Comments
-
Cosmos Created Mind
Nor am I. But the 17th century Enlightenment revolution (Age of Reason) tried to draw a hard line between rational Science & emotional Religion, between empirical Physics and theoretical Metaphysics. Thereafter, "soft" Philosophy was typically lumped, by hard rational scientists, into the off-limits Religion category. And that Mind/Matter segregation worked for several centuries. Eventually though, 20th century Quantum Physics turned the Either/Or hard line into a Both/And probability wave. Today the Matter/Mind line of distinction is between Hardware and Software, but the mechanical stuff doesn't work without the mental stuff.Not sure why you would say this. I am neither against religion nor philosophy. What I want to point out is to be careful to 'mix' them with science. — boundless
Why I would say that you are afraid of crossing that line in the sand? It's because you repeatedly warn me to be "careful". But I don't accept that arbitrary division of Philosophy into Nature and Supernature. For me, it's all Science and all Philosophy, and Nature includes both Mind and Matter, both flesh and emotions. The human Mind (consciousness, "soul", software) seems to be a product of eons of material evolution. So the study of the intangible, immaterial aspects of Nature should not be taboo for Science or Philosophy*1.
Physics may try to limit its subject matter to Matter only. But Quantum Physics made that policy of apartheid very difficult*2. So, I don't accept that, no longer valid, distinction between Matter Science and Mind Science. Which is why I label my personal philosophy as BothAnd*3. :smile:
*1. Mixing science and philosophy involves using philosophy (like logic, epistemology, metaphysics) to clarify scientific concepts, guide research, interpret findings, and explore implications, while science provides empirical data to inform philosophical questions about knowledge, reality, and ethics, creating a symbiotic relationship where philosophy shapes the 'why' and 'how' of science, and science grounds philosophy in reality. This interplay, historically linked as "natural philosophy," helps refine scientific methods, address biases, and understand humanity's place in the universe.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=mix+science+and+philosophy
*2. Yes, quantum physics explores the link between mind and matter, suggesting consciousness (mind) influences physical reality (matter) through concepts like wave function collapse and the observer effect, where attention changes outcomes, leading to theories like the "quantum mind" that propose consciousness isn't just a brain byproduct but a fundamental aspect of the universe, influencing matter's emergence.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=quantum+physics+includes+mind+and+matter
Note --- The "line" between Mind & Matter is described as a "link" not a divide.
*3. BothAnd vs Either/Or Philosophy :
The BothAnd philosophy requires holistic spectrum thinking instead of reductive & exclusive, black/white, & all-or-nothing reasoning. It assumes that the thinker has no privileged god-like perspective on the world, but instead, a private relative point-of-view. So, its conclusions are not absolute Either/Or, but more like probable Bayesian beliefs. Yet, why would anyone prefer the uncertainty of Probability (maybe-maybe not) to the confidence of two-value (either/or) reasoning? Some philosophers aspire to a complete & perfect Ideal model of the world, but others are content to construct a more realistic interpretation of the data & facts available to human observers.
https://bothandblog9.enformationism.info/page14.html
Note --- Materialism is a hypothetical & idealized model of the natural world, which somehow evolved Minds capable of inferring natural laws and ideal models. -
Cosmos Created Mind
Again, you seem to be afraid of crossing the Enlightenment line between Science and Religion. But Philosophy is similar to Religion only in its focus on the non-physical (mental, spiritual) aspects of the world. Philosophy has no Bible and no Pope. So each thinker can be a rogue priest. My childhood religion was antithetical to Catholicism, in that it downplayed rituals & miracles, and focused on reasonable verifiable beliefs. I still retain some of that skeptical rational attitude, even though I no longer congregate with those of "like precious faith". In fact, Faith is a four-letter word for me.Yes, but I'm still convinced that you're reading too much into the concept. Note however, that this doesn't mean that your metaphysical outlook is 'off' or anything. — boundless
Before I retired, my education was mostly Pragmatic & Realistic. And my only college course related to philosophy was Logic, but that was a math requirement, and not very philosophical. Even though I am now exploring some Idealistic concepts mainly associated with Philosophy, most of my reading sources are professional scientists, not academic philosophers. But if I "go beyond" the bounds of materialistic Physics, my direction is influenced mainly by astro-physicists (cosmologist), such as Paul Davies, and Quantum physicists, such as Albert Einstein, Niels Bohr, Werner Heisenberg, Erwin Schrödinger, and Max Planck. If you are interested enough to invest some time, I can show you how 17th century notions of practical Potential became idealized & philosophized in the 20th century*1. :nerd:Nothing in here and in the reference you quoted go beyond the 'realist' interpretation that is admissible in physics. But despite the appearances it isn't like a 'potential' in the metaphysical sense. — boundless
Of course, the primitive philosophers 1500 years ago, did not have the detailed scientific knowledge of the 21st century. So, their concepts were more general & visionary than our modern technical details. So, as you say, "those ancient concepts are not wrong", but they are more philosophical than physical. Speaking of "physical" can you define Dynamics, Energy, and Potential in material terms --- without using abstract philosophical notions such as "capacity", "ability", "causal" & "essence"? What is Energy made of? Where can I find Potential in the real world? :wink:I dispute the fact that these philosophers had what we label as 'energy' in mind when they talked about 'dynamis', 'energeia' and 'potentiality'. These concepts might have inspired later physicists to develop the concept of 'energy' but they aren't necessarily referring to the same thing.
Also, this doesn't mean that these ancient concepts are wrong. — boundless
Again, you seem "careful" to draw a hard line between Physics and Philosophy. But, especially since the quantum revolution, Physics was forced, by the Uncertainty Principle and the indeterminacy of quantum phenomena, to resort to philosophical reasoning for descriptions & interpretations of the real world's ideal foundation*4. Physics is no longer purely mechanical, nor purely philosophical, but a complex adaptive system of both. :cool:Yes, hence the confusion. Actually, I believe that physicists themselves should be more careful in how to explain the concepts they use. . . . .
I say 'controversial' because it is unclear if such a concept is amenable of scientific research or if it still purely philosophical. — boundless
*1. The word "potential" maintained its core meaning of "possible as opposed to actual" across both the 17th and 20th centuries, but its usage evolved significantly, particularly with its development as a specific scientific term in the later period.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=potential+17th+century+20th+century
Note --- That "later period" was the era when Einstein's Relativity, Shannon's Information, and Quantum Physics revolutionized the science of Physics. Possible does not "go beyond" Actual & Real, it is a priori and Ideal. Potential is not a physical thing, it is a Metaphysical concept.
*2. Energy : In essence, while energy's definition (ability to do work) remains, quantum physics reveals its granular nature, probabilistic behavior, and mathematical description through operators and wave functions, revolutionizing our understanding of the microscopic world.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=what+is+energy+in+quantum+physics
*3. Yes, quantum physics is deeply intertwined with philosophy, especially the philosophy of physics, because its strange findings (like superposition, non-locality) challenge our fundamental understanding of reality, causality, and knowledge, forcing physicists and philosophers to debate interpretations of what the math truly means for the universe, moving beyond simple "shut up and calculate" to explore profound questions about what exists.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=quantum+physics+is+philosophy
*4. Quantum idealism connects quantum physics's strangeness (like wave-particle duality and measurement problems) with philosophical idealism, suggesting reality isn't independent but depends on observation or mind, proposing that physical properties only manifest upon interaction. While early founders like Bohr and Heisenberg hinted at this, modern physics often uses decoherence to explain collapse without consciousness, though some philosophers and physicists still link quantum phenomena to mind-dependent reality or information.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=quantum+physics+idealism -
Cosmos Created Mind
Have you ever looked at the concept of Energy from a philosophical perspective? You ought to try it sometimes. It might broaden your understanding of Philosophy itself. Humans have been puzzled by the mysterious invisible cause of physical change for thousands of years. Primitive notions of Animism*1. imagined that living things were motivated by some spiritual agency, similar to the invisible wind that causes trees to sway & tremble as-if internally energized.You're free to use the word 'energy' in a way that is different from the way it is used in Physics. However, you might encounter a problem when you try to equate the two concepts or say that they are equivalent in some sense. I was just pointing to this.
Ironically, I actually believe that a 'non-realist' view of physical quantities actually is a problem for some forms of 'metaphysical physicalism'. — boundless
The ancients viewed Causation as purposeful. But modern Physics*2 imagined Energy as some intangible eternal property/quality of inert temporal matter that could be quantized (a quart of vacuum) for practical applications. 19th century pragmatic Science conveniently ignored the ultimate Cause of Change, and focused on the proximate instances of Transformation. Do you think we should not equate Energy with such creative processes as Metamorphosis (form change) and Evolution (physical change over eons of time)?
Ancient Greeks began to formulate primitive ideas about Causation & Change that would later influence modern physics. For example, Plato talked about dunamis (dynamics) and energeia (power). Even pragmatic Aristotle*3 characterized what we now call Energy, as un-actualized Potential seeking to become real in a process-of-becoming called Telos (purpose or goal).
Modern Physics uses the same old terms, but avoids any teleological or philosophical implications. Early on, quantum physics imagined Energy as tiny billiard balls, called Photons. But eventually, scientists were forced by the evidence to define the fundamental level of physics, not as tiny particles of matter, but as wishy-washy waves in a universal Field of potential (statistical) mathematical relationships.
Practical Physics is content to say that "sh*t happens", as long as it can quantize each event. But Theoretical Philosophy goes beyond observations of what happens to ask "why?" Are Energy & Causation & Transformation "unreal"*5 for you? :smile:
*1. Animism is a worldview, often found in indigenous cultures, that believes spirits or souls inhabit all things—living and non-living, like animals, plants, rocks, and rivers—giving them a spiritual essence, volition, and power, contrasting with Western ideas of separate mind/matter, and viewing the world as interconnected, where appeasing these powerful spirits through rituals maintains balance and well-being. It's seen less as a specific religion and more as a fundamental way of relating to a world full of conscious, experiencing entities, where human life and natural phenomena are deeply intertwined, influencing health, fortune, and history.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=animism
*2. In physics, energy is the fundamental property of matter and systems that quantifies their capacity to do work or cause change, existing in diverse forms like kinetic (motion), potential (stored), thermal, chemical, or electromagnetic, and crucially, it's a conserved quantity, meaning it can transform but never be created or destroyed, only converted.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=what+is+energy+in+physics
*3. In philosophy, "energy" (from Greek energeia) originally meant activity, actuality, or being "at work," a concept developed by Aristotle to describe something in motion or fulfilling its function (telos), contrasting with potentiality (dynamis). While modern physics defines energy quantitatively (ability to do work), philosophical uses remain broad, encompassing mental/spiritual forces (psyche), vital life forces (pneuma, ka), and the fundamental "stuff" of the universe, linking to ideas of consciousness, being, and transformation beyond just physics.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=what+is+energy+in+physics
*4. Causality in philosophy explores the fundamental relationship where one event (cause) produces another (effect), investigating what makes this link real, how we know it, and its role in explaining the world, moving beyond mere correlation to understand necessary connections, agency, and purpose, a concept debated from Aristotle's Four Causes (Material, Formal, Efficient, Final) to Hume's skepticism about observing actual force, highlighting its importance for logic, science, and understanding reality's progression.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=philosophy+of+causation
*5. Metaphysics isn't "real" in the sense of a tangible object, but it's a fundamental, "real" branch of philosophy exploring the nature of reality (existence, mind, time, causality, etc.), using logical reasoning, not empirical science, to ask questions science can't always answer, though some critics find its abstract speculation unfruitful compared to scientific reality. Its reality lies in its existence as a field of study and its foundational role in shaping how we understand the world, not in providing provable facts.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=is+metaphysics+reality
Note --- Physics explores Nature, while Metaphysics (philosophy) explores Human Nature. -
Cosmos Created Mind
As you say, I'm "reading" Energy" in a "Metaphysical way" instead of a Physical way. If this was a Physics forum, that interpretation --- as a non-physical Qualia --- would be inappropriate. However, Please note that I never said or implied that Energy is not a physical Quantity. In philosophy though, we don't measure ideas in terms of numbers, but of meanings. Physically, Energy is measured in units of change : before & after difference*1, not in terms of substance. In philosophy, Causation & Change are measured in terms of information value*2 (meaning), not thermodynamic units.In the case of energy, I believe you're reading too much in that physical quantity. . . . .
Note that this isn't a direct criticism on your own metaphysical position. It is just an observation on how careful I think we should be in interpreting physical quantities in a metaphysical way. — boundless
I'm currently reading a book by Federico Faggin, who is not a philosopher, but a scientist : the inventor of the first practical microprocessor. However, this book, Irreducible, is about a philosophical worldview. Specifically, the nature & role of Consciousness in the real world. In his first two chapters, though, Faggin makes a philosophical distinction between Physical Reality and Quantum Reality. He says, "we experience and know the physical world around us, as well as our inner world, through Qualia." He goes on to divide Consciousness into three categories : perception, emotion, and qualia. He notes that "the third category is thoughts, although most scholars do not regard thoughts as qualia." Then he discusses how the human mind translates private immaterial meanings into public words that other humans can understand. "We are so used to the automatic reification of thoughts into symbols that we have stopped noticing the 'quale' which is the sentient experience of a thought."
Your comment seems to be implying that we should express units of Energy in physical Joules, instead of metaphysical meanings. However, I'm not a physicist, so in my philosophical thesis, I look at Energy from a different perspective*2. I take an abstract concept, which is invisible & immaterial --- known only by its effects on matter --- and represent it in concrete metaphors & analogies. That's the opposite of reification*3. Therefore, I am not denying that Energy has physical effects in the Real world*4. I'm merely noting the metaphysical*5 implications of that causal power in the mental meanings of human conception. On this forum, I do have to be very "careful" when I discuss distinctions between Physics and Meta-Physics. :smile:
*1. Information :
Knowledge and the ability to know. Technically, it's the ratio of order to disorder, of positive to negative, of knowledge to ignorance. It's measured in degrees of uncertainty. Those ratios are also called "differences". So Gregory Bateson* defined Information as "the difference that makes a difference". The latter distinction refers to "value" or "meaning". Babbage called his prototype computer a "difference engine". Difference is the cause or agent of Change. In Physics it’s called "Thermodynamics" or "Energy". In Sociology it’s called "Conflict".
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page11.html
*2. Energy :
Scientists define “energy” as the ability to do work, but don't know what energy is. They assume it's an eternal causative force that existed prior to the Big Bang, along with mathematical laws. Energy is a positive or negative relationship between things, and physical Laws are limitations on the push & pull of those forces. So, all they know is what Energy does, which is to transform material objects in various ways. Energy itself is amorphous & immaterial. Therefore, if you reduce energy to its essence of Information, it seems more akin to mind than matter.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page8.html
*3. Reify : to represent something abstract as-if it's concrete.
Note --- In my post I was not reifying an abstraction, but just the opposite. Some people tend to imagine abstract Energy as-if (counterfactual) a material substance : "misplaced concreteness". Instead, I was Idealizing & generalizing the causal forces of the cosmos in terms of philosophical metaphors & analogies.
*4. Yes, energy is real, but it's best understood as a fundamental property of matter and fields, not a physical substance you can hold; it's the capacity to do work, always conserved (never created or destroyed), and manifests as motion (kinetic), stored potential, heat, light, and mass itself, allowing us to see its effects (movement, heat, light) even if energy itself isn't a tangible "thing" like a ball.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=is+energy+real
*5. Meta-Physics :
Physics refers to the things we perceive with the eye of the body. Meta-physics refers to the things we conceive with the eye of the mind. Meta-physics includes the properties, and qualities, and functions that make a thing what it is. Matter is just the clay from which a thing is made. Meta-physics is the design (form, purpose); physics is the product (shape, action). The act of creation brings an ideal design into actual existence. The design concept is the “formal” cause of the thing designed.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page14.html -
Cosmos Created Mind
This is a philosophy forum, not a physics seminar. So why not reify that which is invisible & intangible? Energy is a non-thing concept, it's a knowable-but-not-seeable relationship between things. Energy is unreal & unbound Potential or Probablity that temporarily takes on actual bound forms (matter), causes change of shape or position, and then returns to its unreal immaterial state as latent possibility. Matter dissolves as energy dissipates, but only the Energy is conserved, in its formless form.I wouldn't 'reify' energy as I wouldn't reify any other physical quantities. — boundless
Energy is an abstract ethereal concept, which is easier to conceive in the form of material metaphors or physical analogies. For example, Gravity was long imagined as-if a pulling force on an invisible rope, But the falling apple was not attached to a rope. So Newton defined his unseen force in abstract mathematical terms, and Einstein re-imagined it figuratively as curved empty space, even as he redefined it as a geometrical ratio. Can you imagine the number 5 without reifying it as something concrete? :wink:
THE GRAVITY GRID IS IMAGINARY. We reify what we know but can't see.
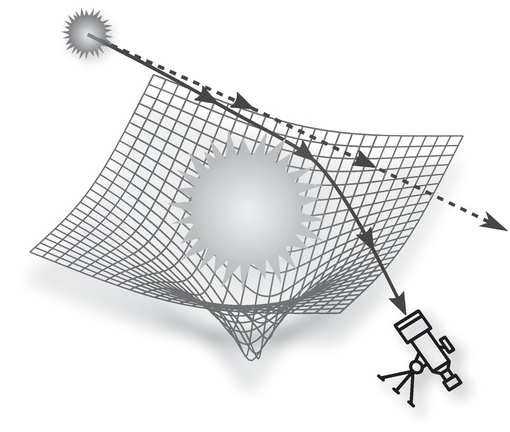
-
Cosmos Created Mind
According to the Buddha, my Reality is an Illusion based on a misinterpretation. Presumably, the Reductionism of modern Science constructs an illusory, yet practical, model of reality, that allows humans to control Nature for their own ends. Hence, for practical purposes, in the physical world, we don't need to know much about the ghostly metaphysical Ideality that supposedly surrounds us. Knowledge of Metaphysical Truths is only useful for arguing with other philosophers about True Reality. Ideality is how we imagine how the world ought to be.↪Gnomon
I was hoping that someone else could explain how they know that the Cosmic Mind is transmitting thoughts into human brains.
Well the way I envision this is that I consider the idea that separation is illusory. In which case there is no requirement for anything to be transmitted. The information is already at its destination. In a sense our whole world, body, brain, mind is an elaborate mechanism preventing us consciously accessing the information that we already know. — Punshhh
I'm currently reading Federico Faggin's, Irreducible, which also posits that Mind (Consciousness) per se is the true Reality. He calls that universal Mind : The One*2, which is defined as the Whole of which we human persons are a minuscule particle. It's as-if the metaphorical One is an ocean and I am a sentient molecule of water, ignorant of its own all-encompassing habitat. Or another metaphor is that The Cosmos is like a sentient being, and I am just a single semi-sentient cell in her body.
However, lacking a direct revelation from the Cosmic Consciousness, my local physical & mental reality is all I can know for sure. Which is why I no longer accept the Judeo-Christian-Islam scriptures as evidence of a higher reality : they don't speak directly to me. So I would have to accept their Holy Word on blind faith. The scriptures explain that my own self-conceit is what "prevents" me from conceiving of The Cosmic Self. I can accept The One as an allegory --- God knows or realizes Herself via humans --- but not as an actual loving Being. If I already possess that divine "information", I am not aware of it. :smile:
*1. In Buddhism, the "illusion"isn't that nothing exists, but that our perception of reality is fundamentally distorted by ignorance, leading to suffering (dukkha). Key Buddhist illusions include the belief in a permanent, independent self, clinging to impermanent things as lasting, and seeing the continuous world as static. By understanding these misperceptions through practices like meditation, one can dismantle the ego and realize interconnectedness, achieving liberation from suffering.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=buddha+illusion
Note --- I have my little aches & pains, but very little emotional suffering. So, my attempts at meditation didn't provide much Moksha. And I'm too close to The End for the impermanence of life to be scary.
*2. "The One" : refers to physicist and inventor Federico Faggin's theory of consciousness, where "the One" is a universal, holistic quantum field that is the fundamental basis of reality, desiring to know itself through self-reflection, with individual consciousnesses as points of view within this unified field, bridging science and spirituality through concepts like love and unity. Faggin, known for inventing the microprocessor, experienced a profound spiritual awakening that shifted his focus from materialist science to consciousness as the ground of being, exploring how mind and matter interconnect.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=faggin+the+one
Note --- Faggin obviously has broad & deep knowledge of Science and Philosophy. But how does he know what the universal quantum field "desires"? Can I choose to accept or to block Mystical Knowing? -
Cosmos Created Mind
Yes. Energy is the cause of physical change, while material particles are the things that are in flux. Change >>> Time ; Matter >>> Space. The initial state of the Big Bang theory required two pre-bang things that can't be accounted for : Causal Energy and change-regulating Natural Laws. Both must be pre-existent in order to explain the something-from-nothing event*1 that Cosmologists have calculated by back-tracking current events. So, if Cause & Laws pre-date the space-time bubble we now inhabit, then for all practical purposes, they are eternal. Hence, Energy must be "conserved" because it is essential to the continuing existence of the physical universe.The problem with 'energy' is that it is defined in physics as a property of physical objects and physical systems. And while, for instance, in experiments it has been observed that energy is conserved while particles are not. . . . .
In the same way, energy is not a substance that composes matter. — boundless
And yes, Energy is not a physical or material substance, but a quality or property of the world that transforms & sustains the stuff we, and the world, are made of*2. Aristotle knew nothing of modern physics, but he inferred from his observations of Nature (Phusis) that the "stuff" of reality (hylomorph) is a combination of tangible Matter (raw potential : e.g. clay) and knowable Conformation (Platonic Form ; design pattern : sculptural intent). Therefore, Energy is the immaterial power (essence) that causes Matter to take-on different forms.
The physical Universe is known to be temporary, but the metaphysical Cosmos may be eternal*3 (i.e. the source of Cause & Laws that powered and enformed the Big Bang). The OP noted that the philosophy of Noetics postulates that the eternal Cosmos is the "Mind of God". And that the cosmic Mind somehow transmits Ideas (morph ; form) into human Brains (hyle ; matter). I can understand that as a philosophical metaphor, but how could we confirm that spooky notion as a scientific fact? Is Energy a signal from Cosmos to local minds & matter? :wink:
*1. The Big Bang theory describes the universe expanding from an incredibly hot, dense state about 13.8 billion years ago, marking the beginning of space, time, matter, and energy, but it doesn't fully explain what caused that initial state or what existed "before". Modern physics suggests "nothing" isn't truly empty; quantum fluctuations in a pre-existing quantum vacuum might have seeded the Big Bang, or theories like cosmic inflation describe the rapid growth from a near-nothing state, with ideas like the "Big Bounce" suggesting a previous universe's end catalyzed ours
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=big+bang+something+from+nothing
*2. Substances : primary realities ; qualities, quantities, etc., depend on them for existence.
Matter : The physical stuff, changeable, potential.
Form : The essence, structure, or universal definition that makes something what it is
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=aristotle+substance
*3. "Space-time bounded by eternity" suggests a concept where the vast, four-dimensional fabric of the universe (space-time) isn't infinite but exists within a greater, timeless reality (eternity) or that all of time and space exist simultaneously as a fixed "block," challenging our perception of linear time, often explored in physics (eternalism) and philosophy to reconcile the universe's existence with timeless concepts of God or ultimate reality, implying our experienced time is just a slice of an ever-present whole.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=space-time+bounded+by+eternity -
Cosmos Created Mind
misinterpreted my reference to Energy as a "postulated force"*1, analogous to "spiritual energy"*2. That was not intended as a religious assertion, but simply as a philosophical (metaphysical) concept. Over the years, scientists have postulated the existence of things they couldn't demonstrate. For example Einstein's postulate of curved space sounded silly, but it's now accepted by physicists as a "basis for reasoning"*3. Likewise, some religious believers postulate the existence of ghosts, as a basis for "belief", even though the only evidence may be vague wispy light reflections or spooky sounds.energy isn't just a 'postulated force' — Wayfarer
When one gets tired, it isn't that one is low on energy, but that one is low on useful energy - the kind that the muscles need. The quality of energy can decay, but never its quantity. — PoeticUniverse
Energy, even in the form of photons, is invisible & intangible until it is transformed into matter. But it is capable of causing phenomenal changes in the real world. So, what you mean by "quality of energy" may refer to the distinction between "free" (causal) energy and "bound" energy (matter). In my own thesis, Energy is described as a "shape-shifter" : changing form from qualitative Potential to quantitative Actual and back again.
Free Energy (useable, available, potential) is also associated with mental processes*3, such as Inference & FreeWill. Likewise, my notion of Universal Causation (EnFormAction) applies to both physical Energy and metaphysical Inference. So, when your muscles get tired, available physical/material energy (e.g. ATP) has been transformed into motion, and then into waste energy (CO2 & H2O). But the latter are only Potential (metaphysical), not Actual (physical) Energy, until a causal transformation recombines them via form change. :nerd:
*1. Postulate : a thing suggested or assumed as true as the basis for reasoning, discussion, or belief.
Planck's Quantum Postulate
Bohr Model Postulates
Conservation of Energy
Schrödinger Equation Postulates
In essence, "energy is postulated" means these core ideas about energy's behavior are fundamental assumptions upon which larger, successful physical theories are built, often confirmed by experiments
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=energy+is+postulated
*2. "My point was simply that Energy is not a tangible material substance, but a postulated immaterial causal force (similar to electric potential) that can have detectable (actual) effects in the real world : similar to the spiritual belief in ghosts."
*3. The free energy principle is based on the Bayesian idea of the brain as an "inference engine." Under the free energy principle, systems pursue paths of least surprise, or equivalently, minimize the difference between predictions based on their model of the world and their sense and associated perception.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=%22free+energy%22+faggin
Free Energy
The wind is free, the machine is not.
You ether build, or pay a lot.
If you look, and really see.
Nothing is, truly free.
By Josefh Lloyd Murchison -
Cosmos Created Mind
My point was that Energy is logically inferred, not physically observed. I was not implying that it is not a real phenomenon. But over many centuries, various "energies" have been postulated or dismissed as spiritual (metaphysical) forces. Personally, I don't think in terms of spiritual forces*1, or deeper essences, or degrees of reality. However, I do use the term "physical energy" as an instance of a Universal Causal Force*5 in the world : EnFormAction. Which I label as metaphysical*4, because it is inferrable, but not observable. It's intended to be a science-based update to ancient spiritual speculations.My point was simply that Energy is not a tangible material substance, but a postulated immaterial causal force (similar to electric potential) that can have detectable (actual) effects in the real world : similar to the spiritual belief in ghosts. — Gnomon
The comparison to a 'spiritual belief' misses the mark because energy is a strictly defined physical property, not a metaphysical posit. While it isn't a 'tangible substance' like a rock, it is inextricably linked to matter via e=mc2. It has measurable physical effects, including gravity. — Wayfarer
In my reply to I noted : "Scientists & philosophers have for many years attempted to account for the otherwise inexplicable evolutionary emergence of Life (animated matter) and Mind (thinking matter) with a variety of hypothetical postulations : ancient Greek vitalism, Eastern Chi or Prana*2, Bergson's elan vital*3, Schopenhauer's will-to-live, and more recently Whitehead's Process philosophy (evolutionary change over time)". :smile:
*1. Spiritual energy is an invisible life force connecting all living things, known by names like prana, chi, or life force, felt as a subtle vibration influencing physical, mental, and emotional well-being, fostering peace or depletion based on balance. It's seen as a deeper essence of life, linking individuals to the universe and a greater purpose through practices like self-care, compassion, and connecting with nature, art, or community, often managed through energy centers like chakras
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=spiritual+energies
*2. In Hinduism, Prana (प्राण) is the Sanskrit word for "life force" or "vital energy," the universal principle that animates all living beings, flowing through the body in channels (nadis) and associated with breath, which is a primary way to absorb and control it. It's considered the subtle energy that fuels our physical, mental, and spiritual existence, categorized into five vital airs (Vayus) like Apana, Samana, Vyana, and Udana, with practices like Pranayama (breath control) used to balance and direct it for health, focus, and spiritual growth.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=prana+hinduism
*3. Élan vital (French for "vital impetus" or "vital force") is a philosophical concept by Henri Bergson describing the creative, driving force behind evolution, an inner push that makes life complex and diverse, diverging from simple matter and mechanical processes. It's a dynamic, non-physical energy that propels living organisms to adapt and grow, contrasting with materialistic views and influencing ideas on consciousness, creativity, and the spirit of life itself.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=elan+vital
*4. Gravity waves, both atmospheric (in fluids like air/water) and spacetime ripples (gravitational waves), are fundamentally physical phenomena, described by physics, but they intersect with metaphysics in deeper questions about the nature of spacetime, quantum gravity, and reality itself, especially when trying to unify relativity and quantum mechanics. While the observation and description are physics, interpreting their ultimate nature (e.g., is spacetime truly a "thing"?) delves into metaphysical realms.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=gravity+waves+physical+or+metaphysical
*5. Federico Faggin "Vital Force" refers to the theories of physicist and microprocessor inventor Federico Faggin, who posits that consciousness is fundamental to reality, not a byproduct of matter, and is the "vital force" driving the universe, explaining quantum physics and free will. He developed Quantum Information Panpsychism (QIP) suggesting consciousness is a primary quantum phenomenon, with matter as the "ink" it uses to know itself, bridging science and spirituality
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=faggin+vital+force -
Cosmos Created Mind
My comment was a response to your post about philosophical notions on the Reality vs Ideality of Potential vs Actual*1. I was simply referring to a common scientific/philosophical position on a practical distinction between objective observed concrete Knowable Reality and subjective imaginary abstract Hypothetical Concepts .Energy is considered a real thing even though it's knowable only in its effects, not in its material substance. — Gnomon
Nope. Not the point. The profound point is that there are real degrees of reality. — Wayfarer
My point was simply that Energy is not a tangible material substance, but a postulated immaterial causal force (similar to electric potential) that can have detectable (actual) effects in the real world : similar to the spiritual belief in ghosts. The mundane implication is that Potential is functionally not-yet-real, but I made no assertion about its parallel existence in an immaterial invisible realm of Platonic Forms. Which I don't envision as a higher plane of existence, but merely a concept about a possible unknown source of ideas for the human mind. Perhaps a mythical Cosmic Mind as in Noetics.
But your Point is that reality is a simultaneous multi-level phenomenon??? Is that similar to the belief that there are "degrees" or levels-of-reality*2 that are obvious to our physical & technological senses, and other realms (parallel universes?) that are invisible and occult, except to extra-sensory perception, or through the eyes of Faith? Sadly, I seem to be blind to Hyperreality*3. :wink:
*1. From Wayfarer post above :
"In the... paper, three scientists argue that including “potential” things on the list of “real” things can avoid the counterintuitive conundrums that quantum physics poses."
Note --- That sounds like an arbitrary assignment to a category, not a verifiable class of "things".
*2. "Degrees of reality" refers to philosophical ideas that existence isn't all-or-nothing, but rather a hierarchy where some things are "more real" than others, often based on independence (like Plato's Forms vs. physical objects) or structure (like Descartes' substances vs. modes). These concepts vary, ranging from objective vs. subjective views (scientific facts vs. beliefs) to layered realities (personal, social, physical) or even spiritual levels (Plotinus's God, intellect, soul, matter).
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=degrees+of+reality
*3. Hyperreality describes a state where simulations and representations become indistinguishable from, or even preferred over, genuine reality, a concept developed by Jean Baudrillard in postmodern culture,
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=hyperreality -
Cosmos Created Mind
No. It doesn't make sense to me. That's why I posted the reference to Noetics (study of sentience & intellect) in the OP. I was hoping that someone else could explain how they know that the Cosmic Mind is transmitting thoughts into human brains. So far, no-one has commented on the Noetic angle, but merely continue the ancient & everlasting Idealism vs Realism arguments that make-up the bulk of diametrically opposed TPF threads. Panpsychism*3 is not exactly the same as Noetics, but quite a few serious secular scientists have publicly stated that they accept it as an axiom for cracking the Hard Problem of Consciousness. My personal Noetic nut-cracker is EnFormAction*4. :smile:The key presumption is that Consciousness is non-local, but Cosmic (Pantheism ; Panpsychism). — Gnomon
Could you please explain how and why this is the case? Does it make sense? — Corvus
*1. From OP --- Background : I recently finished Dan Brown's new novel, Secret of Secrets, and enjoyed the intellectual thrill ride completely. Spoiler Alert! : If you are not familiar with the book, I'll reveal the "secret" hidden in plain insight : human consciousness, and its alter ego The Mind, is not generated by the brain, but is instead a signal from out there somewhere*2b. If so, what are the special "Noetic faculties" of the human animal*3? Are these spiritual signals the distinguishing factor of homo sapiens?
Note --- The notion of the human brain receiving broadcasts from the universal Mind is merely a fictional device used by Brown to serve as the spooky "secret" in his novel. But Noetics is a real philosophical position postulated by real people. But, as I said in the OP : " I find it difficult to accept that my thoughts & feelings are signals from some central transmitter, like the robotic clone army of Star Wars."
*2. Noetics and idealism are related philosophical concepts concerning the nature of reality and knowledge, with idealism being a metaphysical stance and noetics a branch of philosophy focused on the mind and intellect. Noetics is often explored within an idealist framework.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=noetics+vs+idealism
*3. Scientists and philosophers are increasingly exploring panpsychism, the idea that consciousness is fundamental to the universe, not just complex brains, to solve the "hard problem" of consciousness, though it faces challenges like the "combination problem" (how micro-consciousness forms macro-consciousness) and lacks direct experimental proof, with some physicists and neuroscientists supporting it as a valid scientific avenue for integrating mind into matter, while others remain skeptical, calling for concrete physics.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=scientists+and+panpsychism
*4. "Enformaction" isn't a standard English word but appears in philosophical discussions (especially on The Philosophy Forum) to describe the concept of information as potential or the power to change form, linking energy, form, and action in a metaphysical sense, suggesting information is the underlying "structure" or "ideal" behind physical reality. It's used to explore how abstract data (like ideas or memories) can manifest physically (on paper, hard drives) and vice versa, emphasizing that the physical carrier (paper, disk) matters less than the information itself.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=enformaction
Note --- This is an AI version of my concept of EnFormAction, not in my own words. -
Cosmos Created Mind
Yes. I suppose it's accounting for physical changes that would otherwise seem like magic. Give it a mundane name, and it sounds more technical, and seems less spooky. In my thesis, I call that "deeper structure" EnFormAction*1. Scientists & philosophers have for many years attempted to account for the otherwise inexplicable evolutionary emergence of Life (animated matter) and Mind (thinking matter) with a variety of hypothetical postulations : ancient Greek vitalism, Eastern Chi or Prana, Bergson's elan vital, Schopenhauer's will-to-live, and more recently Whitehead's Process philosophy (evolutionary change over time).Energy is an accounting number, its conservation suggesting some deeper structure. — PoeticUniverse
But all of these motivating & transforming forces seem similar, in causal effect, to the modern notion of physical Energy (power, ability, potential, capability), in various invisible intangible forms : gravity, photons, vacuum energy, virtual particles, etc. So, I lump them all together into the concept of EnFormAction*2. Note the Cosmic Mind interpretation below that may be relevant to the OP. What makes the world go round : energy or conatus? :smile:
*1. The concept of a river of causation running through the world in various streams has been interpreted in materialistic terms as Momentum, Impetus, Force, Energy, etc, and in spiritualistic idioms as Will, Love, Conatus, and so forth. EnFormAction is all of those.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page8.html
*2. EnFormAction :
As a supplement to the mainstream materialistic (scientific) theory of Causation, EnFormAction is intended to be an evocative label for a well-known, but somewhat mysterious, feature of physics : the Emergent process of Phase Change (or state transitions) from one kind (stable form) of matter to another. These sequential emanations take the structural pattern of a logical hierarchy : from solids, to liquids, to gases, and thence to plasma, or vice-versa. But they don't follow the usual rules of direct contact causation.
Expand that notion to a Cosmological perspective, and we can identify a more general classification of stratified phase-like emergences : from Physics (energy), to Chemistry (atoms), to Biology (life), to Psychology (minds), to Sociology (global minds). Current theories attribute this undeniable stairstep progession to random accidents, sorted by “natural selection” (a code word for “evaluations” of fitness for the next phase) that in retrospect appear to be teleological, tending toward more cooperation of inter-relationships and entanglements between parts on the same level of emergence. Some AI enthusiasts even envision the ultimate evolution of a Cosmic Mind, informed by all lower level phases.
https://bothandblog3.enformationism.info/page23.html
# Some people said that energy doesn't exist physically and it is not fundamental, but it is a relationship between other fundamental things.
https://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/484707/does-energy-exist-or-is-it-just-a-relationship-between-other-fundamental-things

-
Cosmos Created Mind
Yes. In modern physics, Energy is considered a real thing even though it's knowable only in its effects, not in its material substance. Energy as potential is an Aristotelian "substance" only in the sense of an invisible essence that is capable of transforming into the tangible substance we know as Matter.↪Paine
↪Gnomon
↪Esse Quam Videri
(I have to briefly sign back in - shhhh - to mention an article I've found interesting, about how Heisenberg re-purposed Aristotle's 'potentia' in respect to quantum physics Quantum mysteries dissolve if possibilities are realities:
In the... paper, three scientists argue that including “potential” things on the list of “real” things can avoid the counterintuitive conundrums that quantum physics poses. — Wayfarer
Ari's notion of two-phase substance (potential & actual) has always been confusing from a materialist perspective. In my own thesis, I combined potential Energy & Information into the coinage EnFormAction : the power to transform potential Form (design, essence, information) into actual Shapes (structure, matter, hylomorph) and vice versa. Which is what Einstein's equation spells out : (E = MC^2). :smile:
Energy, in the form of Light, is not a local thing, but a dynamic "disturbance" propagating through the universal quantum Field of mathematical points. What we experience locally as Mass (matter) is proportional to the speed of light, which slows-down to form particles of rest-mass-matter. Unfortunately, our matter-based language makes it difficult to express such immaterial (knowable but unsensable) essences & transformations in words. :nerd: -
Cosmos Created Mind
I'll have to admit that Aristotle's definition of a Soul is not clear to me. But it reminds me of similar definitions of Energy as the capacity or ability or potential for work (i.e. material change). In that case, the capacity is not the same as the actuality. It seems more like the potential for actualization, to become realized. So perhaps his Soul is more like our modern notion of Energy : both potential (abstract) and actual (embodied). Embodied Energy is transformed into Matter [E=MC^2, where E is just a number or value, and M is the property (inertia) that makes matter seem actual & real to us]. Anyway, I'm not an Aristotle scholar, so I won't press the issue. :cool:Your depiction of Actual and Potential reverses their roles given in Aristotle's writing:
"But our view explains the facts quite reasonably for the actuality of each thing is naturally inherent in its potentiality, that is in its own proper matter. From all this it is clear that the soul is a kind of actuality or notion of that which has the capacity of having a soul" — Paine
The statement "soul is a kind of actuality" comes from Aristotle's philosophy, specifically his work On the Soul (De Anima), where he defines the soul as the "first actuality (entelecheia) of a natural body that has life potentially". This means the soul isn't just a potential (what a body could be) but the very realization or form that makes a body actually living, like the knowledge a person has even when sleeping, making it the principle that brings matter into a living organism.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=soul+is+a+kind+of+actuality+ -
Cosmos Created Mind
Most of the posts on this thread seem to be various philosophical opinions favoring either traditional Idealism (transcendentalism) or Realism (immanentism). But I just came across a book in my library that offers a scientific version of the Cosmic Mind concept. Music publisher, Howard Bloom's 2000 book, Global Brain, presents his postulation of "collective information processing"*1*2*3 on a universal scale. Which is relevant to my own amateur philosophical thesis of Enformationism. Bloom is also the author of The God Problem : How a Godless Cosmos Creates.what is the relationship between World-at-large & local Brain & personal Mind? — Gnomon
Obviously, Global Brain is a speculative hypothesis, and there is no more empirical evidence for a GB than for a Transcendent Deity. In the Prologue, Bloom says, "we living beings have been modules of something current evolutionary theory fails to see". He goes on to postulate that "we are parts of a greater mind constantly testing fresh hypotheses". Do these statements sound more like religion than science? Note --- the use of "brain" instead of "mind" may be an attempt to avoid spiritual connotations.
Has anyone else read the book? How do you think it relates to the theme of this thread? Is there a Cosmic Mind, and are human minds the offspring of that mysterious progenitor? Is human culture on Earth just one element of a top-down Universal Intelligence? Or are human agents, inadvertently and unwittingly, in the process of creating a Cosmic Mind --- or a Singularity --- from the ground-up, so to speak? :smile:
*1. The concept of a "global brain" relates to the theory that humanity, together with its technological agents and communication networks like the Internet, is evolving into a single, interconnected, information-processing system, which functions as the nervous system for a social superorganism
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=global+brain+study+group+superorganismic+intelligence
*2. Global Brain : The Evolution of Mass Mind from the Big Bang to the 21st Century by Howard Bloom argues that life on Earth is a single, evolving "global brain," a complex adaptive system where individuals are part of a larger social learning machine, from bacteria to humans. The book traces this evolution from the Big Bang, showing how groups (like bacterial colonies, insect swarms, and human societies) have always functioned as collective intelligences, using mechanisms like conformity and diversity to test ideas and adapt, with the internet being the latest phase of this process.
Group Selection :
Bloom posits that evolution isn't just about individual genes, but about groups competing and learning from each other, with successful group traits being passed on.
Social Learning Machine :
He proposes that all life forms, from microbes to humans, are part of a massive, interconnected system for processing information and learning.
Mechanisms of the Global Brain :
The system relies on elements like "conformity enforcers" (to maintain stability) and "diversity generators" (to innovate), which are seen in everything from bacterial colonies to human cultures.
Historical Examples :
The book uses examples like marching lobsters, bee colonies, and ancient Sparta to illustrate how different species have engaged in collective problem-solving and social learning.
The Internet as a New Phase :
The World Wide Web is presented as the most recent and powerful stage in the evolution of this global brain.
Key Takeaway
The book challenges traditional Darwinian views by suggesting that the purpose of life is not just individual reproduction, but the exploration and survival of the "mass mind" through group-level experimentation and competition.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=howard+bloom+global+brain
*3. A global brain emergent structure is the concept that the interconnected internet, social media, and AI form a planetary-scale, self-organizing information system, analogous to a biological brain, where collective human and machine intelligence arises from countless interactions, creating higher-level cognition for problem-solving, though decentralized and without a single controller, much like neurons forming a brain. This emergent intelligence processes information globally, similar to how neural networks function, allowing for complex, large-scale tasks beyond individual capacity.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=global+brain+emergent+structure -
Cosmos Created Mind
Aristotle distinguished between Soul & Body, just as he made a distinction between abstract Form & concrete Matter. The quote doesn't say this specifically, but I interpret the Soul (ousia, essence, form -- subject?, person?) as Transcendent & Potential, and Body (matter, flesh, substance) as Immanent & Actual.The passage is no starting point for the distinction between immanence and transcendence in the theological sense because nothing is possible if it is not "natural." Aristotle questions the freedom of the "Craftsman" in the Timaeus. A topic that leads to the third paragraph:
412a16. Since it is indeed a body of such a kind (for it is one having life), the soul will not be body; for the body is not something predicated of a subject, but exists rather as subject and matter. The soul must then, be substance qua form of a natural body which has life potentially. Substance is actuality. The soul, therefore, will be the actuality of a body of this kind. — ibid. 412a16 — Paine
So when Potential is Actualized --- e.g. sperm & egg quicken to become one person --- Soul & Body are united into a living-thinking Hylomorph. Theologians later interpreted the Soul as existing eternally and supernaturally, so at death the Soul separates from the natural concrete material body, and returns to its supernatural abstract potential form. Hence, the imaginative notion of a disembodied ghost lurking in some intermediate realm between Nature and Super-nature.
But, going back to the OP, where does the human Mind & Person come into play? Does the transcendent Soul think like a mind? If so, what does it think about? What is it like to be a disembodied Mind? Does the non-personal Cosmic Potential (Nature) somehow create the actual embodied Mind by joining Form & Flesh (abstract essence & concrete substance) into a natural person? :chin: -
About Hume, causality and modern science
Perhaps Hume somehow anticipated the discovery of Quantum Causation*1, which is statistical & uncertain & non-local instead of actual & deterministic & particular. From a local close-up position, we see only single pairs of cause & effect elements. Yet, from a few causal experiences, we can generalize and infer that this current causal event is an effect of a prior cause, and an unbroken chain of causes extending back into infinity. For example, scientists concluded from snapshots of the current expanding astronomical state, we can trace cause & effect back 14 billion Earth-years to a hypothetical physical First Cause : the Big Bang.I just find that Hume's sceptical account of everyday causality, very true in itself, doesn't really take into account the advances of modern science, say like theoretical physics. — hwyl
Therefore, from a cosmic perspective (imaginary of course) we can "see" long chains of cause & effect, or possible teleological trends in transformation. So, by combining a few direct observations with creative conceptualization, we derive the common and scientific notion of energetic-transfer causation.
Hume's skeptical & reductionist & purposeless view disallows optimistic & holistic interpretations of world processes*2. But from a more open-minded perspective*3, the Cosmos seems to show signs of Progression & Teleology*4. :nerd:
*1. Quantum Causality : Bell's Theorem shows that conditions of "local causality" in experiments involving quantum entanglement result in non-classical correlations predicted by quantum mechanics. Despite these subtleties, causality remains an important and valid concept in physical theories.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=quantum+causality
*2. David Hume's view on causality argues that we don't perceive a necessary connection between cause and effect, only a "constant conjunction" of events (Event A always followed by Event B). This repeated experience creates a mental habit or expectation, leading us to believe in a necessary power or link, but this isn't a logically certain or empirically observable feature of the world; it's a psychological projection, making causality a matter of custom, not reason or direct perception, a core tenet of his empiricism.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=hume+causality
*3. Kant agrees with Hume that neither the relation of cause and effect nor the idea of necessary connection is given in our sensory perceptions; both, in an important sense, are contributed by our mind. For Kant, however, the concepts of both causality and necessity arise from precisely the operations of our understanding—and, indeed, they arise entirely a priori as pure concepts or categories of the understanding.
https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/kant-hume-causality/
Note --- Correlation does not prove Causation. But it does seem "necessary" to our normal "operations of understanding". An event that does not seem necessary feels like magic.
*4. Whitehead's process teleology : posits that the universe isn't moving toward a fixed goal but is inherently driven towards the production and intensification of beauty, understood as the harmonious contrast of diverse experiences, lured by a divine "primordial nature" that presents possibilities for richer, more complex unifications. This teleology is open and creative, meaning purpose emerges from each moment (actual occasion) making decisions about possibilities (eternal objects) to form new experiences, leading to an evolving, never-finished cosmos where beauty, novelty, and value are intrinsic aims, not just human constructs
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=whitehead+process+teleology
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF APPARENT COSMIC EXPANSION?
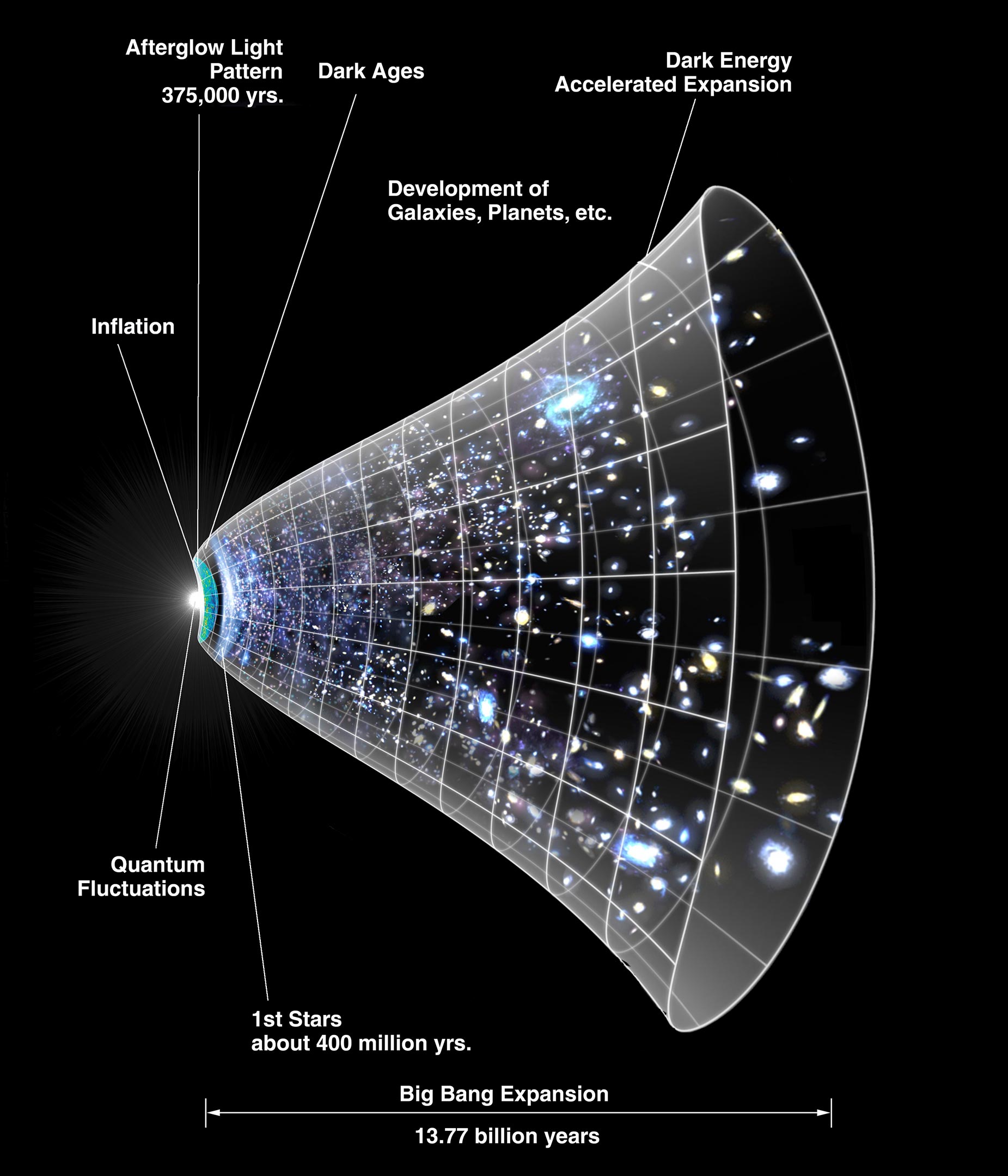
-
Cosmos Created Mind
Apparently, disagrees with your definition of Philosophical questioning. He seems to picture himself as a Socratic gadfly, arguing against the Sophists, whose fallacious logic and situational rhetoric was goal-oriented instead of truth-seeking. In my early reading about Philosophy, Socrates was portrayed (by Catholic theologians?) as the good-guy, separating True from False, and the Sophists*1 were bad-guys, preaching relativity & subjectivity. Yet, unlike 180's sneering & disparaging & humiliating trolling-technique, Socrates' philosophical method*3 was dialectical & didactic & persuasive.How else do we know "what is true"? — Gnomon
Notice that in the context of science, this is usually limited to a specific question or subject matter, but can also then be expanded to include general theories and hypotheses. Philosophical questions are much more open-ended and often not nearly so specific. That is the subject of another thread, The Predicament of Modernity. — Wayfarer
Now, I'm beginning to see that the Sophists' "practical wisdom" may have been anticipating the subjective relativity*2 of Einstein. Today, the notion of absolute Truth is relegated to revealed religions, while pragmatic Science makes-do with Bayesian truths. My own "open-ended" BothAnd philosophy is holistic & complementary & inclusive, instead of a dogmatic Either/Or belief system, which is reductive, binary, & exclusive.
I guess the Predicament of Modernity is highlighted by the Classical (deterministic) vs Quantum (probabilistic) revolution in worldviews. Transcendent truths are inherently subjective conjectures, not objective observations. So, how does 180 know what is objective capital-T-truth*4, while I have to get by with my little subjective perspective? :cool:
*1. The Sophists were ancient Greek thinkers who emphasized relativism, believing truth, knowledge, and morality are subjective and depend on human perspective, famously stated by Protagoras' maxim, "Man is the measure of all things". They taught rhetoric as a vital skill for success in politics, focusing on practical wisdom and the power of persuasive speech (logos) to shape reality, often contrasting with Socrates' search for universal, objective truths. Key beliefs included skepticism, conventionalism (laws are human-made), and humanism, seeing humans and their needs at the center of philosophy, not divine mandates.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=sophists
*2. Einstein's Relativity fundamentally changed philosophy by showing space and time aren't absolute but relative to an observer (Special Relativity) and that gravity is the curvature of spacetime (General Relativity), challenging concepts of universal "now" and introducing a geometric view of the cosmos, influencing epistemology, metaphysics (reality of space/time), and even religion through his idea of a "cosmic religion" based on nature's order.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=einstein+relativity+philosophy
*3. The Socratic Method is a teaching and discussion technique named after Socrates, using persistent, probing questions to guide individuals toward deeper understanding, uncovering assumptions, identifying contradictions, and fostering critical thinking rather than simply giving answers. It's a dialectical process of dialogue, discovery, and self-examination, moving from what a person knows to complex truths by systematically challenging ideas through carefully planned questions, aiming for clearer, more consistent thought
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=socratic+method
*4. "Capital T Truth" (or Big T Truth) refers to universal, absolute, objective reality or fundamental principles beyond personal belief, contrasting with "little t truths," which are subjective, contextual, or individual perspectives/facts (e.g., "my truth"). Think of it as the ultimate, overarching reality versus specific, smaller truths or experiences, often used in philosophy and religion to discuss transcendent concepts like Beauty, Good, or Truth itself, as opposed to mere factual statements
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=capital+t+truth -
Cosmos Created Mind
Ha! I don't do a lot of "presuming" about such technical questions, because that is peripheral to my amateur philosophy hobby. But I'm currently reading a book by Federico Faggin*1, who is a credentialed expert in computer-related technology. And he details a variety of "problems" and "specific issues" that could limit software & hardware design from reaching the goal of duplicating human reasoning.You're presuming that "real world" human reasoning is somehow beyond duplicating. I don't see any problems at all, because any specific issue you might bring up could be dealt in the design- either in software or hardware. — Relativist
Faggin seems to be an Idealist, who believes that Consciousness is fundamental, and the human Mind is irreducible to physical processes. Personally, I have a slightly different view of the foundations of human thought. But hey! What do I know? I'm just an untrained amateur philosopher, and he is an experienced computer guru. :smile:
*1. Irreducible : Consciousness, Life, Computers, and Human Nature is a 2024 book by Federico Faggin, the inventor of the microprocessor, that argues consciousness is a fundamental quantum phenomenon, not an emergent property of complex computation, challenging the idea that humans are just biological machines.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=irreducible+book -
Cosmos Created Mind
Of course fuzzy logic is algorithmic to some degree or it wouldn't be programmable for digital computers. But it's much more flexible & adaptable to the non-algorithmic real world than sharp line-item programming. Perhaps it was attempt to simulate human-style Bayesian logic*1 (degrees of truth) by introducing uncertainty & probability into an otherwise deterministic & predictable program.Fuzzy logic and paraconsistent logic ARE algorithmic- it's feasible to program these. The programmming could keep it predictable (a given input will necessarily produce the same output), or randomness could be introduced. — Relativist
Footnote*2 indicates that just fuzzing the algorithms was not enough to make computers think like humans. AI and ChatBots are getting closer to that dumbing-down goal by introducing human-like if-then rules. But self-awareness seems to require something a bit beyond just fuzzing the focus : a generalized contextual worldview and an embodied subject. :smile:
*1. "Non-algorithmic fuzzy logic"generally refers to the conceptual foundation of fuzzy logic (dealing with degrees of truth and human-like reasoning), distinct from the specific algorithms or hardware implementations that make it work in computer systems.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=non-algorithmic+fuzzy+logic
*2. Fuzzy logic was an overhyped 90s phenomenon that was largely based on the belief that one could design a control system without an understanding of control theory and somehow it would magically turn out better. That reality never materialized. . . . .
fuzzy logic is itself a mathematical concept born out of fuzzy sets and probability. It's basically just a tool to describe imprecise or incomplete information when working in a discrete system.
https://www.reddit.com/r/engineering/comments/pwht4f/whatever_happened_to_fuzzy_logic/ -
Cosmos Created Mind
That's an interesting way to look at the consciousness conundrum. Living organic plants could not survive if they didn't sense their environment, and interact with it in a manner controlled by self-interest. The Consciousness definition below includes a social factor (with) that might help to distinguish human-style awareness from plant & amoeba sensitivity to internal needs and external goods. As social beings, we need to be aware of what our fellows are aware of. :smile:Now I hold that plants are conscious, just not like us. But they are alive and present and conscious in a more meditative state than us, because they don’t have a brain. . . . .
Describing and recording data about something and transferring that data to us. But just in a different way, a way that includes conscious behaviour, but which the tree is entirely unconscious of, rather like the way the AI is entirely unconscious of what it is doing. — Punshhh
*1. The word consciousness comes from Latin conscientia, meaning "shared knowledge," combining con- (with) and scire (to know), initially implying joint awareness or a shared secret. It evolved in English in the 17th century, first meaning "internal knowledge," then expanding to "awareness of one's own mind" (1670s) and later "awareness of anything" (1740s). The term has roots in the Latin conscius (knowing with) and its Greek predecessor syneidesis, highlighting a core idea of knowing alongside or within oneself.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=consciousness+etymology -
Cosmos Created Mind
Yes. As an anti-social introvert, I am not temperamentally attracted to emotional social religions. I suppose dull rational internet philosophy is my religion substitute. :nerd:There's also the matter of temperament. Some are temperamentally drawn to religious ideas, others are temperamentally averse to them. — Wayfarer -
Cosmos Created Mind
Yes. Non-algorithmic Fuzzy Logic*1 is an attempt to make digital computers think more like humans. And it may be necessary for Chat Bots to deal with imprecise human dialog. Yet it reduces the primary advantage of computers : precision & predictability.can True/False computers replace Maybe/Maybe-Not human philosophers?* — Gnomon
Fuzzy logic and paraconsistent logic address this, at least to a degree. — Relativist
Microprocessor inventor, Federico Faggin says : "There is an unbridgeable gap between artificial and human intelligence, which is characterized by comprehension : a non-algorithmic property of consciousness that is often underestimated and inaccessible to computers"
I suspect that, if developers want to create a more realistic humanoid companion robot, they will have make them out of non-algorithmic flesh & blood instead of silicon semiconductors. But we may then have to deal with loveable ditzy dames, instead of stolid Mr. Spock robots.. :wink:
*1. Fuzzy logic's main advantages include its ability to handle imprecise, vague, or uncertain information (like human language), mimicking human reasoning for more natural decisions, and its robust, cost-effective nature, allowing simple sensors and easy performance tuning for complex control systems in areas like appliances, automotive, and AI. It provides smooth, gradual control and can model complex, non-linear systems without needing exact mathematical models
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=fuzzy+logic+advantages

-
Cosmos Created Mind
Me too. Apparently, because my BothAnd philosophy is so offensive to his Either/Or worldview, he seldom engages me in philosophical dialog. So normally, I ignore his trolling taunts & gibes, unless he happens to raise a question pertinent to the current topic.I'm not interested in being drawn into comments about debates with 180proof. From time to time I may respond to his comments directed at me. — Wayfarer
In this thread, I think his two-value logic is not appropriate. So, I tried to explain to myself why philosophy does not deal in yes-no questions. I only include his reply-name because, in years past, he objected to my talking behind his back, without naming him. I don't know why he wastes time actually reading my posts on topics that seem to viscerally upset him. :smile: -
Cosmos Created Mind
I have no experience with AI, other than Google Search. But I suspect that the human programmers of Chat-Bots necessarily include a self-reference algorithm in the basic code. But whether that kind of reflection constitutes self-awareness, I have to agree with Claude : "I'm genuinely uncertain whether I have experiences with the qualitative character that humans do, or whether there's "something it's like" to be me processing these words". :smile:Meaning requires a Me. A digital computer has no self-concept to serve as the Subject to interpret incoming data relative to Self-interest. Does AI know itself? — Gnomon
I tossed this to Claude. Read on if you wish. — Wayfarer
A self-referential algorithm is a computational process that can inspect, modify, or interact with its own structure, data, or operation, often creating a feedback loop where the algorithm's behavior influences its future state or even its own code.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=self+referential+algorithm -
Cosmos Created Mind
How else do we know "what is true"? asserts that Formal or Mathematical Logic is the arbiter of true/false questions. And algorithmic computers are known as the masters of math. But philosophy is supposed to be a search for Wisdom, while religion is presumed to provide absolute divinely-revealed Truth. Some disparagingly call philosophy "the study of questions without answers". Yet ancient Philosophy has spawned empirical Science as a tool to provide pertinent facts (not truths) to guide us in our exploration of a puzzling world.Another difficult subject. Suffice to say, I think it's the understanding, taken as obvious by a lot of our contemporaries, that science is the arbiter of what is truly the case. But scientific method embodies certain characteristic attitudes and procedures which are problematic in a philosophical context. — Wayfarer
A Scientific American Nov25 article is entitled "Can AI outdo mathematicians?" The article author, professor of mathematics at Johns Hopkins, warned : " Although so-called reasoning models are prompted to break problems down into pieces [analysis] and explain their 'thinking' step-by-step [logic], the output is as likely to produce an argument that sounds logical but isn't as to constitute a genuine proof". She concludes by noting : "in life, there is a lot of uncertainty".
A related question may be : can True/False computers replace Maybe/Maybe-Not human philosophers?*1 In a formal (ideal) world, digital and large-language computers may outperform human reasoning. But that's precisely because the machines omit & avoid the complexities & contradictions ("shades of color" & nuances of meaning) characteristic of informal human thinking about real world inter-subjective situations. 1/0 and true/false deliberately "exclude the middle" of uncertainties & infinities that plague imperfect analog humans.
As Wayfarer repeatedly notes : Logical Math, Reductive Science, and Digital Computers have no self-perspective to put the world into a meaningful dynamic context relative to personal questioners. Hence, their absolute either-or, black-vs-white, ideal-world outputs cannot account for real-world problems & questions of fallible-but-goal-oriented humans. Computers supply yes/no answers, but they don't ask philosophical questions*2. Socrates asked a lot of questions, and aspired to ideal Truth, but admitted in intellectual humility that he knew nothing for certain.
Consequently, in my humble opinion, bivalent (two-value) reasoning has no place on an informal forum like this, where we ask not-what-is-true-or-false, but what-is-meaningful in a specific situation. Is this a Science & Technology Forum or a Philosophy forum? :nerd:
*1. What is the difference between mathematical reasoning and philosophical reasoning?
I think the big difference between mathematics and philosophy is that mathematics tends to start from something like a formal system, and see how much can be proven within it. Philosophy approaches the question of "what formal systems are right?" If a formal system proves something non-intuitive, Philosophers will immediately start studying the axioms of the formal system to see if they may be missing something. Philosophers admit more shades of "color" into their arguments than mathematicians can.
https://philosophy.stackexchange.com/questions/21304/what-is-the-difference-between-mathematical-reasoning-and-philosophical-reasoning
*2. Computers can simulate asking and answering philosophical questions by processing vast amounts of text and mimicking philosophical discourse, but whether they can truly ask original, conscious philosophical questions is a major debate, largely hinging on consciousness, understanding (semantics vs. syntax), and the nature of ideas, with most experts currently saying no, as current AI manipulates symbols without genuine comprehension or subjective experience (qualia).
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=can+computers+ask+philosophical+questions -
Cosmos Created MindThe "logical fallacy" of a two-value (right/wrong) posturing is ... — Gnomon
False. Bivalence, or law of the excluded middle, is an axiom of classical logic (indispensable for determining many formal and informal fallacies) as well as Boolean logic (the basis of computational and information sciences). — 180 Proof
↪180 Proof
It's one of those ideas that kind of straddles philosophy and science, that we can say.
Depending on how you look at it :rofl: — Wayfarer
In Faggin's chapter on The Nature of Machines, he makes a distinction between deterministic (true/false) digital computers, and freewill analog (maybe/probability) meat brains*1. Apparently, 180 prefers cold, hard binary (true/false) computing to warm-blooded holistic human thinking*2.
Ironically, Binary Logic is Idealistic, in the sense of presuming mechanical perfection*3*4. But human Logic is Realistic, in the sense that living organisms are imperfect, yet adaptable to contingencies in the evolving real world. Binary computers are bound by their programming, and require "interrupts" to call for human help when the program encounters unexpected obstacles.
As you noted, human nature seems to straddle both sides of the imaginary True/False, Either/Or omniscience of the gods & robots, and the realistic Maybe/Truish, Both/And knowing of human animals. 180's god-like view is absolute & indisputable, but Wayfarer's mundane view depends on your personal perspective and is philosophically moot. :cool:
*1. Federico Faggin : "Note that the only recognition required of the hardware is to reliably distinguish the state "0" from the state "1". This recognition does not produce any meaning."
"The operation of the computer, however, is extremely fragile, because it would take just one wrong bit to turn a machine that seems intelligent and deliberate into a completely useless box of metal, plastic, and silicon."
"Within a deterministic machine there is no free will"
Note --- Meaning requires a Me. A digital computer has no self-concept to serve as the Subject to interpret incoming data relative to Self-interest. Does AI know itself?
*2. Boolean Logic versus Human Reasoning :
The opposite of binary thinking (black-and-white, either/or) involves embracing complexity through Spectrum Thinking, Non-Binary Thinking, or Grey Thinking, focusing on nuances, gradations, and multiple possibilities rather than rigid categories like good/bad or right/wrong. It's about recognizing the "both/and," finding common ground, exploring the space between extremes, and seeing the interconnectedness of ideas, allowing for more flexible, nuanced solutions.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=binary+antonym
*3. "Mechanical perfection" refers to the ideal, flawless operation of a machine, free from errors, wear, or friction, though it's often a theoretical concept;
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=mechanical+perfection
*4. Superiority Complex : A person who thinks they're perfect might be called a perfectionist, an elitist, or a narcissist, often displaying traits like setting unrealistic standards, being hypercritical, demanding flawlessness, and struggling with criticism, sometimes masking deep-seated insecurity or a superiority complex where they feel inherently better than others.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=person+who+thinks+he%27s+perfect -
Cosmos Created Mind
The material & practical success of quantum science is undeniable : atom bombs, cell phones, etc. But what about the immaterial theoretical foundation of that pragmatic progress? Is quantum theory & philosophy compatible with your own worldview?*1Except that a lucky guess modeled the quantum fields as harmonic oscillators by performing a Fourier transform on all sorts of waves to be as sinusoidal, and, lo, the quantum model of rungs of quanta falling out matched the reality of experiments and made for quantum field theory to be the most successful in the history of science. — PoeticUniverse
Faggin interprets quantum indeterminism in terms of philosophical Idealism. And he dismisses deterministic Realism as an illusion. He makes a rational reasonable case for his All One philosophy, but for me it still requires a heaping helping of emotional Faith to accept, as a metaphysical Fact, that The One uses the physical world as a way to "know itself and self-actualize". That sounds like an old theological rationalization for why omnipotent/omniscient/eternal/infinite Jehovah created a space-time world and populated it with imperfect & temporary worshipful beings*2. :smile:
*1. I guess it comes down to what are you going to believe, your own senses, or the mystical myths of science-priests? Who do you trust, your own eyes, or the tea-leaf readings of atom-smashing scientists? When I see the world with my built-in ocular instruments, I see a continuous reality, not a discrete digital quantum ideality. So, is quantum science, and it's implicit transcendent belief system, a perversion of the world as it really is? ___Gnomon post above
*2. The idea that "God knows self by means of humans" is a philosophical or theological concept not directly stated in mainstream religious texts but explored in various interpretations of divine self-knowledge and human purpose.
Mainstream Christian theology generally holds that God is a self-existent, omniscient being who understands Himself through Himself, independent of His creation.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=god+knows+self+by+means+of+humans
*3. Rhetorical Question :How are invisible "harmonic oscillators" different from a heavenly choir of angels continually singing praises to God? The quantum vibrations (on-off, +/-) somehow manifest as a tangible physical world, and the celestial vibrating voices support the ego of God, who in turn continually creates a reality for humans down below.
An Essay on Man
" by Alexander Pope
"Know then thyself, presume not God to scan;
The proper study of mankind is Man." -
Cosmos Created Mind"You cannot think the Thinker of thinking. You cannot understand the Understander of understanding. That is Ātman." ___Upanishad — Wayfarer
The title of this thread was intentionally chosen to evoke some relationship between the Universe, as a whole system, and human consciousness as a part (and maybe participant) in that system. In Federico Faggin's book Irreducible, he tends to use Plotinus' notion of The One (ultimate source of reality) instead of the Platonic notion of Cosmos (the universe conceived as a beautiful, harmonious, and well-ordered system). But some people prefer the religious term “God” in their discussions of Ontology (what we can know about our existence). The question here is about the ultimate source of human Being, and specifically the self-conscious Mind that is supposed to be our primary distinction from biological plants & sentient animals. Faggin defines The One as “the totality of what exists”, and makes the questionable assertion that “One wants to know Itself and self-actualize”.
Ancient people didn't understand some frightening features of Nature : how can it be blue sky one day and dark & stormy the next? Thunderstorms, volcanoes, and earthquakes are just a few of the scary deviations from the warm & cozy character of Mother Nature (Cosmos personified). So, they must have imagined that there is some invisible deeper or higher level of SuperNature, which some pictured as humanoid gods above the clouds. Faggin is a modern scientist though, with a much more detailed understanding of how Nature works, including the invisible realm of Quantum physics.
Now even a sober secular scientist has come to believe in unseen aspects of the world, that our physical senses are not innately tuned to detect. Yet, he knows about the hidden Quantum dimension of total Reality only by mathematical reasoning, supported by mystifying experiments. Instead of postulating anthro-morphic gods though, he uses more abstract, operational, and relational terminology. He also refers to our commonsense knowledge of the world as “the illusory model of reality created by our senses”*1. Quantum scientists now describe the mysteries of the unseen reality by less anthro-morphic, but oddly weird language. Instead of super-human gods, he refers to the Ideality behind Reality as “Fields”. But it's still spooky, and probably offensive to philosophical Realists.
Like Einstein, is a Realist, and seems to be spooked by any idealistic reference to super-nature or deeper-reality or transcendent realms or quantum infinity, that are insensible to our physical senses. So, he lashes-out at those infidels, who dare to speak of a non-classical model of reality. Isaac Newton was realistic, except for his assumption of a personal God in his eternal immeasurable heaven, somewhere above our 3-dimensional physical world. Einstein's secular notion of God was more like an impersonal Cosmos, as described by Spinoza in 1677. And in 1935, Einstein published a paper (EPR paradox) arguing that quantum physics was “incomplete” because it violated the “locality principle”, implying that our finite reality was actually infinite. Despite Einstein's skepticism, Faggin reports that the Bell “experiment and all subsequent ones have shown that quantum physics is correct and that Einstein's objections were not valid".
Nevertheless, I have to take Faggin's interpretations as hearsay, because I have no personal experience of such immaterial non-things as mathematical Fields, and Holistic entanglement of statistical particles. So, I can understand why 180proof would be freaked-out by such ghostly non-sense. I guess it comes down to what are you going to believe, your own senses, or the mystical myths of science-priests? Who do you trust, your own eyes, or the tea-leaf readings of atom-smashing scientists? When I see the world with my built-in ocular instruments, I see a continuous reality, not a discrete quantum ideality. So, is quantum science, and it's implicit transcendent belief system, a perversion of the world as it really is?
180's Either/Or worldview, like Spinoza's 17th century unified monistic system, and like Newton's 17th century mechanical deterministic divine system, is pure & perfect. So 21st century scientists and metaphysicians, like you and me, seem to be shitting on his pristine porcelain. For years, I thought he was just a disgruntled troll. But now I see that there is a logical philosophical viewpoint underlying his Good versus Evil worldview, unsullied by the uncertainties, indeterminism, unpredictability and general fuzziness of Quantum philosophy. By contrast, my world seems to be imperfect, incomplete, and still evolving toward some unknowable future state, that may or may not include flawed flesh & blood humans like me. If we can't believe our personal concrete senses, can we rely on abstract reasoning to reveal the true nature of the world around us? :chin:
*1. Late Lament
song by Moody Blues
. . . . . . .
But we decide which is right
And which is an illusion -
Cosmos Created Mind
Ironically, would troll Neils Bohr as a wishy-washy woo-purveyor, if he had the audacity to post his on this forum. I just realized the significance of the alcohol-purity screenname : A> it may symbolize the ideal of a trump-like "perfect" worldview : Black vs White & True vs False & Immanent vs Transcendent*1 with no watered-down adulterants. Or B> it dumbs-down philosophical complexities to Either/Or dualities that a simple mind can handle.He regarded the 'complementarity principle' as the most important philosophical discovery of his life. — Wayfarer
The "logical fallacy" of a two-value (right/wrong) posturing is the arrogant presumption of absolute knowledge. Which often causes imbalance & disharmony among imperfect humans. I suppose 180's "ideal" of perfect omniscience is admirable in a way, but it's not Plato's way.
For the rest of the story : Rutherford-Bohr's original classical planetary model of an atom was later invalidated by Heisenberg's statistical Uncertainty Principle. But, as you noted, Bohr --- with intellectual modesty --- later came to accept the Yin-and-Yang Complementary Principle illustrated in the Taoism symbol. Note, I also use that Holistic image as a bullet in my blog posts.
For most philosophers and scientists, the search-for-truth is motivated by the lack of omniscience. But 180, on his pure-white perch above us mortals, can despise any signs of ignorance and intellectual modesty. :joke:
*1. "Either/or black vs white" refers to the logical fallacy of a false dilemma (or false dichotomy), where only two extreme options (black or white, good or bad, for or against) are presented, ignoring the vast spectrum of possibilities, nuances, and "shades of gray" that actually exist, often used to oversimplify complex issues or force a choice. It's a way of thinking that reduces complex realities to simple, opposing choices, hindering deeper understanding and compromise.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=either+or+black+vs+white&zx=1765662725371&no_sw_cr=1
*2. In philosophy, the search for truth is the fundamental, ongoing quest to understand reality, knowledge, and existence, using reason, logic, and critical inquiry to answer big questions, even without definitive answers, with various methods like correspondence, coherence, and pragmatism offering different paths to what is real or useful. It's seen as a core activity, even if philosophers often debate what truth is, with some defining it as what works (Pragmatism), what matches reality (Correspondence), or a coherent system of ideas.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=philosophy+search+for+truth
*3. The Yin Yang principle is a foundational concept in Chinese philosophy describing the belief that opposing forces are interconnected, complementary, and interdependent. Represented by the Taijitu symbol, yin (the dark, passive, feminine force) and yang (the light, active, masculine force) are not static but are in a dynamic, ever-changing balance, where each contains a seed of the other. The principle emphasizes that harmony is achieved through the balance of these two forces, not through extremes.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=yin+yang+principle
COMPLEMENTARY YIN-YANG PRINCIPLE OF HOLISM

-
Cosmos Created Mind
Faggin is indeed idiosyncratic compared to eclectic New-Age-type religious philosophy. But his empirical & rational approach may be acceptable to some strands of Consciousness Studies*1. So far, his book is mostly about a scientific worldview, not a religious belief system. The word "god" does not appear in his glossary, but the term "panpsychism" does. Consequently, I get the impression that his worldview is Philosophical & Scientific, not Religious ; intellectual & practical, not emotional.As regards Faggin - I sense that the One resonates with the One of Plotinus' philosophy. He has taken ideas from a variety of sources, and also developed his own using metaphors from quantum physics and computing. But still see him as rather idiosyncratic. He's not going to get noticed much in the 'consciousness studies' ecosystem for that reason. — Wayfarer
His chapter 2 is about The Nature of Quantum Reality, and his "creator" is abstract & impersonal. Speaking of universal quantum fields, he says : "These fields have space & time in common and are the fundamental entities that, interacting with each other, create everything that exists physically". The fields themselves may be construed as Metaphysical, but it remains to be seen if Faggin views them as created by some higher power, or are self-existent : i.e. god-like.
In discussing quantum particles, he describes them, not as Lucretius' tiny hard balls of stuff, but as foggy "clouds" of mathematical probability. To me, that sounds more like Platonic Ideality (shadows in the cave) than Aristotle's Physics. Personally, for all pragmatic purposes, I act as-if my world-model is Aristotelian (practical) Reality, but for theoretical exploration I can also imagine a Platonic metaphysical Ideality. Not Either/Or, but BothAnd.
As I read chapter 2, a thought occurred to me : Classical Newtonian physics was compatible with the Bible God, who creates a world, like a wind-up toy, and sets it on a straight & narrow path in a specific direction. But non-linear & probabilistic Quantum physics is more like the erratic & random ancient religions based on natural cycles. Their polytheistic gods (e.g. Olympian) were not all-powerful, and argued amongst themselves. Which left their worshipers grappling with mysteries beyond comprehension, wandering guided only by faith. On the other hand, non-religious Philosophy can deal with Quantum Mysticism, not by Faith, but by Reason. :nerd:
*1. Consciousness Studies is an interdisciplinary field exploring the nature of subjective experience, blending neuroscience, philosophy, psychology, physics, and more, to understand how the brain creates self-awareness and reality, focusing on identifying neural correlates, developing theories like Global Workspace Theory or Integrated Information Theory, and investigating altered states like meditation, aiming to bridge the gap between physical brain processes and phenomenal experience.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=consciousness+studies -
Cosmos Created MindSo since then philosophy has tended to adopt either materialism (matter is everything), idealism (mind is everything) or dualism (it is both), across a range of forms. — Wayfarer
Perhaps. I explore various philosophical positions, but I don't label myself as Idealist or Materialist or Mystic. . . . . nor Immanentist nor Transcendentalist, . . . maybe a Causalist? My emerging & evolving amateur non-dual holistic philosophy is what I call BothAnd*1. Which is anathema to those of dogmatic Either/Or beliefs, such as . Your expressed views though are usually broad & flexible, yet rigorous & informed enough, to be amenable to my own dilettante dabblings.I think that your essay is attempting to fashion a theory out of these ingredients. — Wayfarer
I don't adhere to any religious or mystical beliefs, but I try to be open to plausible ideas circulating within the human orbit. Admittedly, my autodidactic personal philosophy/cosmology*3 is much more influenced by the diverse posits of Quantum theorists*3 than of Academic philosophers, ancient or modern. :cool:
*1. Both/And Principle :
My coinage for the holistic principle of Complementarity, as illustrated in the Yin/Yang symbol. Opposing or contrasting concepts are always part of a greater whole. Conflicts between parts can be reconciled or harmonized by putting them into the context of a whole system.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page10.html
*2. Enformationism :
A philosophical worldview or belief system grounded on the 20th century discovery that Information, rather than Matter, is the fundamental substance of everything in the universe. It is intended to be the 21st century successor to ancient Materialism. An Update from Bronze Age to Information Age. It's a Theory of Everything that covers, not just matter & energy, but also Life & Mind & Love.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page8.html
*3. Quantum Philosophy :
Understanding and Interpreting Contemporary Science by Roland Omnès is a book that bridges quantum physics and philosophy, arguing that modern quantum mechanics, particularly the "consistent-histories" approach, provides a new foundation for understanding knowledge, causality, and reality, reconciling them with common sense.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=quantum+philosophy -
Cosmos Created Mind
If, by "that term' you mean "cosmic consciousness" you may be correct. I just used that New-Agey Mystical term in place of his more cryptic concept of The One. But he does use the more specific term Seity*1 throughout the book. He postulates, in great detail, how he imagines that Quantum Physics adds up to self-conscious & causal Cosmic Mind. Although he avoids ascribing human-like personality to The One, it still sounds like a 21st century God ; whose oblique revelation is inscribed in quantum uncertainty . . . . perhaps, to keep us biological agents guessing about divine intentions.I suppose Faggin's notion of Seity is another attempt to define Cosmic Consciousness in scientific and non-anthropomorphic terms. — Gnomon
Wait until you read it. I don’t think that term is used anywhere in the book. (I’d love to see a discussion between Faggin and Glattenfelder. They’re both kinds of ‘techno mystics’.) — Wayfarer
I don't think of myself as a Mystic, but my philosophical exploration is currently reconnoitering the margins of Quantum Mysticism. And I see a lot of parallels with ancient Greek & Oriental philosophies, although the technical terminology may seem idiosyncratic (out of place) to those with more traditional philosophical backgrounds. Faggin does quote the Vedas.
My "Right Stuff" blog post*2 was written before I got Faggin's book. But it begins by quoting the Epicurean poet Lucretius, whose Atomism may have been the ancestor of modern Quantum physics --- materialism minus the mysticism. Ironically, the modern Atom is not a hard little ball, but a locus of incorporeal mathematical information, that Faggin multiplies and adds-up to a woo-woo Cosmic Mind : The One or The Universe (one whole)*3. :smile:
*1. Seity : "a quantum entity with three irreducible and indivisible fundamental properties : consciousness, agency, and identity. The elementary seities, which I have called consciousness units, emanate directly from One." ___ Irreducible book glossary
*2. Right Stuff for Consciousness :
“If matter, in all its forms, were nothing but mindless substance, then of course it would follow by mere definition that conscious material is impossible. But that is specifically the "question-begging presumption" I was referring to.” ___Janus
https://bothandblog9.enformationism.info/page10.html
*3. "One is a Whole, both in potentiality and in actuality, irreducibly dynamic and holistic."
___ from Introduction to Irreducible
PS___ I just came across this quote in an article on the philosopher Friedrich Schelling, of whom I know nothing :
“idealism is the soul of philosophy; realism is its body only both together can constitute a living whole”.
# Then this from Google Search, which sounds a bit like Faggin's One.
Is the notion of Ungrund, a form of Idealism or Mysticism or 180proof's :sparkle:? :
Schelling's Ungrund (German for "non-ground" or "groundless ground") is a profound concept in his later philosophy, representing the mysterious, irrational abyss or primal darkness that underlies all existence, even God, a "nothing" from which being and all oppositions emerge, serving as the source of freedom, creativity, and the possibility of new realities, distinguishing his thought from Hegel's rational idealism by positing a pre-rational, chaotic potential before any self-conscious Spirit. It's a fundamental, ungroundable basis, a "ground of all grounds," essential for explaining how something new, evil, or individual can arise from the absolute.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=Schelling+and+his+Ungrund. -
Cosmos Created Mind
I suppose Faggin's notion of Seity is another attempt to define Cosmic Consciousness in scientific and non-anthropomorphic terms. It's his technical description of a fundamental unit of consciousness, and may be similar to A.N. Whitehead's "occasions of experience", which I found hard to grok. Personally, I prefer a holistic concept of Cosmos : the totality of existence, including matter & mind. I'll leave the atoms of consciousness to others.Not peculiar - I think Federico Faggin is highly intelligent and genuine. I did tackle that book - actually I think I have the Kindle edition, but I couldn't really follow the argument. He introduces a term, seity, ' a seity is defined as a self-conscious entity that can act with free will.' However not necessarily a conscious being. ...'A seity is a field in a pure state existing in a vaster reality than the physical world that contains the body. A seity exists even without a physical body.'
I couldn't really get my head around it. — Wayfarer
Ironically, when he describes Seity as a Field, it begins to sound like a scientistic version of religious Spirit. Fields in physics (e.g. electromagnetic & quantum fields) are real in their effects, but immaterial in substance. On the other hand, I'm exploring the use of Energy (causation) in a similar manner. But exactly how the universal Power to Transform can result in sentient Matter, is the question being begged in my theory.
He refers to Max Planck's Quantum of Action as a fundamental constant. Yet it's not a thing in itself, but more like a Field of Potential that can only be defined mathematically & functionally. So I'd label Faggin's "Seity" as Quantum Field Spirituality, which may not align with your more traditional philosophical understanding of the Mind/Matter relationship.
Anyway, Faggin seems to imagine the Conscious Cosmos in terms of Potential, whereas the material world is Actual. And that is close to my own emerging understanding of the origin of Mind in a physical world. Somehow, in a not-yet-understood manner, the self-conscious Cosmos has created a world of little selfish minds with ideas of their own. But unlike the mythical & literary Jehovah, CC leaves it up to us to "know the mind of God". :nerd:
PS___ The "vaster reality" seems to be what several Mind/Matter theorists (e.g. Noetic Science & Ideonomy) call "higher dimensions". Some even claim to have experienced those ideal or spiritual dimensions. -
Cosmos Created Mind
By "idiosyncratic", do you mean peculiar or individualistic? For an autobiography, I would think individualistic would be a good thing. I've only read the introduction, but so far it seems to be a fairly typical expression of the Consciousness is Fundamental worldview, as imagined or experienced by a quantum scientist. Kastrup seems to find him to be a fellow-traveler on the slender Idealism branch of modern science. Incidentally, Faggin defines The One as "the totality of all that exists" but refrains from using religious terms like "God".oh yeah, I know Faggin. I read (actually, listened to) his autobiography, Silicon. I’ve looked at Irreducible a few times but I have mixed feelings about it, I think his approach is a bit too idiosyncratic. — Wayfarer
I know your time is limited, but I would appreciate a quick review of the blog post on The Right Stuff to Evolve Consciousness*2 (it's only two pages). It presumes that human-like Consciousness is not fundamental to physics or metaphysics, but a late development from eons of physical evolution : i.e. an emergent property. So, it may be closer to Janus' worldview ; although I think causal Energy is more fundamental than tangible Matter, which is also emergent.
However, it assumes that some mysterious precursor to sentient awareness in physical bodies existed at the beginning of space-time evolution, and is the irreducible necessity to explain how & why you & I now consciously experience Seity*3. Would you call that prerequisite The One or The Form or Cosmic Mind or something else?
I'm hoping that Janus will also chip-in his opinions on the blog post, so I can compare two eloquent defenders of philosophical positions in the great dialog/debate on the role & nature of Mind in the real & ideal world. :nerd:
*1. Irreducible :
The book "argues consciousness is a fundamental, quantum phenomenon, not an emergent property of matter, proposing an idealist model where the physical world is a symbolic representation of a deeper, conscious reality".
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=irreducible+book
*2. Right Stuff : Spirit or Causation?
“In essence, the Big Bang transformed a highly energetic, almost featureless state into the structured, information-rich cosmos we observe today, with energy providing the fuel and quantum randomness providing the initial blueprint.” ___Google search
Note ---
How could Chaotic “randomness” create the “blueprint” for an orderly & organized Cosmos with a logical structure of natural Laws? Randomness does imply freedom for exploration of possibilities. But only purposeful, systematic, and intentional design can impart systematic order upon Chaos.
https://bothandblog9.enformationism.info/page10.html
*3. [u]Seity[/u] means the quality of being uniquely oneself, selfhood, or individuality, referring to something peculiar or particular to a specific person or thing, derived from the Latin word "se" (oneself). It signifies that unique essence or identity that sets something apart, often used in philosophical or spiritual contexts to describe the fundamental, unique reality of a person or even the divine.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=seity+meaning -
Cosmos Created Mind
Ha! I was in the Navy --- killing the little yellow man, figuratively not literally --- while the US was going through that New Age of Aquarius, when "love will steer the stars".↪Gnomon
Yes. And don't forget, we are stardust, we are golden, we are billion year old carbon. And we got to get ourselves back to the garden. — Wayfarer
I'd be interested to get your reaction to the Right Stuff for Consciousness post*1 that I linked in my reply above. It was a response to Janus' reply to Wayfarer in this thread. If not "stardust", what then was the "mindless substance" that became "conscious material"? Although the post is trying to be Realistic, any discussion of Consciousness is necessarily going to skirt the line between Realism and Idealism. What is the question being begged by Philosophers on one hand, and Scientists on the other?
I have just begun to read a new book by Federico Faggin --- quantum physicist and microprocessor inventor --- IRREDUCIBLE, Consciousness, Life, Computers, and Human Nature*2. Although he began as a pragmatic computer engineer, he had a mid-life Mystical (not-religious) experience --- a spiritual awakening --- that turned him to the Light Side of Idealism. I personally have never had such an "ineffable unitive experience", so his encounter with The One is hearsay for me. But I'm currently exploring various views of the Science-Philosophy Hard Problem.
Faggin asserts that "consciousness is a quantum phenomenon" and the fundamental "substance" of the world. My blog post is a slightly different view of that mindful substance ; and I reserve the term "consciousness" as an evolved phenomenon/noumenon instead of the fundamental substance. But he boldly goes way beyond my timid postulations to affirm that "everything is made of love". Does that sound New Agey to you? Does the notion of a Love Substance fit your philosophy of Idealism? :cool:
*1. Right Stuff to Evolve Consciousness
“If matter, in all its forms, were nothing but mindless substance, then of course it would follow by mere definition that conscious material is impossible. But that is specifically the "question-begging presumption" I was referring to.” ___Janus
https://bothandblog9.enformationism.info/page10.html
*2. "Federico Faggin is probably the most well-rounded idealist alive. He embodies the near-perfect combination of hard-nosed, scientifically informed thought with direct introspective insights into the primacy of consciousness." ___ Bernardo Kastrup

-
Cosmos Created Mind
Janus & Wayfarer do tend to view the Mind-Matter problem of Philosophy-Science somewhat differently. So I learn different-but-valuable perspectives from each of you. As I graphically indicated in a previous post, Wayfarer seems to view the world through a Platonic lens, while Janus prefers the Aristotelian view. But I think a complete worldview would include elements of both.↪Wayfarer
Well, we see things very differently. — Janus
Earlier in this thread, Janus' realistic reply*1 to Wayfarer's idealistic take on the Hard Problem rang a bell for me. So, I added a new post*2 to my blog on the topic of a Cosmos Evolved Mind. It's not intended to take sides in the debate, but to look at Both Sides Now*3. :grin:
*1. The question begging presumption :
“If matter, in all its forms, were nothing but mindless substance, then of course it would follow by mere definition that conscious material is impossible. But that is specifically the "question-begging presumption" I was referring to.” ___Janus
*2. Right Stuff to Evolve Consciousness :
The intending, observing & knowing Mind itself is the “question-begging presumption” that needs to be explained, in order to understand how subjective Mind could evolve from objective Matter.
https://bothandblog9.enformationism.info/page10.html
Note --- Perhaps Quantum randomness & probability may be the "arational" element in the evolution of sentient & logical beings from a burst of cosmic energy. Post 147 is just one of many on the Consciousness conundrum that has bugged philosophers for ages. The second page gets more directly to the point of this forum reply.
*3. BOTH SIDES NOW
. . . . . . . . .
I've looked atlifeMind from both sides now
From win and lose and still somehow
It's life's illusions I recall
I really don't know life at all
It's life's illusions that I recall
I really don't know life
I really don't know life at all
Songwriter : Joni Mitchell -
Cosmos Created Mind
Yes, Realism vs Idealism is a dualistic simplification of a multi-faceted complex concept that contains various aspects of both outlooks : what I facetiously call Redealism : the top-down view of a material world populated with imperfect people who create little perfect worlds in their own minds.I think this is a serious oversimplification. Aristotle does not abandon Forms; his hylomorphism is still a form–based ontology—the difference is that Forms are no longer conceived as existing in a separate, self-subsisting realm, but as ontologically prior principles instantiated in matter. Matter, for Aristotle, has no actuality or determinate identity on its own; it exists only as pure potentiality until it receives form. — Wayfarer
Whether that duality is an "over-simplification" depends on personal preference : perfect models vs messy actuality. Deep thinkers have been arguing over absolute truth (philosophy) vs practical usefulness (science) for at least 2500 years.
In the context of this thread, my preference is to over-simplify the philosophical battleground between Plato and Aristotle as a focus on either Transcendence or Immanence. And then, to put each notion into its proper context --- whatever that may be. Both views may be ultimately proven valid or invalid depending on its application : universal or local.
Therefore, my wishy-washy BothAnd*1 position varies, depending on the context of the moment. In this thread, I stand mutably in the moot mushy moderate middle-ground of maybe; where I get shot-at from both sides, by those standing on the firm ground of certainty. :smile:
*1. The BothAnd Philosophy :
Philosophy is the study of ideas & beliefs. Not which are right or wrong – that is the province of Religion and Politics – but which are closer to relevant wisdom. That unreachable goal can only be approximated by Reason & Consensus, which is the method of applied Science and Philosophical dialog. In addition to ivory tower theories, practical Philosophy attempts to observe the behavior of wild ideas in their natural habitat.
The BothAnd philosophy is primarily Metaphysical, in that it is concerned with Ontology, Epistemology, & Cosmology. Those categories include abstract & general concepts, such as : G*D, existence, causation, Logic, Mathematics, & Forms. Unlike pragmatic scientific "facts" about the physical world, idealistic Metaphysics is a battle-ground of opinions & emotions.
The BothAnd principle is one of Balance, Symmetry and Proportion. It eschews the absolutist positions of Idealism vs Realism, in favor of the relative compromises of Pragmatism. It espouses the Practical Wisdom of the Greek philosophers, instead of the "Perfect" divine revelations of the Hebrew Priests. The BA principle of practical wisdom requires “skin in the game”* to provide real-world feedback, which counter-balances the extremes of Idealism & Realism. That feedback establishes limits to freedom and boundaries to risk-taking. BA is a principle of Character & Virtue, viewed as Phronesis** or Pragmatism, instead of Piety or Perfectionism.
The BA philosophy is intended to be based on empirical evidence where possible, but to incorporate reasonable speculation were necessary. As my personal philosophy, the basic principle is fleshed-out in the worldview of Enformationism, which transcends the Real world only insofar as to establish the universal Ground of Being, and the active principle in Evolution.
* ref : Skin In The Game, by Nassim Nicholas Taleb; researcher in philosophical, mathematical, and (mostly) practical problems with probability.
** Phronesis : an Ancient Greek word for a type of wisdom or intelligence. It is more specifically a type of wisdom relevant to practical action, implying both good judgement and excellence of character and habits, or practical virtue.
https://blog-glossary.enformationism.info/page10.html
-
Cosmos Created Mind↪Wayfarer
:roll: When you stop with the shitty misrepresentations of what I've said I might respond. — Janus
Since Janus and Wayfarer seem to be among the most philosophically erudite posters on this forum, such combative dialog conjures an image of Plato and Aristotle duking-it-out in the Academy or Forum. Today, we honor both of those ancient Greeks as Past Masters of the philosophical arts. But back in the day, I suspect they passed some harsh words between them.↪Janus
I do endeavour to address your arguments with courtesy, reciprocation would be appreciated. — Wayfarer
Maybe constructive agreement, in the search for truth, has always been elusive & arduous. So we in the midst of the ongoing creative work of wisdom-building notice mainly the piles of debris from "constructive disagreement". Perhaps history will record this thread as a win-win : both Real and Ideal; both Physical and Metaphysical. :smile:
Plato and Aristotle differed significantly in their approach to reality, with Plato emphasizing an ideal, abstract realm of Forms as the ultimate reality, accessed through reason, and Aristotle focusing on the tangible, physical world as the primary reality, understood through empirical observation and the senses. This led Plato to an idealistic philosophy and Aristotle to a more pragmatic, scientific approach.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=plato+vs+aristotle+philosophy
Transcendent! . . . . . . . . . . . . . . No, Immanent!

-
Cosmos Created Mind
I agree :Mind (consciousness) is not a "separate, non-physical entity" — Gnomon
It would be a different kind of 'physical'. It had to have evolved, with life, for once there was no life and consciousness on Earth, and now there is. — PoeticUniverse
# First, Mind (consciousness, thoughts, feelings) is not an entity, but a process.
# Secondly, Mind (power to create imaginary ideas) is not physical, but meta-physical*1. By that I mean : Physics refers to the things we perceive with the eye of the body. Meta-physics refers to the things we conceive with the eye of the mind.
# Thirdly, the "cognitive leap" became apparent in eon-long-lifeless-mindless evolution when signs of learned-social-human-culture emerged from a background of evolved-genetic-animal-instinct : jazz hands :cheer: .
# Fourthly, the Agency*2 we call Mind is always associated with complex living organisms : animated matter, not inanimate rocks. But what is the complexifying & animating force, vital principle, elan vital? What input transforms raw matter, into living bodies, thinking beings, and intentional agents?
# Fifthly, Mind has never been found separate from a physical organism of some kind. I can imagine a disembodied soul (ghost), but for me, it's obviously not real, but ideal. So, obviously, to be a causal & interactive agent in the real world, Mind must be embodied, and a physical manifestation of Mind is Culture.
# Sixthly, Mind is the active processing of meaningful Information*3. And Action in the real world is always associated with some form of Energy. the currency of Mind is Information : EnFormAction.
# Seventhly, we can only discuss mental processes in philosophical or poetic metaphors*4.
# Eighthly, After decades of searching the Cosmos, scientists have never found verifiable signs of life or mind (culture), apart from a single rocky planet, on the cusp of an ordinary galaxy, among two trillion star constellations. Matter & Energy seem to be everywhere, so why is Mind so rare? What is the secret sauce . . .? I have a philosophical hypothesis, and it is mentioned in this post. :nerd:
*1. Metaphysics uses rational, philosophical inquiry to understand reality, while mysticism is based on direct, subjective, and intuitive experiences of reality.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=difference+between+metaphysics+and+mysticism
*2. mind is the capacity for agency—the ability to act, make choices, and exert control over one's actions and life circumstances.
https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=%22mind%22+is+agency
*3. Information is Physical and Metaphysical :
To explain the “active” element of Information, Peat says “I suggest that Information is the final element in a triad—information is that which gives form to energy”.
https://bothandblog8.enformationism.info/page29.html
*4. What Is Mind?
What is called Mind?
The flow of your thoughts!
The internal dialogue
When we do not talk.
We think and think,
shaping our words
to speak, the process
of thinking is Mind.
The platform in which
the thoughts move
like people move
in a railway station.
Mind is where words
move in whirls before,
it finally make it to
the conversations.
Controlling Mind
is then controlling
your thinking.
Mind is thoughts.
Narayanan Kutty Pozhath
Gnomon

Start FollowingSend a Message
- Other sites we like
- Social media
- Terms of Service
- Sign In
- Created with PlushForums
- © 2026 The Philosophy Forum