only with a god-like agency)".
Note --- Physical Eternity must have some way to deal with destructive Entropy. On Earth, Life has adapted to the seeming inevitability of Death, by importing energy from outside the living organism. Hence, Life is an open system --- organized in a manner to capture and make use of the Morphological Potential that is inherent in ambient Energy.
*3. Is conformal cyclic cosmology really debunked?
". . . . CCC is wrong because it violates the conservation of information, something that you need to do physics in the first place, and the 2nd law of thermodynamics, . . ."
https://www.reddit.com/r/cosmology/comments/jfu7mm/is_conformal_cyclic_cosmology_really_debunked/
Note --- Meyer labels his Intelligent Designer theory generically as "Theism", which could apply to any of the thousands of world religions and god-models. Yet, he avoids specifying that his designer is supposed to be the God of Abraham, Issac, and Jacob. Ironically, his scientific arguments are identical to those of Deists, who don't accept the Bible as the Word of God. Instead, they read Nature as the Work of G*D. -
The Mind-Created World
How do you justify a preference for parsimony? Does it allow you to summarily eliminate the entities you don't like?A preference that can't be justified has no place in a discussion. In this case the justification for eliminativism would be parsimony. — goremand
Qualitative Experience can't be dissected by scientists, so simply eliminate it as immaterial. But then, Metaphysics is all about immaterial ideas, so eliminate Philosophy : yes/no? :smile:
Because it can lack firmness and consistency when applied to complex ideas or phenomena, Occam's razor is more commonly seen as a guiding heuristic than as a principle of absolute truth. ___Wikipedia
Perhaps the most parsimonious way to eliminate Qualia is suicide. :joke:But of course. Qualia is the very thing to be eliminated, there will be no Love and no Redness. That is not the problem but the solution. — goremand -
Cosmology & evolution: theism vs deism vs accidentalism
Actually, I had never heard of the term, Accidentalism, until I stumbled across it while researching the opposite of Creation & Causation & Determinism. Apparently, it's an ancient concept to characterize a chaotic worldview. So, it was not made-up by Craig or Meyer or Gnomon to troll those who troll Intelligent Design proponents. Apparently, the Accidentalists (Epicureans ?) preferred "dumb luck" to "design".An aside. One of the problems for me is the emotional ladenness of this kind of wording. 'Accident' is already contrived as unfortunate. 'Chance' and 'haphazard' also sound like they have a criticism built into the very wording. It's a way of wrapping it all up as 'meaningful' versus 'dumb luck'... Essentially a William Lane Craig move. — Tom Storm
Denial of Design in the real world seems to require Accidentalism*1 as an explanation for the natural rational order that Science depends on. For example, how did the Big Bang begin with nothing but extreme heat & pressure, yet then evolve into what Darwin described as "From so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being, evolved".
Many cosmologists, who recognize the "unfortunate" "haphazardness" of Accidentalism, postulate (by inference, not evidence) that the Bang was organized by pre-existing logical Natural Laws, which in the works of men, are signs of design. Since the advent of Quantum Theory, the role of randomness*2 in physics is undeniable, except by Einstein. However, Darwin's theory combined Randomness (variation) with Selection (design) to describe how Nature has evolved into Cosmos instead of Chaos*3. :smile:
*1. Accidentalism
Theory that the flow of events is unpredictable, or for Epicureans, that mental events are specifically unpredictable. See also chaos, determinism, libertarianism, tychism.
https://philosophy.en-academic.com/20/accidentalism
*2. Tychism (Greek: τύχη, lit. 'chance') is a thesis proposed by the American philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce that holds that absolute chance, or indeterminism, is a real factor operative in the universe. This doctrine forms a central part of Peirce's comprehensive evolutionary cosmology. It may be considered both the direct opposite of Albert Einstein's oft quoted dictum that: "God does not play dice with the universe" and an early philosophical anticipation of Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty principle.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tychism
*3. Cosmos vs Chaos
In Plato's Timaeus, he describes the universe as a rational, ordered cosmos created by a divine Craftsman, or Demiurge, from a pre-existing chaos. Plato's use of the term "chaos" is not meant to imply a complete lack of order, but rather a type of order that is opposed to reason. Plato's cosmos is dynamic, with a chaotic tendency that can undermine the rational order of the world.
___Google AI overview -
The Mind-Created World
I don't know anything about Eliminativism, beyond the Wikipedia article that discusses both sides of the argument. But my first impression is that both Materialism/Eliminativism, and Mentalism/Positivism --- or whatever the opposite theory is called --- are metaphysical conjectures, not scientific facts. So, lacking slam-dunk physical evidence pro or con, the argument could go on forever, as in this thread. Therefore, the contrasting views seem to be based on a personal preference for one kind of world or another : tangible, physical stuff vs imaginary, metaphysical*1 concepts.No, you tend to overinterpret what I write somewhat. I only know Strawson as a critic of eliminativism, and that's the role he plays in the article. — goremand
The Mental world has been interpreted in terms of Souls & Spirits and Ghosts & Goblins ; but also in terms of Intelligence & Information. On the other hand, the Eliminativist position seems to be lacking any notion of a mechanism by which conceptual Qualia, such as Redness & Love could emerge from perceptual Matter by natural means. Hence, your preference for "clear" Black vs White dichotomies seems doomed to frustration. Unless of course, you simply believe one or the other based on Faith. Is that an "overinterpretation" of your Either/Or position? :smile:
*1. Metaphysical : relating to "the essentially metaphysical question of the nature of the mind"
___ Oxford dictionary
Note --- Is Mind something that can be dissected by scientists with scalpels, or a holistic function of a material brain, that must be inferred by reason? -
The Mind-Created World
If the philosophical approach of the OP is "trivial, uncontroversial", then why has it evoked polarized controversial arguments for over a year? Apparently, the relationship of material Reality to mental Mind touches a nerve for some posters on this forum.There is nothing arrogant about advancing clear arguments. And I ever said his approach was humble, I said his claim was humble. Meaning: trivial, uncontroversial. — goremand
The only thing unclear about the OP is that it is not a simplistic Either/Or argument, but as I see it, a sophisticated Both/And position of complementarity*1. Few philosophers would deny that the Real world includes both Matter and Mind. The debate is about how to reconcile that apparent Cartesian duality within a general worldview. Strawson has one solution, and another. What's yours? :smile:
*1. Complementarity is the realization that a single thing, when considered from different perspectives, can appear to have different, or even contradictory, properties. Complementarity alerts us that answering different kinds of questions can require radically different approaches.
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/the-mind-expanding-power-of-complementarity/
Apparently, you like nice neat Either/Or dichotomies. Did you interpret Strawson's position as an attack on Physicalism? Ironically, he claims to be a proponent of Physicalism*2. But how, then, can he say that "physicalism entails panpsychism"? Maybe his position is complementary*2, which you interpret as "lame". :grin:What a shame. I'd love to read an attack on physicalism, especially of the eliminativist variety. Though I wouldn't expect much from an article that quotes Galen Strawson, the lamest critic I've ever read. — goremand
*2. Is Galen Strawson a physicalist?
As a real physicalist, then, I hold that the mental/experiential is physical, and I am happy to say, along with many other physicalists, that experience is 'really just neurons firing', at least in the case of biological organisms like ourselves.
https://www.sjsu.edu/people/anand.vaidya/courses/c2/s0/Realistic-Monism---Why-Physicalism-Entails-Panpsychism-Galen-Strawson.pdf
Note --- The subtitle of the linked article is : "Realistic Monism : Why Physicalism Entails Panpsychism"
Yes. I think Wayfarer's notion of Mind/World is "compatible" with Realism, in the sense that Mind & Matter are complementary, not oppositions : not one to the exclusion of the other. But it's difficult to articulate that subtle inter-relationship in terms of our matter-oriented language. For example, to say that mind is immaterial, could be interpreted to mean that "mind doesn't matter" : i.e. trivial. :nerd:In other words, it is a claim that is compatible with some forms of realism. — goremand
DEATH EATER : gluttonous gourmand or moderate-idea consumer?

-
The Mind-Created World
Please pardon my intrusion. Yes, is not the type to make arrogant or aggressive attacks on debatable philosophical positions. He's usually more subtly nuanced. And his "humble" approach may seem less impressive than the more arrogant assertions of Scientism.I'm sure that's true, but it isn't obvious to me from the OP or from what I've read in your other posts. The proposition that "reality is created by the mind" at first seems like an attack on physicalism/realism (whichever term you like), but when I look at your explanation in detail the term "reality" instead seems to refer to "our particular conception of reality", which is amounts to a rather humble claim, not really an attack at all. — goremand
For example, his stated position in the OP does not deny the physical "reality" (science) that we all sense, but his interpretation also includes some aspects of Idealism (philosophy). I can't speak for Wayfarer, but this thread has been going on for over a year. Yet, some posters still can't reconcile his "proposition", that harks back to the ancient origins of theoretical philosophy, with the Physicalism/Materialism/Realism of modern pragmatic science. Each has it's own purview, but Philosophy specializes in inferred generalizations, not observed details. For philosophers, the "mind-created world" is a Cosmos, not an aggregation of particles. Just keep that distinction in mind.
FWIW, Marc Wittmann Ph.D. --- research fellow at the Institute for Frontier Areas in Psychology and Mental Health in Freiburg, Germany --- recently wrote an article in Psychology Today magazine entitled Physicalism Is Dead*1. It's less an attack on Physicalism/Realism than a presentation of alternative views of the Mind/Body relationship. It's not about specific scientific facts, but about the philosophical interpretation of general principles. :smile:
*1. Wittman's key points are :
# The reductionist physicalist position entails that phenomenal consciousness does not exist.
# Scientists increasingly realize that phenomenal consciousness can't be explained by the workings of the brain.
# For idealism, subjectivity undeniably has primacy when it comes to knowledge about ourselves and the world.
# For dual-aspect monism, consciousness and the brain are two different aspects of a same underlying reality.
Note --- Phenomenal Consciousness is the Mind that we experience subjectively, not the Brain that scientists study objectively.
"Yes, phenomenal consciousness is the subjective aspect of experiencing the world. It's the rich, first-person experience of what it's like to be you, including your thoughts, memories, and internal biological processes." ___Google AI overview
Physicalism Is Dead :
Alternative views on the mind-body problem are becoming increasingly popular.
https://www.psychologytoday.com/intl/blog/sense-of-time/202411/physicalism-is-dead -
The Mind-Created World
Although I know very little about medieval philosophy, I get the impression that the debate between Realism and Nominalism would be pertinent to the topic of a Mind-Created World vs whatever the alternative might be : a Self-Existent Material World?Schopenhauer, more than Berkeley. Where I part company with Berkeley, is his dismissal of universals - his nominalism, in short. I think it leaves many gaps in his philosophy. But whenever I read his dialogues, I'm reminded of how ingenious a philosopher he was. — Wayfarer
Contrary to the definition below, I naively assumed that Realism could be summarized as "what you see is all there is". Which would exclude Universals & Abstractions & Qualia, and Universal Mind, that are knowable only as ideas. Please comment on those alternative worldviews. Thanks. :smile:
Nominalism
The theory that only physical particulars in space and time are real, and that universals are only names or labels for groups of things or events. Nominalists believe that the mind cannot create concepts or images that correspond to universal terms.
Realism
The theory that universals exist in addition to particulars, and that all entities can be categorized as either particulars or universals. Realist philosophies include Platonic realism and the hylomorphic substance theory of Aristotle.
Nominalism and realism were two major theoretical positions in the later Middle Ages, and were particularly important to theological scholars. For example, Thomas Aquinas was a prominent realist philosopher who argued that essence and existence were distinct. William of Ockham was a prominent nominalist philosopher who argued that universals were psychological labels.
___Google AI overview -
Cosmology & evolution: theism vs deism vs accidentalism
In 's Immanentism worldview, the probability of a Creator outside of space-time is minimal-to-impossible, because he doesn't allow any inference from what-is to what-logically-must-be. Yet, cosmologist Max Tegmark constructed an extreme mathematical/logical hypothesis (modal reality) of an infinite array of simultaneously existing universes, of which ours is merely one of uncountable possibilities. Few physicists take his postulation seriously, but some mathematicians might accept it as reasonable. And some philosophers may view his hypothesis as an interesting Thought Experiment.In other words, the improbability that 'an uncreated, transcendent creator of universes' exists (e.g. Plato, Aquinas) is, at minimum, equal to the improbability that 'an uncreated, autopoietic universe' exists — 180 Proof
So you're saying the probability God exists is extremely low? — RogueAI
For me, the God-postulate is also not a provable fact, or even a belief to be taken on faith, but a logical conjecture about what must have caused the Big Bang beginning of the only universe we know anything about. Hence, the Platonic First Cause and the Aristotelian Prime Mover remain as examples of valid reasoning, even in the absence of material evidence. So, as Bayesian Probability exemplifies, your posterior statistical conclusions are dependent on your prior subjective beliefs. {generic you}
Quantum Gravity physicist Stephen Unwin wrote a book, The Probability of God, to present his "simple {Bayesian} calculation that proves the ultimate truth". Of course it's a mathematical proof, not a physical proof. Like Meyer in the OP, he concludes that the bible-god is highly probable. But he also admits that "the math probability does not transfer to the notion of belief".
is making a statement of personal belief, not a fact of science. So, I'm guessing that his Bayesian calculation assigned a low prior probability to anything outside of the physical world (transcendent), which makes the calculation of a low posterior probability almost a foregone conclusion. And that firm belief makes any postulation of a transcendent creator seem absurd. Which may be why he responds to such threads as this one with the sarcasm, derision, and mockery of a true believer, instead of modest & respectful philosophical dialog.
Ironically, until the Darwinian 19th century, most scientists & physicists*1 found the god concept to be both rational and believable, and in the absence of any better explanation : logically necessary. So, what has changed since then, to make a self-existent universe seem plausible? Perhaps, it's because cosmologists have traced the chain of causation back 14B years, which seems almost an eternity. But Quantum physicists have found that the foundation of material reality is grounded on probability, not certainty. Hence our scientific worldview is muddled, whereas religious --- and some philosophical --- worldviews are based on the certainty of Faith. :smile:
*1. Newton's God
Isaac Newton's view has been considered to be close to deism, and several biographers and scholars labelled him as a deist who is strongly influenced by Christianity. However, he differed from strict adherents of deism in that he invoked God as a special physical cause to keep the planets in orbits.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Religious_views_of_Isaac_Newton
PS__ says that his Immanentism worldview is "an application of Occam's Razor". But that pragmatic rule of thumb may not apply to the theoretical question of Cosmic Causation. Nevertheless, if you want the simplest causal entity, a single Mind seems to require fewer assumptions than a hypothetical infinite chain of Multiverses, or Many Worlds, or pre-bang vacuum fluctuations. All are conjectural, and unprovable. So, as I said, to insist on any of those ontological explanations requires either a leap of faith, or a conditional Bayesian belief. The latter is my preference, because it's the only one that addresses the Hard Question of how Mind emerged in a material world. :grin:
Gnomon

Start FollowingSend a Message
- Other sites we like
- Social media
- Terms of Service
- Sign In
- Created with PlushForums
- © 2026 The Philosophy Forum
